GCSE Maths - Pythagoras' Theorem And How To Use It #120
Summary
TLDRThis educational video script teaches viewers how to apply Pythagoras' theorem to find missing side lengths in right-angled triangles. It emphasizes the importance of identifying the right triangle, knowing two sides, and recognizing the hypotenuse. The script walks through step-by-step examples, demonstrating how to label sides as 'a', 'b', and 'c', and then use the formula a^2 + b^2 = c^2 to solve for the unknown side. Practical examples with calculations and the use of a calculator are included to clarify the process, making the concept accessible for learners.
Takeaways
- 📐 To use Pythagoras' theorem, the triangle must be a right-angled triangle with one 90-degree angle.
- 🔍 You need to know the lengths of two sides to apply the theorem; it doesn't matter which two, but there must be one missing length.
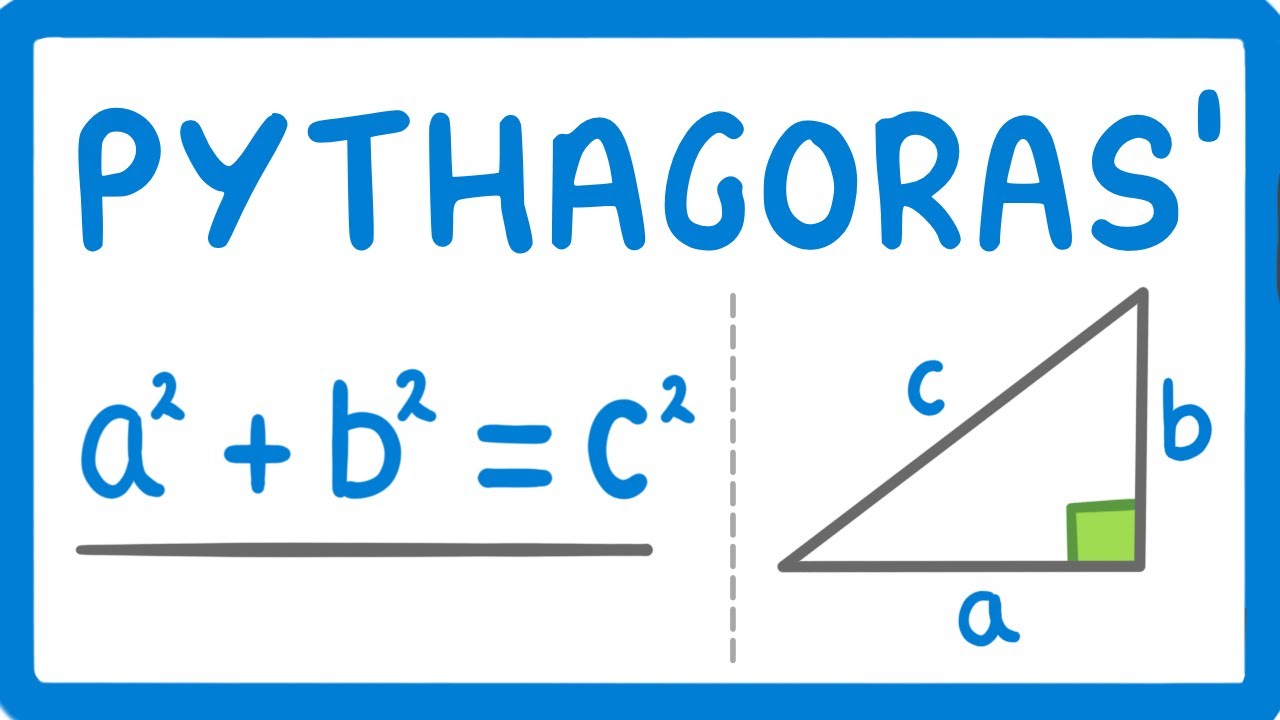
- ✅ The Pythagorean equation is a^2 + b^2 = c^2, where c is the hypotenuse (the longest side) and a and b are the other two sides.
- 📝 It's important to memorize the equation as it's frequently used in mathematics.
- 🔄 The order of a and b doesn't matter, but c must be the hypotenuse opposite the right angle.
- 🧮 Substitute the known side lengths into the equation and solve for the unknown side.
- 📉 When solving, simplify the equation and use mathematical operations to isolate the unknown side.
- 📏 For example, if sides are 3 and 4 units, and you're solving for the hypotenuse, 3^2 + 4^2 = c^2 simplifies to 9 + 16 = c^2, and c = √25 = 5 units.
- 📘 In exam questions, the sides are often labeled with letters, and you should label them as a, b, and c for clarity.
- 🔢 Use a calculator to find the square and square root when dealing with decimal values or to simplify the calculation process.
Q & A
What is the main topic of the video?
-The main topic of the video is how to use Pythagoras' theorem to calculate the missing length of a triangle.
What is the first condition to use Pythagoras' theorem as mentioned in the video?
-The first condition to use Pythagoras' theorem is that the triangle must have a right angle, which is 90 degrees.
Which sides of a right-angled triangle are referred to as 'a' and 'b' in Pythagoras' theorem?
-In Pythagoras' theorem, the sides that are not the hypotenuse (the longest side opposite the right angle) are referred to as 'a' and 'b'.
What is the hypotenuse of a right-angled triangle called in the context of Pythagoras' theorem?
-In the context of Pythagoras' theorem, the hypotenuse of a right-angled triangle is referred to as 'c'.
What is the formula of Pythagoras' theorem?
-The formula of Pythagoras' theorem is a squared plus b squared equals c squared, where a and b are the lengths of the two shorter sides, and c is the length of the hypotenuse.
How do you determine which side is the hypotenuse when applying Pythagoras' theorem?
-In applying Pythagoras' theorem, the hypotenuse is determined by identifying the longest side of the triangle, which is always opposite the right angle.
What is the significance of the equation 'a squared plus b squared equals c squared' in the video?
-The equation 'a squared plus b squared equals c squared' is significant as it is the core formula of Pythagoras' theorem, which is used to find the missing side of a right-angled triangle.
Can you use Pythagoras' theorem if two sides of a triangle are known but not the hypotenuse?
-Yes, you can use Pythagoras' theorem if two sides of a triangle are known, and you can determine the hypotenuse or the missing side using the theorem.
What is the process to solve for the missing side using Pythagoras' theorem as described in the video?
-The process involves labeling the sides as 'a', 'b', and 'c', plugging the known side lengths into the Pythagorean equation, and solving for the missing side by performing algebraic operations and taking the square root.
How does the video demonstrate solving for the missing side of a triangle with given side lengths of 1.7 and 3.2?
-The video demonstrates solving for the missing side by squaring the given side lengths, adding them together, and then taking the square root of the sum to find the length of the hypotenuse.
What is the final step to find the length of the missing side after setting up the Pythagorean equation?
-The final step is to take the square root of the sum of the squares of the known sides to find the length of the missing side.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示
GCSE Maths - Pythagoras' Theorem And How To Use It #120

Matematika Kelas 9 | Kesebangunan pada Segitiga Siku-siku
Area of a Triangle, Given 3 Sides, Heron's Formula
Video Pembelajaran Perbandingan Trigonometri Kelas X SMK

Contoh Soal Perbandingan Trigonometri pada segitiga siku siku

Menentukan Nilai Trigonometri Segitiga Siku Siku Perbandingan Trigonometri segitiga Siku Siku
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
