Statistika #3 Ukuran Pemusatan : Mean - Modus - Median | Kelas X Fase E Kurikulum Merdeka
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the fundamental concepts of measures of central tendency: mean, median, and mode, specifically in grouped data. It provides clear formulas and step-by-step examples on how to calculate each measure. The mean is calculated by multiplying the frequency of each group by the midpoint, while the mode and median are derived using class intervals and frequency calculations. Through examples, viewers can learn to apply these statistical techniques to grouped data. The video emphasizes the importance of understanding these concepts in data analysis.
Takeaways
- 😀 The video discusses key measures of central tendency: mean, median, and mode, specifically for grouped data.
- 😀 The mean (average) is calculated using the formula: sum of (frequency × midpoint) divided by the total frequency.
- 😀 The mode represents the most frequently occurring value in a dataset, and for grouped data, it’s calculated using a specific formula involving the modal class, class widths, and frequency differences.
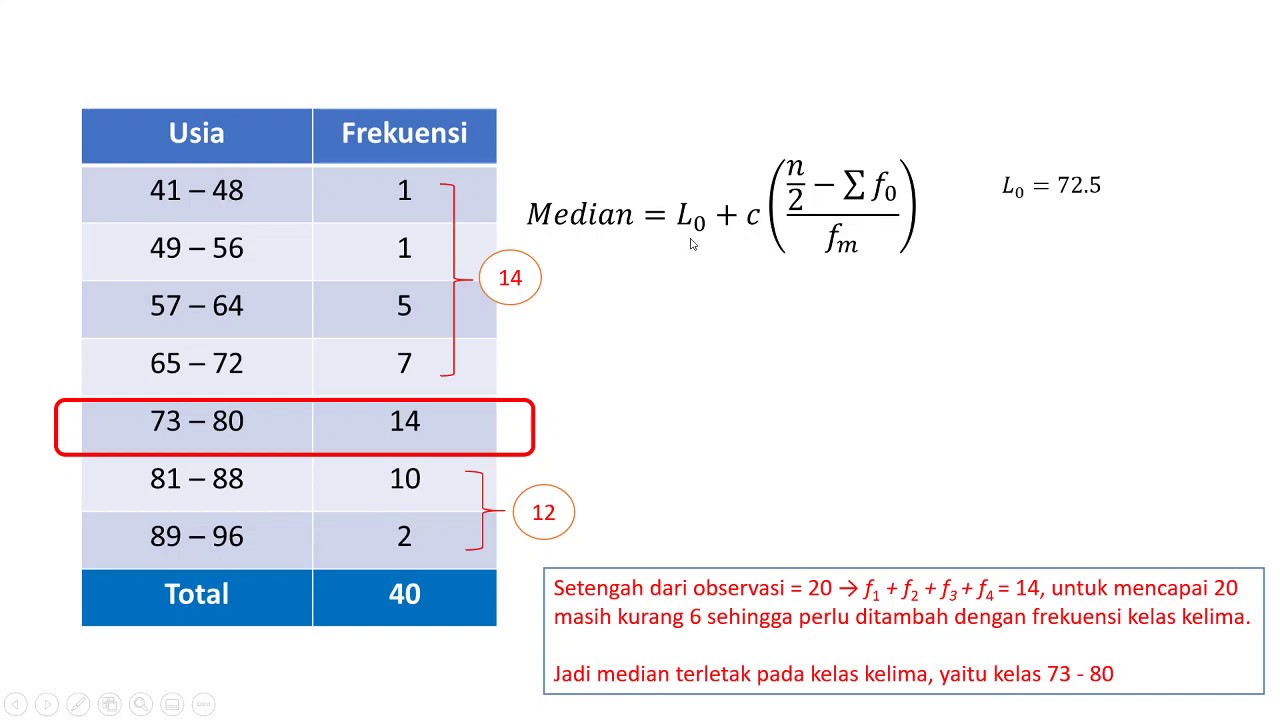
- 😀 The median is the middle value in a dataset, and for grouped data, it’s computed using a formula that accounts for the cumulative frequency and class width.
- 😀 The script emphasizes that the mean for grouped data is found by multiplying frequencies by midpoints and summing the results.
- 😀 When calculating the mode, it is crucial to identify the modal class, which is the class with the highest frequency.
- 😀 The formula for the mode involves the lower boundary of the modal class, the differences in frequencies (D1 and D2), and the class width.
- 😀 For the median, the script explains the process of finding the median class and using the cumulative frequency to calculate the median value.
- 😀 Practice and understanding the formulas for mean, median, and mode are important to mastering statistical measures for grouped data.
- 😀 The video encourages viewers to overcome the fear of failure, stressing that success requires persistence and practice, especially when learning statistics.
Q & A
What is the purpose of this video?
-The purpose of this video is to explain how to determine measures of central tendency—mean, median, and mode—using grouped data in statistics.
What does 'mean' represent in statistics?
-The 'mean' represents the average value of a data set, calculated by summing all data values and dividing by the total number of values.
How is the mean calculated for grouped data?
-For grouped data, the mean is calculated by multiplying the midpoint of each class interval by its frequency, summing these products, and then dividing by the total frequency.
What is the formula for calculating the mean in grouped data?
-The formula for calculating the mean in grouped data is: Mean = (Σ(f * X)) / N, where f is the frequency, X is the midpoint of the class, and N is the total frequency.
What is 'mode' in the context of statistics?
-The 'mode' is the value that appears most frequently in a data set. For grouped data, it is found in the class with the highest frequency.
What is the formula for calculating the mode in grouped data?
-The formula for calculating the mode is: Mode = L + [(D1 / (D1 + D2)) * p], where L is the lower boundary of the modal class, D1 and D2 are the frequency differences, and p is the class width.
How do you identify the modal class?
-The modal class is identified as the class interval that has the highest frequency in the frequency distribution table.
What does the 'median' represent in statistics?
-The 'median' represents the middle value that divides a data set into two equal parts. It is the value that lies at the center of the data distribution.
What is the formula for calculating the median in grouped data?
-The formula for calculating the median in grouped data is: Median = L + [((N/2) - F) / f] * p, where L is the lower boundary of the median class, N is the total frequency, F is the cumulative frequency before the median class, f is the frequency of the median class, and p is the class width.
How is the median class determined?
-The median class is determined by finding the class interval that contains the cumulative frequency value that corresponds to half the total number of data points (N/2).
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

STATISTIKA: Ukuran gejala pusat dan ukuran letak 1

Ukuran Pemusatan Data Kelompok

Statistika Dasar Ukuran Pemusatan Data (Mean, Modus, Median) Data Tunggal dan Data Kelompok
UKURAN PEMUSATAN DATA BERKELOMPOK | Rataan Median Modus Kuartil Desil Persentil

Ukuran pemusatan data, mean median modus, Statistika

KULIAH STATISTIK (5) - UKURAN PEMUSATAN DATA
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
