VLAN dan Trunk - Penjelasan dan Latihan - 3.6.1 Implement VLANs & Trunking
Summary
TLDRThis tutorial covers the process of configuring Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs) in network switches. It guides viewers through setting up VLANs, assigning ports to specific VLANs, configuring trunk ports, and understanding the role of native VLANs. The video also explains the difference between static and dynamic trunking, the importance of a management VLAN for remote access, and how to troubleshoot common issues like port mismatches. Finally, the speaker highlights real-world use cases of VLANs for network segmentation, traffic control, and improving network security.
Takeaways
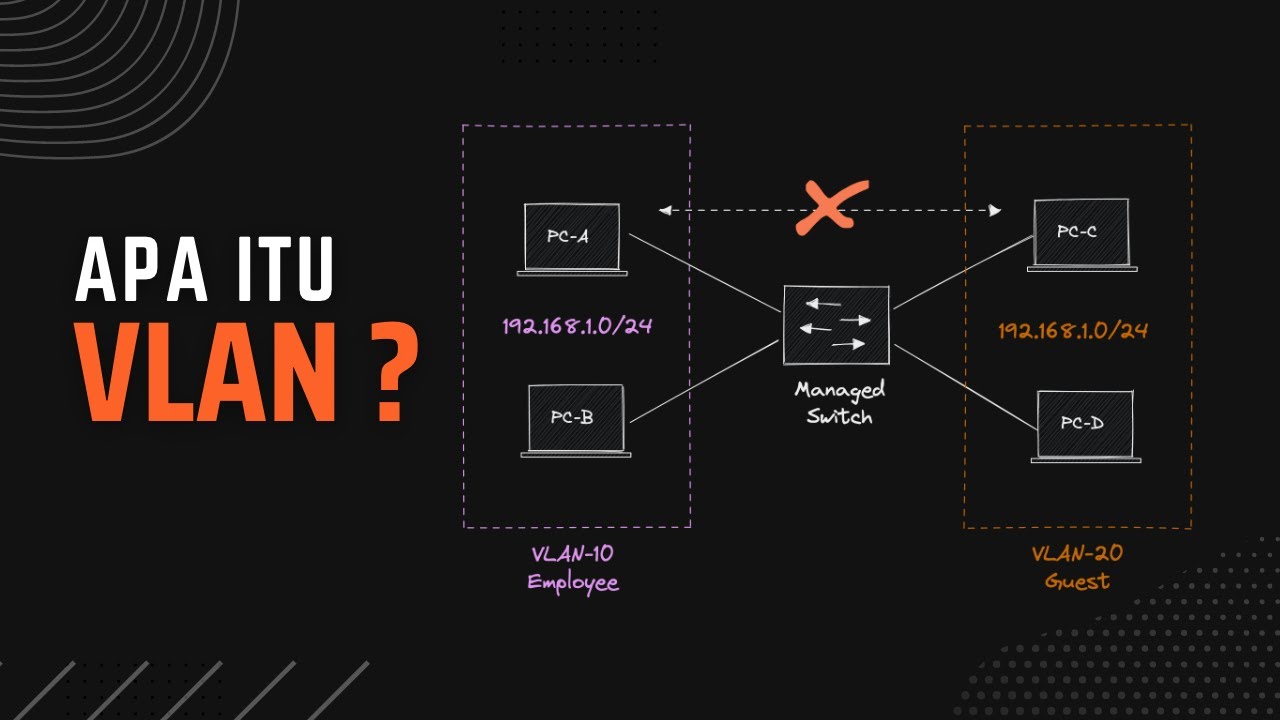
- 😀 VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) allows logical network segmentation, improving management and security across physical networks.
- 😀 VLANs can be configured on switches using software, enabling devices in different locations to belong to the same virtual network.
- 😀 Access mode on a switch port assigns it to a single VLAN, meaning it can only carry traffic from that specific VLAN.
- 😀 Trunk mode on a switch port allows it to carry traffic from multiple VLANs, which is essential for inter-switch communication.
- 😀 Dynamic mode (Auto/Desirable) allows switches to negotiate whether a port should operate in access or trunk mode based on the other end's configuration.
- 😀 Voice VLAN (e.g., VLAN 40) prioritizes voice traffic, ensuring high-quality, uninterrupted communication for voice and video applications.
- 😀 A management VLAN (e.g., VLAN 99) is dedicated for remote switch management through protocols like SSH or Telnet, adding a layer of security.
- 😀 Each VLAN needs a specific IP address to allow remote management, and the management interface should be configured properly for access.
- 😀 The native VLAN is used for untagged traffic on trunk links, ensuring backward compatibility with older devices or devices not supporting VLAN tagging.
- 😀 Static trunking configuration (e.g., setting ports to trunk mode and disabling DTP) ensures consistent VLAN communication across switches, avoiding configuration errors.
- 😀 VLAN configuration errors, such as mismatched VLAN IDs or native VLAN misconfigurations, can disrupt network communication and require troubleshooting.
Q & A
What is a VLAN and why is it important in networking?
-A VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) is a logical partitioning of a physical network into multiple distinct broadcast domains. It allows network administrators to group devices together based on function, department, or application, regardless of their physical location. VLANs improve network efficiency, enhance security, and simplify management by isolating traffic between different groups of users.
What is the difference between access mode and trunk mode in VLAN configuration?
-Access mode is used when a single port is assigned to one VLAN, and the port only carries traffic from that VLAN. In contrast, trunk mode allows a port to carry traffic from multiple VLANs, making it suitable for inter-switch links where data from several VLANs needs to pass through.
Why is the concept of a native VLAN important in trunking?
-The native VLAN is used to carry untagged traffic across a trunk link. It is important because it ensures that devices that do not support VLAN tagging, or older switches that don’t understand VLAN tags, can still communicate by sending their traffic through the native VLAN. By default, this is VLAN 1, but it can be changed for security reasons.
How does dynamic trunking work and how is it different from static trunking?
-Dynamic trunking uses a negotiation protocol (DTP - Dynamic Trunking Protocol) to automatically configure a port as a trunk or access port based on the connection at the other end. Static trunking, on the other hand, requires manual configuration to designate a port as a trunk, ensuring it will always allow traffic from multiple VLANs.
What role does the Voice VLAN (VLAN 40) play in a network configuration?
-The Voice VLAN is dedicated to carrying voice traffic, such as IP phone data. It ensures that voice packets receive priority treatment and can be handled according to QoS (Quality of Service) rules, thus reducing latency and improving the clarity of voice calls. It is essential for ensuring that voice traffic does not get delayed or dropped during peak network usage.
How do you assign a port to a specific VLAN on a switch?
-To assign a port to a specific VLAN on a switch, you first enter the interface configuration mode for that port and set the switchport mode to 'access'. Then, specify the VLAN you want the port to be associated with using the command 'switchport access vlan [VLAN number]'.
What is the purpose of a management VLAN and how is it configured?
-A management VLAN is used for remote management of network devices, such as switches, through protocols like SSH or Telnet. It is typically configured with an IP address and assigned to a specific VLAN (e.g., VLAN 99), allowing administrators to manage devices securely over the network. The management interface is activated using the 'no shutdown' command after setting the IP address.
What does the command 'switchport trunk native vlan 100' do?
-The command 'switchport trunk native vlan 100' configures the native VLAN of a trunk port to VLAN 100. This means that any untagged traffic on that port will be assigned to VLAN 100. The native VLAN is important for handling traffic from devices that do not tag their VLAN information.
What happens if a port is misconfigured with inconsistent VLAN settings between switches?
-If there is a mismatch in VLAN settings, such as one switch port being configured with VLAN 1 as the native VLAN and another switch port being configured with VLAN 100, the link will not be able to pass traffic properly. This can lead to errors like 'inconsistent port' or 'mismatch', causing communication failure between the switches. The configuration should be synchronized across both ends.
Why should VLANs be used instead of traditional subnetting in certain situations?
-VLANs offer greater flexibility than traditional subnetting by allowing network administrators to group devices based on their functional needs rather than their physical location. This grouping can improve security, simplify network management, and facilitate tasks like bandwidth control, access restriction, and more precise traffic routing within different segments of the network.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenant5.0 / 5 (0 votes)