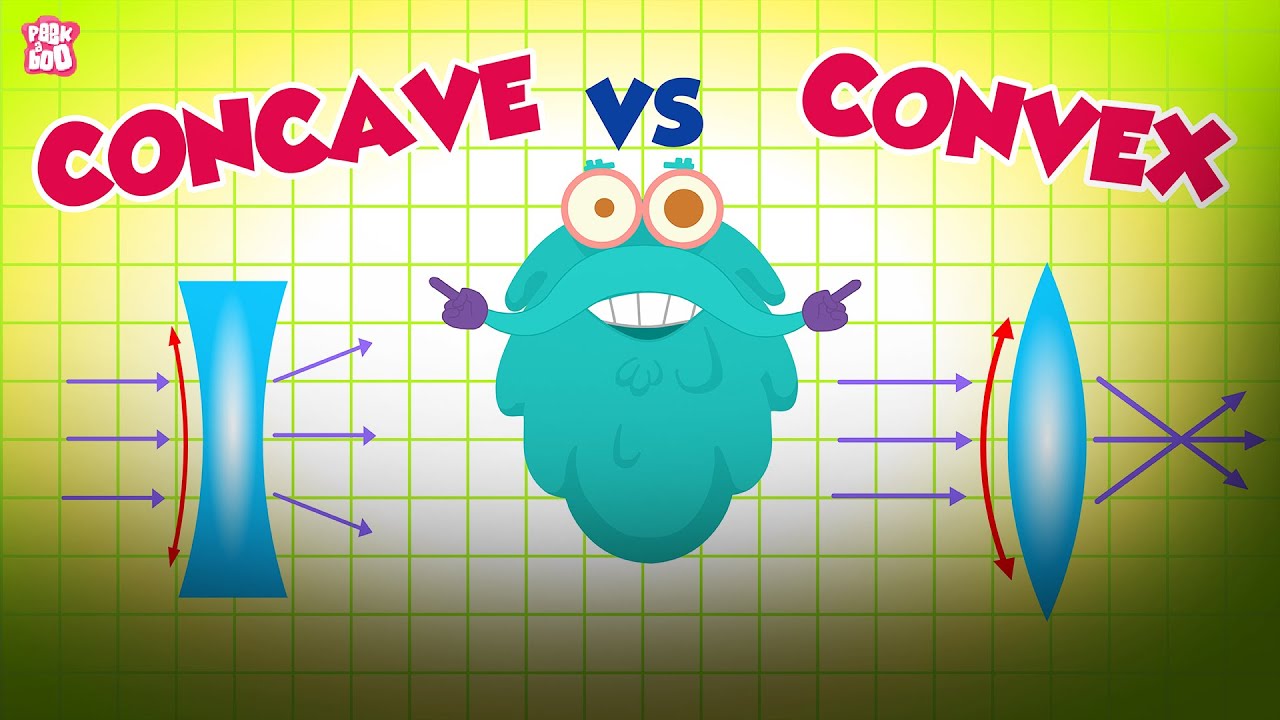
Lensa Cekung dan Lensa Cembung
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the concept of lenses, which are transparent objects with concave or convex surfaces that bend light. It covers the two main types of lenses: convex and concave. The video delves into the special rays used to describe light refraction through these lenses and how they help form images. The properties of images formed by both convex and concave lenses depend on the object’s position. It also explains lens equations, magnification, and the lens' focusing ability. The importance of focal length and lens power is highlighted, providing an in-depth understanding of optics.
Takeaways
- 😀 Lenses are transparent objects with concave or convex surfaces, designed to bend light.
- 😀 Convex lenses are thicker in the center and thinner at the edges, while concave lenses are thinner in the center and thicker at the edges.
- 😀 In convex lenses, special rays include those parallel to the main axis that refract towards the focal point behind the lens.
- 😀 The second special ray in convex lenses comes through the passive focal point and refracts parallel to the main axis.
- 😀 A ray passing through the optical center of a convex lens continues straight without refraction.
- 😀 The image formed by a convex lens depends on the object's position relative to the lens.
- 😀 In concave lenses, special rays also follow similar rules to convex lenses but with a focus point in front of the lens.
- 😀 A concave lens creates a virtual, upright, reduced image located in front of the lens, regardless of object positioning.
- 😀 Ray diagrams and special rays help in understanding how images are formed through concave and convex lenses.
- 😀 The lens equation, involving focal length, object distance, and image distance, applies to both concave and convex lenses.
- 😀 Lenses have different focal strengths, and their ability to focus or disperse light is called lens power, measured in diopters.
Q & A
What is the general definition of a lens?
-A lens is a transparent object with curved surfaces, either concave or convex, that bends light. It can focus or diverge light depending on its shape.
What is the difference between a convex and concave lens?
-A convex lens is thicker at the center than at the edges, while a concave lens is thinner at the center than at the edges.
What are the special rays used in refraction by a convex lens?
-The special rays for refraction by a convex lens are: 1) A ray parallel to the main axis, which is refracted towards the focal point. 2) A ray through the focal point (in front of the lens), refracted parallel to the main axis. 3) A ray passing through the optical center, which is not refracted.
How are images formed by a convex lens?
-Images formed by a convex lens depend on the object's position. Using ray diagrams, at least two special rays are needed to locate the image. The image's properties depend on the object's position relative to the lens.
What are the special rays for refraction by a concave lens?
-The special rays for refraction by a concave lens are: 1) A ray parallel to the main axis, which appears to come from the focal point in front of the lens. 2) A ray aimed at the focal point (in front of the lens), refracted parallel to the main axis. 3) A ray passing through the optical center, which continues without bending.
What are the properties of images formed by a concave lens?
-Images formed by a concave lens are always virtual, upright, reduced in size, and located in front of the lens, regardless of the object's position.
How is magnification calculated for lenses?
-Magnification (M) is calculated as the ratio of the image height (h') to the object height (h), with absolute values. Mathematically, M = h' / h.
What is the lens formula?
-The lens formula relates the focal length (F), object distance (s), and image distance (s') as follows: 1/F = 1/s + 1/s'. The magnification is given by M = s'/s.
How do focal lengths differ for convex and concave lenses?
-For convex lenses, the focal length (F) is positive, while for concave lenses, the focal length (F) is negative.
What is the 'power' of a lens, and how is it calculated?
-The power of a lens indicates its ability to converge or diverge light. It is the reciprocal of the focal length and is measured in diopters (D). The formula is P = 1/F, where F is the focal length in meters.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)