IPA Kelas 9 Semester 2 : Kemagnetan (Part 2 : Medan Magnet dan Magnet pada Bumi)
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the concept of magnetism, focusing on magnetic fields and Earth's magnetism. It covers how magnetic fields are visualized through field lines and how opposite poles attract while similar poles repel. The Earth's magnetic field is discussed, explaining the north and south poles of the Earth and the compass' behavior. The video also touches on magnetic deviations such as declination and inclination, and how Earth's molten core generates its magnetic field. Additionally, it explores auroras, solar winds, and how the Earth's magnetosphere protects it from solar radiation.
Takeaways
- 😀 Magnetic fields are regions around magnets where magnetic forces can affect objects, and they are represented by magnetic field lines that flow from the North pole to the South pole.
- 😀 When opposite poles (North and South) of two magnets are brought together, the magnetic field lines connect smoothly, but like poles (North-North or South-South) repel each other.
- 😀 Earth acts like a giant magnet, with the magnetic South pole located near the geographic North pole, and the magnetic North pole near the geographic South pole.
- 😀 A compass needle aligns with Earth's magnetic field, with its North pole pointing toward Earth's magnetic South pole and its South pole pointing toward Earth's magnetic North pole.
- 😀 Declination is the angle between the direction a compass points and true geographic north, while inclination is the tilt of the compass needle relative to the horizontal.
- 😀 Earth's magnetic field is caused by the movement of molten metals, such as iron and nickel, in Earth's outer core, generating electric currents that produce the magnetic field (dynamo effect).
- 😀 The Earth's magnetic field acts as a protective shield, blocking harmful cosmic radiation and solar particles from reaching Earth's surface.
- 😀 The aurora, or Northern and Southern Lights (Aurora Borealis and Aurora Australis), is caused by charged particles from the Sun interacting with Earth's magnetic field, creating beautiful light displays near the poles.
- 😀 Solar storms, which release a large amount of energy from the Sun, can send charged particles toward Earth, but Earth's magnetosphere protects us from the worst effects of these storms.
- 😀 The auroras occur when solar particles are trapped by Earth's magnetic field and travel toward the poles, creating colorful light displays, but they cannot be seen near the equator.
Q & A
What is a magnetic field?
-A magnetic field is the area around a magnet where magnetic forces are exerted. It is represented by lines of magnetic force, which emerge from the north pole of a magnet and curve into the south pole.
How do magnetic poles interact?
-When opposite poles of magnets (north and south) are brought together, they attract, and magnetic lines of force flow from the north pole to the south pole. When like poles (north-north or south-south) are brought together, the magnetic lines repel each other.
Why does a compass point north?
-A compass is a small magnet, and it aligns with Earth's magnetic field. The north pole of the compass points towards the Earth's magnetic north, which is actually located near the Earth's geographical south pole.
What is magnetic declination?
-Magnetic declination is the angle between the true geographical north and the magnetic north, which varies depending on the location on Earth.
What is magnetic inclination?
-Magnetic inclination refers to the angle at which magnetic lines of force enter the Earth's surface. This angle varies based on the location and the Earth's magnetic field.
What causes Earth's magnetic field?
-Earth's magnetic field is generated by the movement of molten metals like iron in the Earth's outer core. The movement of these metals creates an electric current, which in turn generates a magnetic field.
What protective role does Earth's magnetic field play?
-Earth's magnetic field protects the planet by deflecting harmful cosmic radiation from the Sun and other celestial bodies. It prevents these high-energy particles from reaching Earth's surface, thereby protecting life.
What is an aurora, and why does it occur?
-An aurora is a natural light display seen near Earth's poles. It occurs when charged particles from the Sun, carried by solar wind, interact with Earth's magnetic field and atmosphere, causing the gases in the atmosphere to emit light.
What is the difference between Aurora Borealis and Aurora Australis?
-Aurora Borealis, also known as the Northern Lights, occurs in the Northern Hemisphere, while Aurora Australis, or the Southern Lights, occurs in the Southern Hemisphere.
How do solar storms affect Earth's magnetic field?
-Solar storms, also known as coronal mass ejections (CMEs), release large bursts of solar wind and magnetic fields into space. When these storms reach Earth, they can disturb Earth's magnetic field, causing geomagnetic storms and enhanced auroras.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Force at a distance! Induced magnets and domain theory!
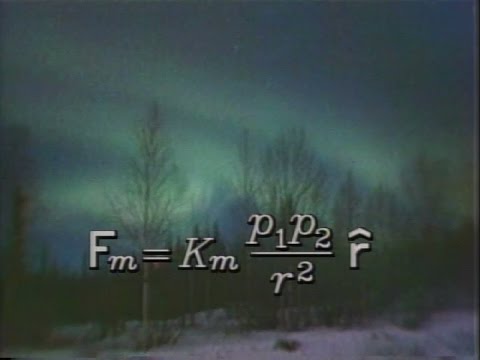
Episode 34: Magnetism - The Mechanical Universe

Magnetism | The Dr. Binocs Show | Educational Videos For Kids

Basic Theory of Magnetism | Magnetic Force Concept | Earth Magnetism Theory - Magnetism | IPA Class9

Magnetism: Crash Course Physics #32

Magnetism and matter revision in 20 minute || Class 12 Chapter 5 Physics Abhishek sahu sir
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)