Teori Perkembangan Atom
Summary
TLDRThis educational video discusses the historical development of atomic theory, tracing its evolution from the ideas of Democritus in the 4th century BC to modern quantum mechanics. It highlights key figures like John Dalton, who proposed the first scientific atomic theory; J.J. Thomson, who discovered the electron; Ernest Rutherford, who identified the atomic nucleus; and Niels Bohr, who introduced energy levels for electrons. The video culminates in the advancements brought by quantum mechanics, emphasizing the probabilistic nature of electron positions, thus illustrating the dynamic progress in understanding atomic structure.
Takeaways
- 🧪 Democritus introduced the concept of the atom in the 4th century BC, proposing that matter consists of indivisible particles.
- ⚛️ John Dalton established the first scientific atomic theory in 1803, stating that atoms cannot be created or destroyed and that they combine in fixed ratios to form compounds.
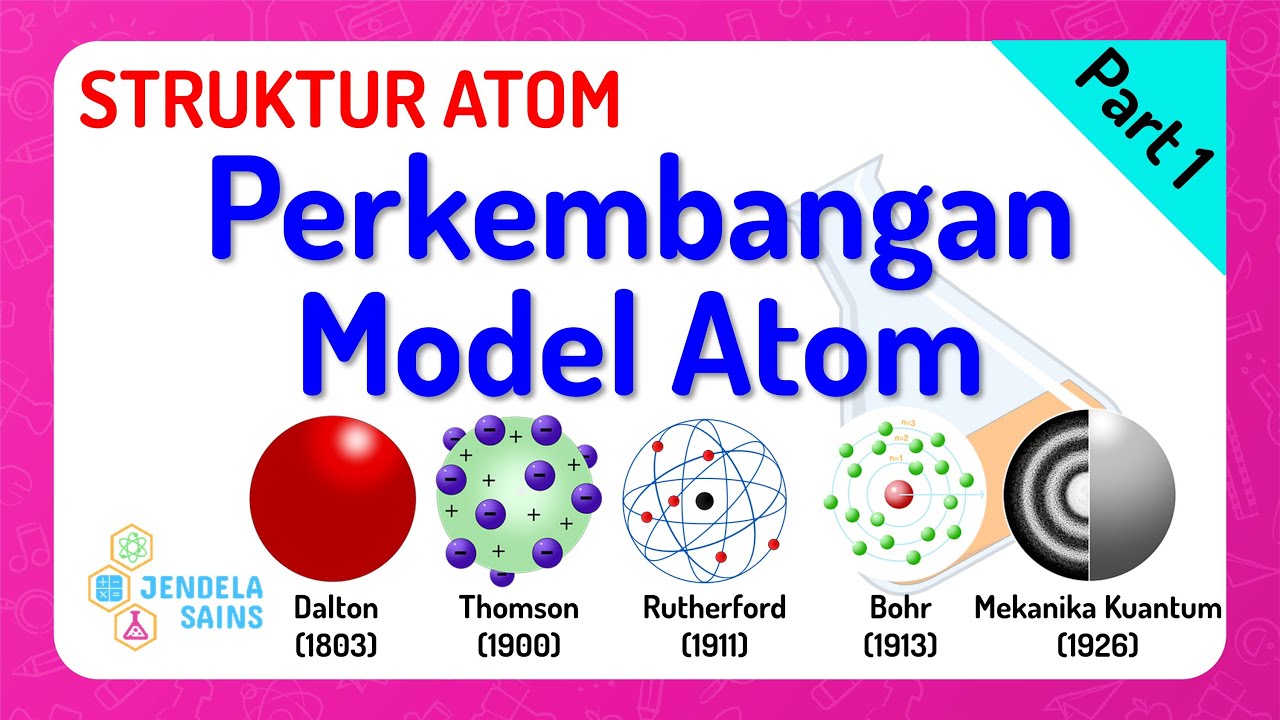
- 🔍 Dalton visualized atoms as solid spheres, similar to bullets, but his model could not explain electrical conductivity.
- 💡 J.J. Thomson discovered electrons in 1893 through cathode ray experiments and proposed the 'plum pudding' model of the atom.
- ⚡ Thomson's model suggested that atoms contain negatively charged electrons within a positive matrix, but he could not confirm the presence of other particles.
- 🔭 Ernest Rutherford conducted the gold foil experiment in 1910, revealing that atoms have a small, dense nucleus surrounded by orbiting electrons.
- 🚫 Rutherford's model could not explain why electrons remain stable in their orbits without spiraling into the nucleus.
- 🌈 Niels Bohr introduced a model in 1913 where electrons occupy fixed orbits with quantized energy levels around the nucleus.
- ❓ Bohr's model was limited to hydrogen and could not account for the behavior of more complex atoms.
- 🔬 The development of quantum mechanics in 1926 by Louis de Broglie, Werner Heisenberg, and Erwin Schrödinger provided a more comprehensive understanding of atomic structure.
- 🌌 Quantum mechanics describes electrons as probability clouds (orbitals) around the nucleus, incorporating wave-particle duality and the uncertainty principle.
Q & A
What is the origin of the term 'atom'?
-The term 'atom' originates from Greek, introduced by Democritus in the 4th century BC, where it was derived from the word meaning 'indivisible'.
Who was the first to propose a scientific theory of the atom?
-John Dalton was the first to propose a scientific theory of the atom in 1803, building upon the concept of atoms having mass and being indivisible.
What significant laws did Dalton's experiments support?
-Dalton's experiments supported the laws of conservation of mass by Lavoisier and the law of definite proportions by Proust, asserting that atoms can rearrange but cannot be created or destroyed.
How did Dalton describe the structure of an atom?
-Dalton described the atom as a solid, neutral sphere, similar to a bullet, without internal structure.
What was J.J. Thomson's contribution to atomic theory?
-J.J. Thomson contributed to atomic theory by discovering the electron in 1897 through his experiments with cathode rays, proposing the 'plum pudding model' of the atom, where electrons are embedded in a positively charged 'soup'.
What did Ernest Rutherford discover through his experiments?
-Ernest Rutherford discovered the nucleus of the atom in 1911 by firing alpha particles at gold foil, concluding that atoms consist of a dense nucleus surrounded by mostly empty space.
What were the limitations of Rutherford's atomic model?
-Rutherford's model could not explain the stability of atoms, as classical physics suggested that electrons should spiral into the nucleus due to electromagnetic radiation.
What did Niels Bohr contribute to atomic theory?
-Niels Bohr proposed a new model of the atom in 1913, suggesting that electrons orbit the nucleus at fixed energy levels, absorbing or emitting energy when they transition between these levels.
What is the significance of quantum mechanics in atomic theory?
-Quantum mechanics, developed by De Broglie, Heisenberg, and Schrödinger in the 1920s, introduced the concept that electrons have wave-like properties and that their positions cannot be determined precisely, leading to the idea of electron clouds or orbitals.
What is an 'orbital' in the context of atomic theory?
-An orbital is a region around the nucleus where there is a high probability of finding an electron, reflecting the probabilistic nature of quantum mechanics in describing electron positions.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

Evolution of Atomic Model 400 BC - 2020 | History of the atom Timeline, Atomic Theories

Materi, Atom dan Sejarah Perkembangan Atom
Struktur Atom • Part 1: Perkembangan Model Atom

Struktur Atom (1) | Perkembangan Teori Atom | Kimia Kelas 10

History of the Atom (Atomic Theory)

Kimia X - Struktur Atom #3 | Perkembangan Teori dan Model Atom
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
