Kimia X - Struktur Atom #3 | Perkembangan Teori dan Model Atom
Summary
TLDRThis video covers the development of atomic theory, starting with Democritus' early idea of indivisible atoms. It progresses through John Dalton's solid ball model, J.J. Thomson's raisin bread model, and Ernest Rutherford's solar system model. The video then discusses Niels Bohr's theory of electron shells and quantum mechanics, introducing modern atomic theory with contributions from Max Planck, Louis De Broglie, Heisenberg, and Schrodinger. The theories show the evolution of atomic models, from indivisible particles to the complex understanding of electron probability and uncertainty, highlighting the key milestones in atomic theory development.
Takeaways
- 😀 Atoms are the building blocks of matter, essential for understanding chemistry and the universe.
- 😀 The development of atomic theory spans from Democritus' early ideas to modern quantum mechanics.
- 😀 Democritus, a Greek philosopher, proposed the concept of indivisible particles called 'atomos' in the 4th century BC.
- 😀 John Dalton's atomic theory described atoms as solid, indivisible particles and introduced the concept of element-specific atoms.
- 😀 Dalton's theory had limitations, including the inability to explain electrical conductivity in solutions.
- 😀 J.J. Thomson's atomic theory, also known as the 'raisin bread model,' introduced the discovery of electrons and their distribution in atoms.
- 😀 Ernest Rutherford's gold foil experiment revealed that atoms are mostly empty space with a dense, positively charged nucleus.
- 😀 Rutherford's atomic model depicted electrons orbiting a central nucleus, similar to a solar system, but couldn't explain electron stability.
- 😀 Niels Bohr's atomic theory introduced electron shells and explained electron movement through energy absorption or emission.
- 😀 Modern atomic theory includes the work of scientists like Planck, De Broglie, Heisenberg, and Schrödinger, leading to the concept of electron clouds and uncertainty principles.
- 😀 The Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle states that the exact position and momentum of an electron cannot be determined simultaneously.
- 😀 Modern atomic theory describes atoms with an atomic nucleus and electron clouds, where the position of electrons can only be predicted probabilistically.
Q & A
What is the main topic discussed in the video?
-The video discusses the development of atomic theory and models, explaining how different scientists contributed to our current understanding of the atom.
Who was the first scientist to propose the concept of the atom?
-The concept of the atom was first proposed by Democritus, a philosopher from Greece in the 4th century BC.
What was Democritus' theory about atoms?
-Democritus proposed that all matter is composed of small, indivisible particles called 'atomos', meaning 'indivisible'. However, he could not experimentally prove this theory.
What is the key idea behind John Dalton's atomic theory?
-John Dalton's atomic theory suggested that atoms are like solid balls that cannot be divided further. He also proposed that atoms of the same element are identical, atoms of different elements are different, and compounds are formed by the combination of atoms in fixed ratios.
What was the main weakness of Dalton's atomic theory?
-A major weakness of Dalton's atomic theory was that it could not explain why solutions conduct electricity, as it did not account for the existence of charged particles like electrons.
What did J.J. Thomson discover about atoms?
-J.J. Thomson discovered the existence of negatively charged particles called electrons through his experiments with cathode rays. His model, known as the 'raisin bread model', suggested that atoms were a positively charged sphere with electrons spread throughout.
What was the flaw in Thomson's atomic model?
-Thomson's model couldn't explain the exact arrangement of positive and negative charges within the atom, nor could it explain how these charges were structured.
What significant discovery did Ernest Rutherford make?
-Ernest Rutherford discovered that the atom has a small, dense, positively charged nucleus at its center, using the gold foil experiment. This led to the 'solar system' model of the atom.
What was a major limitation of Rutherford's atomic theory?
-Rutherford's model couldn't explain why electrons, which move around the nucleus, don't fall into the nucleus due to energy loss in motion, as predicted by classical physics.
How did Niels Bohr improve upon Rutherford's model?
-Niels Bohr introduced the idea of electron shells, suggesting that electrons move in specific, stable orbits around the nucleus and can absorb or emit energy when they jump between these orbits.
What is the main feature of modern atomic theory?
-Modern atomic theory incorporates ideas from quantum mechanics, such as the wave-particle duality of electrons, and the Heisenberg uncertainty principle, which states that the exact position and momentum of electrons cannot be simultaneously known.
What does the Heisenberg uncertainty principle state about electrons?
-The Heisenberg uncertainty principle states that due to the dual nature of electrons, it is impossible to determine both their position and momentum at the same time. Only the probability of finding an electron in a certain region can be calculated.
How does the modern atomic model differ from earlier models?
-The modern atomic model differs from earlier models in that it describes electrons not as particles moving in fixed orbits but as existing in a cloud of probability around the nucleus, with their exact position uncertain.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Modelos de Dalton e Thomson [Módulo 02 - Aula 01]

STRUKTUR ATOM DAN SISTEM PERIODIK UNSUR : Struktur Atom - Materi KIMIA SMA Kelas 10, TKA SMA |Part 1

PERKEMBANGAN TEORI ATOM | Dalton, Thomson, Rutherford, Bohr, Heisenberg, Erwin Schrodinger,

History of the Atom (Atomic Theory)
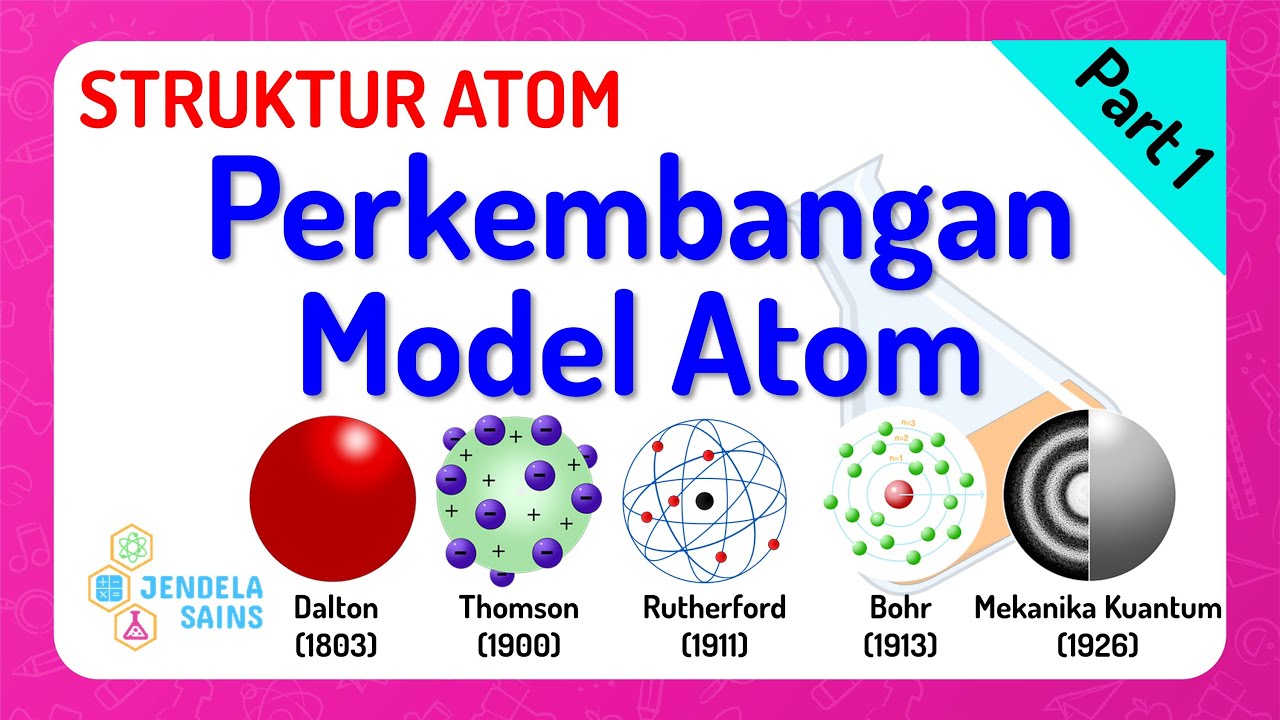
Struktur Atom • Part 1: Perkembangan Model Atom

TEORI MODEL ATOM | Fisika Atom #1 - Fisika Kelas 12
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)