Lesson 7: Types of Lenses (Convex and Concave)
Summary
TLDRIn this lesson, we explore the science of lenses, focusing on concave and convex types. Lenses are transparent objects that bend light through refraction, allowing us to have devices like magnifying glasses, microscopes, and even the human eye. Convex lenses are thicker at the center and can form real or virtual images, while concave lenses are thicker at the edges and typically form upright, reduced, virtual images. The lesson also covers how lenses are used in everyday objects and how defects like myopia and hyperopia affect vision. Through ray diagramming, students learn how to visualize image formation in different types of lenses.
Takeaways
- 😀 Lenses are transparent materials with at least one curved surface, used to bend light rays through refraction.
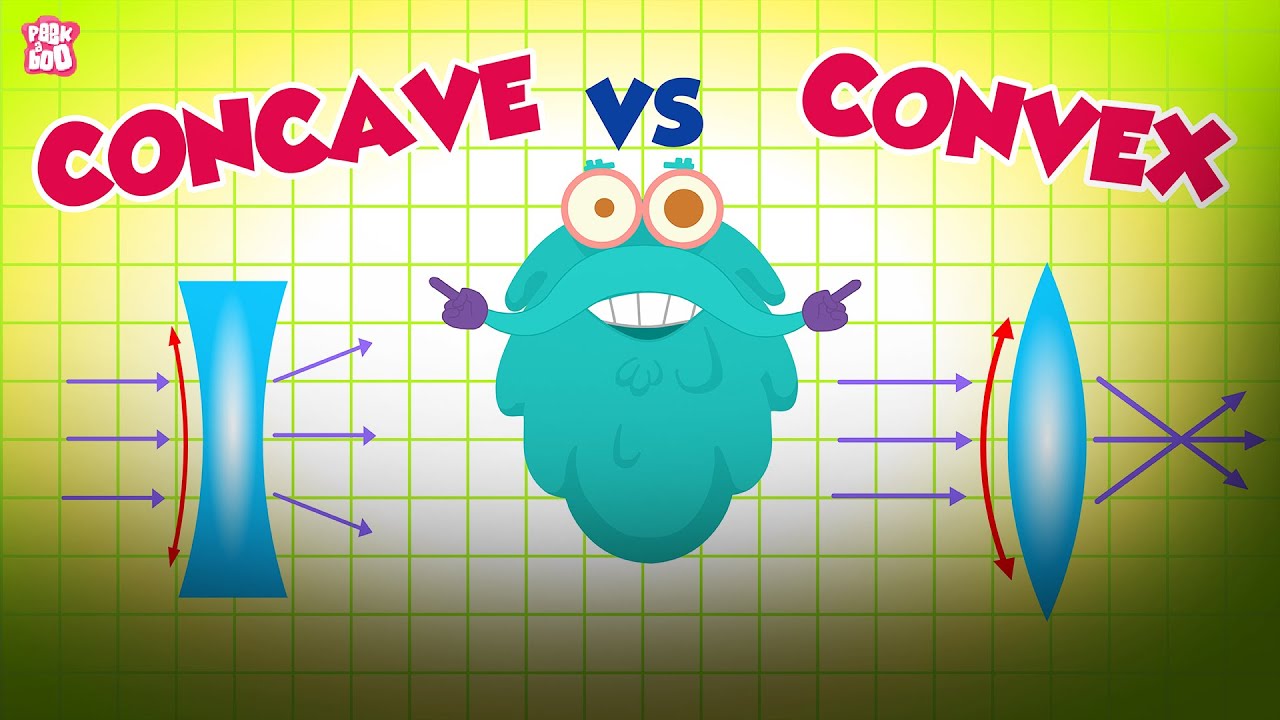
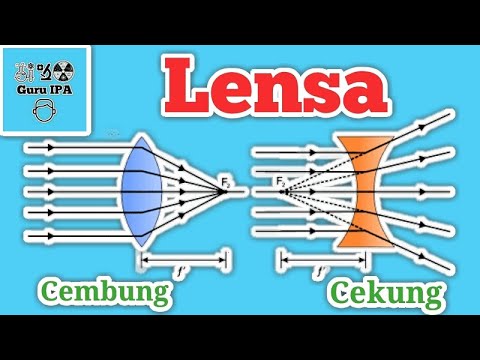
- 😀 Convex lenses are thicker at the center than at the edges, and can form both real and virtual images depending on the object's position.
- 😀 Concave lenses are thicker at the edges and thinner in the center, and always form virtual, upright, and reduced images.
- 😀 The word 'lens' comes from the Latin word for lentil, due to the shape of early lenses.
- 😀 Convex lenses are also known as converging lenses because they focus parallel light rays to a point beyond the lens.
- 😀 Concave lenses are also known as diverging lenses because they spread parallel light rays outward.
- 😀 Ray diagrams are used to describe how lenses form images, using three primary rays: PF ray, FP ray, and V-ray.
- 😀 In a ray diagram, the focal point (F) and the vertex of the lens are key reference points to determine image characteristics.
- 😀 Convex lenses can form both real and virtual images, while concave lenses always form virtual images.
- 😀 The location, orientation, size, and type of image formed by a lens depend on the object's position relative to the lens.
- 😀 The common uses of convex lenses include magnifying glasses, cameras, microscopes, and telescopes, while concave lenses are used in optical devices like eyeglasses and scanners.
Q & A
What is the main topic of the lesson?
-The main topic of the lesson is the study of lenses, specifically concave and convex lenses, and how they work through refraction of light.
What is the definition of a lens?
-A lens is a transparent piece of glass or plastic with at least one curved surface that bends light rays as they pass through it.
Where did the word 'lens' come from?
-The word 'lens' comes from the Latin word 'lentil,' which is a type of bean, due to the lens's shape resembling that of a lentil.
How do lenses work?
-Lenses work by refraction, which is the bending of light rays as they pass through the lens, causing them to change direction.
What are the two common types of lenses?
-The two common types of lenses are convex lenses and concave lenses.
What is a convex lens and how does it function?
-A convex lens is thicker in the center than at the edges. It converges light rays, making them meet at a focal point. It can form both real and virtual images depending on the position of the object.
What is a concave lens and how does it function?
-A concave lens is thicker at the edges and thinner in the center. It diverges light rays, making them spread out, and it typically forms virtual, upright, and reduced images.
What is the focal length of a lens?
-The focal length of a lens is the distance between the vertex (center) of the lens and the focal point, where parallel rays of light converge or appear to diverge.
How do ray diagrams help in understanding lens behavior?
-Ray diagrams are used to graphically represent how light rays pass through lenses and how they form images. They help in identifying the location, orientation, and type of image formed by the lens.
What are some common uses of convex and concave lenses?
-Convex lenses are used in magnifying glasses, microscopes, and cameras, while concave lenses are used in eyeglasses, telescopes, and certain medical equipment, as well as in CD/DVD players and flashlights.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示

Pemantulan dan Pembiasan Cahaya dengan KIT OPTIK
Why Does Light Bend? | Concave & Convex Lenses | The Dr Binocs Show | Peekaboo Kidz
Lensa Cekung dan Lensa Cembung

Perbedaan Bayangan Nyata dan Bayangan Maya

CAHAYA DAN ALAT OPTIK (PART 3) : CERMIN CEMBUNG DAN LENSA CEKUNG IPA KELAS 8 SMP

Convex and concave Lenses - Physics - Eureka.in
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
