DNA Structure HD Animation
Summary
TLDRThe structure of DNA, first described by James Watson and Francis Crick, is a right-handed double helix composed of a sugar-phosphate backbone with nitrogenous bases on the inside. Key features include the pairing of adenine with thymine and guanine with cytosine, stabilized by hydrogen bonds. The strands are anti-parallel, featuring distinct ends, and create major and minor grooves critical for protein binding. The stability of guanine-cytosine pairs, which form three hydrogen bonds compared to two for adenine-thymine pairs, highlights the molecular intricacies of DNA's function in genetics.
Takeaways
- 🧬 The DNA structure was first inferred by James Watson and Francis Crick, using X-ray crystallography data.
- 🔬 Key contributors include Maurice Wilkins and Rosalind Franklin for X-ray data, and Erwin Chargaff for base composition analysis.
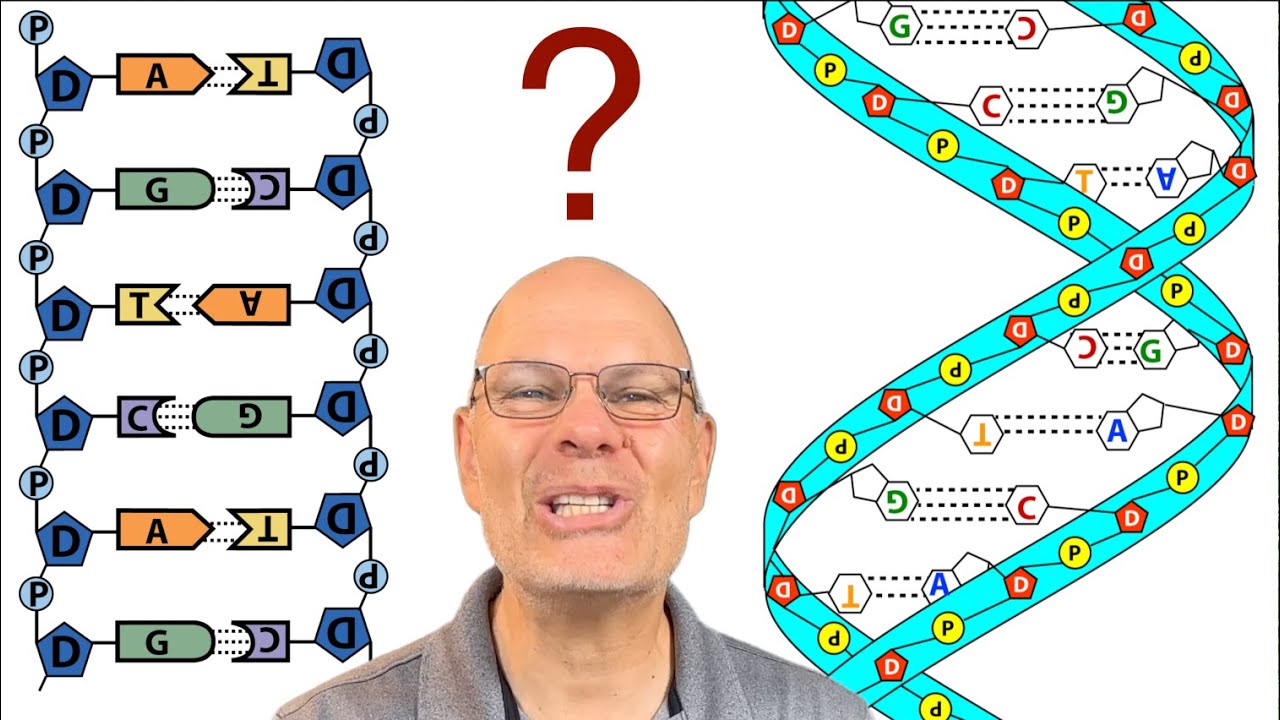
- 📏 DNA has a right-handed double helical structure, with one complete turn covering 10 bases and measuring 3.4 nanometers.
- 🌐 The double helix has a width of 2 nanometers, with an alternating sugar-phosphate backbone and nitrogen bases inside.
- 🔗 Nucleotide bases are hydrogen bonded between strands, with adenine pairing with thymine, and guanine pairing with cytosine.
- 💪 Guanine-cytosine pairs are more stable due to three hydrogen bonds, compared to the two in adenine-thymine pairs.
- 📖 The sequence of bases in one strand determines the complementary sequence in the other strand.
- ↔️ DNA strands have polarity; one end has a free 3' hydroxyl group, while the other end has a free 5' hydroxyl group or phosphate.
- ⏳ The strands are oriented in opposite directions, known as anti-parallel, which is crucial for replication and function.
- 🔄 Asymmetrical spacing creates major and minor grooves in the DNA, important for protein binding and gene regulation.
Q & A
Who first inferred the structure of the DNA molecule?
-The structure of the DNA molecule was first inferred by James Watson and Francis Crick.
What techniques were primarily used to deduce the structure of DNA?
-The structure was primarily deduced using X-ray crystallography data collected by Maurice Wilkins and Rosalind Franklin.
What is the significance of Erwin Chargaff's work in understanding DNA?
-Erwin Chargaff conducted chemical analysis of base composition of DNA, which contributed to understanding nucleotide pairing.
What are the key features of the DNA double helix structure?
-The DNA double helix has a right-handed structure, with an alternating sugar-phosphate backbone and nitrogen bases projecting inward.
How many bases are there in one complete turn of the DNA helix?
-One complete 360-degree turn of the helix covers 10 bases.
What is the distance covered by one complete turn of the DNA helix?
-One complete turn of the helix equals 3.4 nanometers in physical distance along the axis of the molecule.
What are the characteristics of the hydrogen bonds between nucleotide bases?
-Adenine pairs with thymine through two hydrogen bonds, while guanine pairs with cytosine through three hydrogen bonds, making GC pairs more stable.
What does it mean that DNA strands are anti-parallel?
-Anti-parallel means that the two strands of DNA run in opposite directions, distinguished by the free hydroxyl groups at each end.
What role do the major and minor grooves in the DNA helix play?
-The major and minor grooves created by the asymmetric spacing of the helix backbones are important for the binding of proteins that regulate gene transcription.
How does the polarity of DNA strands affect their structure?
-The polarity, indicated by the free three-prime and five-prime ends, allows for unique identification of each strand's ends and contributes to their anti-parallel orientation.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenant5.0 / 5 (0 votes)