What is a PID Controller? | DigiKey
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the fundamentals of PID (Proportional, Integral, Derivative) controllers, illustrating their significance in various applications, from automotive cruise control to industrial equipment like reflow ovens. Viewers learn how PID controllers operate by calculating error values and adjusting outputs to maintain desired setpoints, and the importance of tuning their constants for optimal performance. The presenter emphasizes the historical context of PID development and concludes by encouraging viewers to experiment with implementing their own PID controllers in code, promising future insights on tuning techniques.
Takeaways
- 😀 A PID controller is a control structure used in many closed-loop systems, consisting of Proportional, Integral, and Derivative components.
- 📅 PID controllers were developed by Nicholas Minorski in 1922 and have become essential in control theory applications.
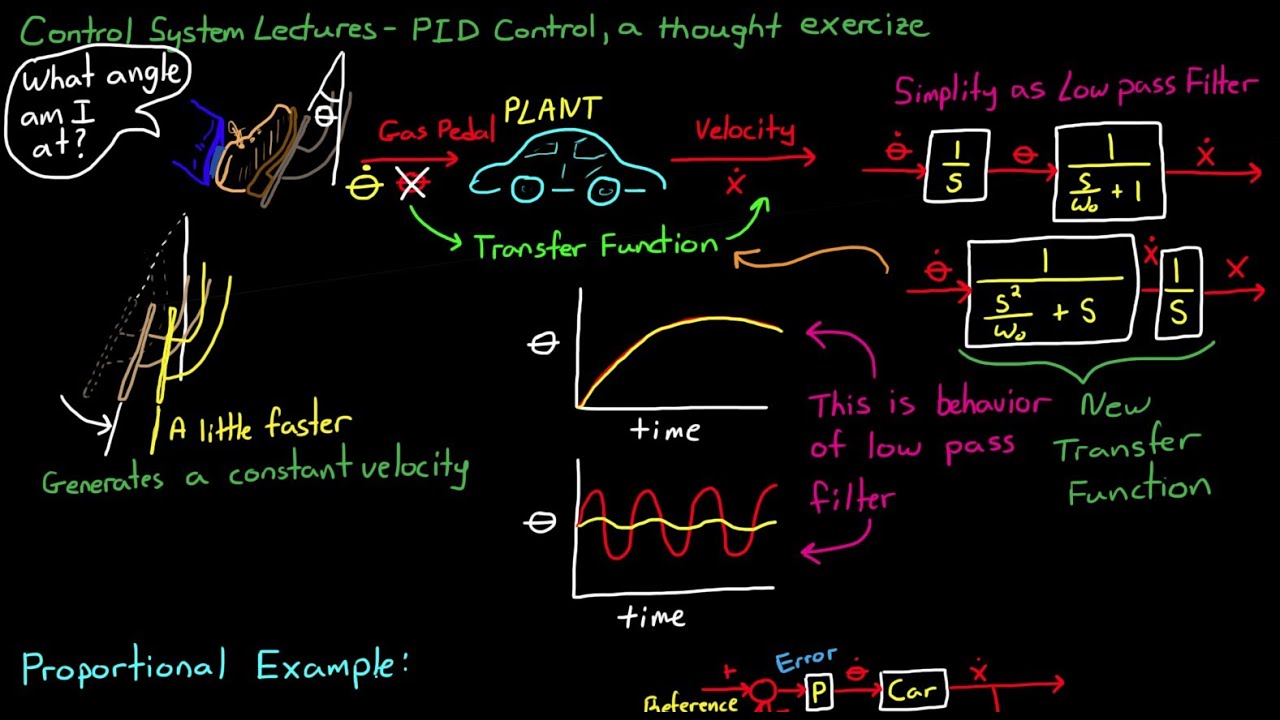
- 🚗 An everyday example of a PID controller is a car's cruise control system, which automatically adjusts the accelerator to maintain a constant speed.
- 🔄 Closed loop systems measure output and adjust inputs based on feedback, whereas open loop systems do not.
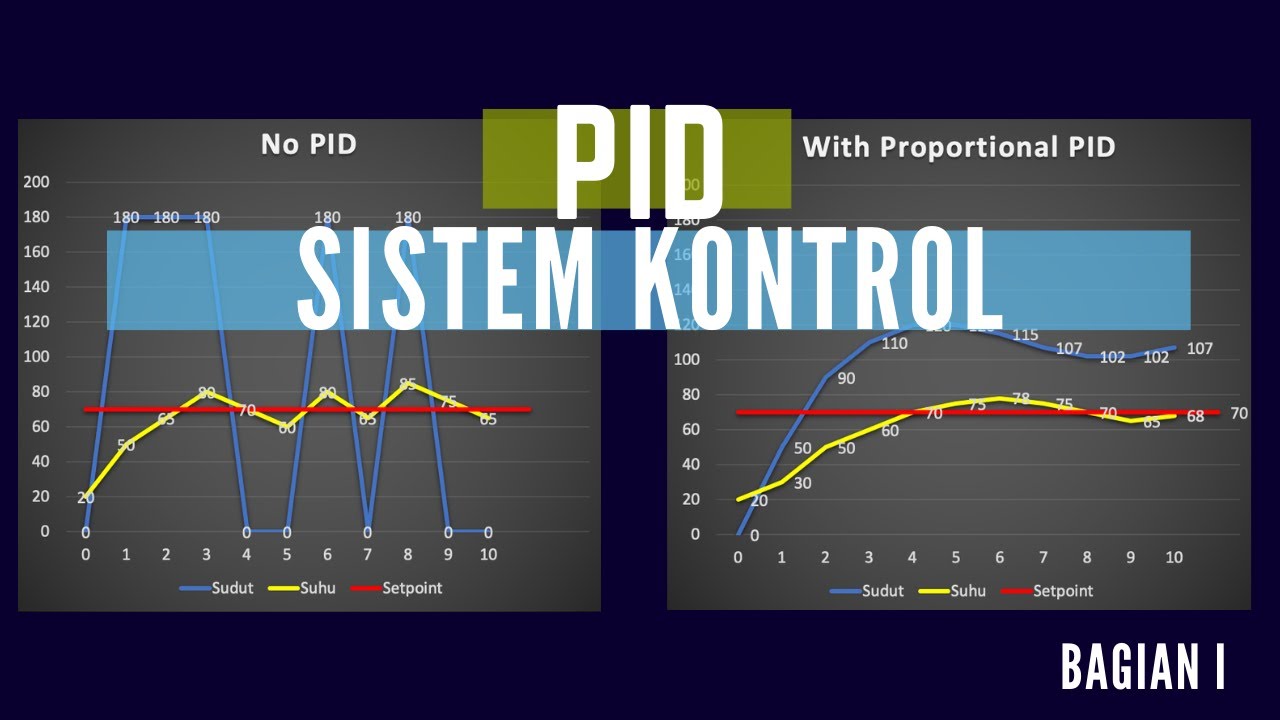
- ⚖️ The Proportional (P) component adjusts output based on the current error, directly affecting system response.
- 📈 The Integral (I) component addresses steady-state error by accumulating past errors over time, allowing for adjustments to eliminate offsets.
- 📉 The Derivative (D) component predicts future errors based on the rate of change of the error, helping to dampen the system's response.
- 🔗 Combining P, I, and D components results in a PID controller that effectively manages system response, balancing speed and stability.
- 🔧 Tuning PID controllers involves adjusting the Kp, Ki, and Kd constants to achieve an optimal system response, with methods like Ziegler-Nichols available to assist.
- 🏭 PID controllers are widely utilized in various applications, including manufacturing processes and temperature control in industrial ovens.
Q & A
What does PID stand for in PID controllers?
-PID stands for Proportional, Integral, and Derivative, which are the three fundamental components of the controller used to manage dynamic systems.
Who developed the theoretical analysis of PID controllers?
-Nicholas Minorski developed the theoretical analysis of PID controllers in the 1920s while researching automatic ship steering methods.
How does a PID controller work?
-A PID controller works by comparing the desired set point with the actual output and adjusting the control signal based on the proportional, integral, and derivative terms to minimize the error.
What is the difference between open-loop and closed-loop systems?
-An open-loop system does not use feedback to adjust its operation, while a closed-loop system continuously monitors the output and uses feedback to adjust the control input.
What role does the proportional component play in a PID controller?
-The proportional component produces an output that is proportional to the current error, which helps reduce the difference between the desired set point and the actual output.
Why is the integral component important in a PID controller?
-The integral component accumulates past errors over time, which helps eliminate steady-state errors that may persist in the system.
How does the derivative component enhance the performance of a PID controller?
-The derivative component predicts future errors based on the rate of change of the current error, allowing the system to respond more effectively and dampen any overshoot.
Can you give an example of a real-world application of PID controllers?
-PID controllers are commonly used in cruise control systems in vehicles, where they adjust the accelerator to maintain a constant speed.
What is the significance of tuning the K constants in a PID controller?
-Tuning the K constants (KP, Ki, KD) is crucial for optimizing the controller's response to changes in the system, ensuring that it performs effectively and achieves the desired performance.
In what industries are PID controllers commonly utilized?
-PID controllers are widely used in manufacturing and industrial applications, such as in reflow ovens for soldering components without damaging the boards.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenant5.0 / 5 (0 votes)