Struktur Atom (1) | Perkembangan Teori Atom | Kimia Kelas 10
Summary
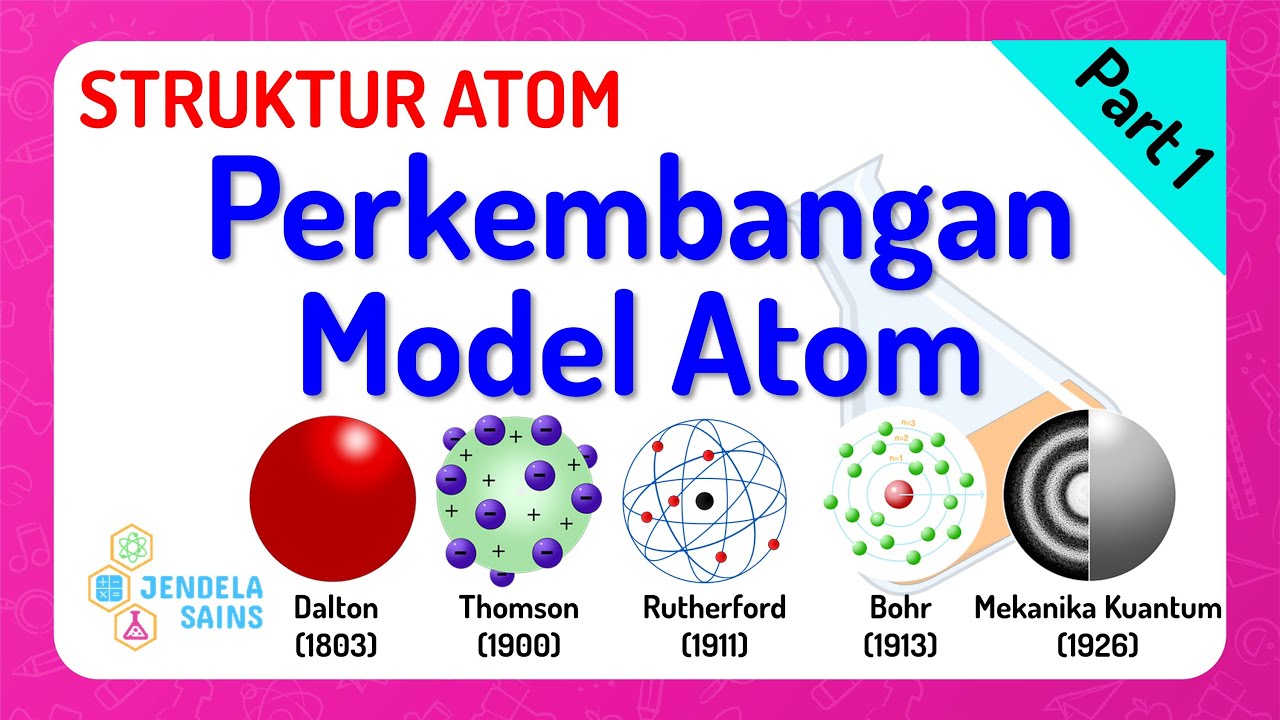
TLDRThis educational video script explores the evolution of atomic theory and models, starting with Democritus' concept of indivisible 'atoms' in 5th century BC Greece. It progresses through John Dalton's atomic theory in 1813, which introduced the law of conservation of mass and the atomic nature of elements. The script then discusses J.J. Thomson's 'plum pudding' model with a positively charged sphere and embedded electrons, followed by Ernest Rutherford's discovery of the atomic nucleus. Niels Bohr's quantum theory and the modern quantum mechanical model, which introduced electron orbitals and probabilistic locations, are also covered. The script concludes with a nod to the contributions of scientists like Louis de Broglie and Erwin Schrödinger, highlighting the transition from particle to wave-like properties of electrons.
Takeaways
- 😀 Democritus, a Greek philosopher, first proposed the concept of atoms, which he described as indivisible components of matter.
- 🔬 John Dalton's atomic theory, introduced in 1813, postulated that atoms are the smallest indivisible particles that make up matter, leading to the understanding of the law of conservation of mass and the law of definite proportions.
- 🌐 Dalton's model depicted atoms as solid, indivisible spheres, which helped explain chemical reactions as rearrangements of these particles.
- 🔋 Joseph John Thomson's 'plum pudding' model, proposed in 1897, introduced the concept of electrons as negatively charged particles within an atom, distributed within a positively charged sphere.
- 💡 The Rutherford model, developed in 1911, revolutionized atomic theory by suggesting a central nucleus with positive charge and electrons orbiting around it, much like planets around the sun.
- 🌌 Niels Bohr's model, introduced in 1913, refined the Rutherford model by proposing that electrons orbit the nucleus in specific paths or shells, with quantized energy levels.
- 🌈 Bohr's model successfully explained the spectral lines of hydrogen, showing that electrons could only occupy certain energy levels and that transitions between these levels resulted in the emission or absorption of specific frequencies of light.
- 🌌 The modern quantum mechanical model of the atom, developed in the 1920s, introduced the concept of electron wave functions and probability clouds, indicating where electrons are most likely to be found.
- 🔬 The quantum model resolved issues with the classical model, such as why electrons do not spiral into the nucleus, by showing that electrons exist in a cloud of probabilities rather than fixed orbits.
- 🌐 The modern theory of the atom is the most comprehensive to date, incorporating principles from quantum mechanics to describe the behavior and properties of electrons within the atom.
Q & A
Who is credited with the first atomic theory?
-Democritus, a Greek philosopher from the 5th century BCE, is credited with the first atomic theory.
What were the limitations of Democritus' atomic theory?
-Democritus' atomic theory lacked experimental evidence, making it less convincing and considered imperfect.
What is the significance of John Dalton's atomic theory?
-John Dalton's atomic theory, proposed in 1813, introduced the concept of atoms as indivisible particles and explained the law of conservation of mass and the law of definite proportions.
How did Dalton's model of the atom look like?
-Dalton's model depicted atoms as solid, indivisible spheres with similar properties for atoms of the same element and different properties for different elements.
What was the main shortcoming of Dalton's atomic theory?
-Dalton's theory could not explain how atoms bond with each other, the electrical properties of matter, and the differences between atoms of different elements.
Who proposed the 'plum pudding' model of the atom?
-The 'plum pudding' model was proposed by J.J. Thomson in 1897, suggesting that atoms consist of a positively charged sphere with negatively charged electrons scattered within.
What was the significance of Thomson's discovery of the electron?
-Thomson's discovery of the electron showed that atoms are not indivisible and are composed of smaller particles, specifically electrons with negative charge.
What did Ernest Rutherford's gold foil experiment reveal about the atom?
-Rutherford's gold foil experiment revealed that atoms have a small, dense, positively charged nucleus with electrons orbiting around it, and that most of the atom's volume is empty space.
How did Niels Bohr's atomic model differ from Rutherford's?
-Niels Bohr's model introduced the concept of electrons orbiting the nucleus in specific energy levels or shells, and that electrons could only change energy levels by absorbing or emitting energy.
What was a major limitation of Bohr's atomic model?
-Bohr's model could not accurately explain the spectra of atoms with many electrons, nor could it explain the intensities of spectral lines or the behavior of electrons in atoms other than hydrogen.
What is the modern quantum mechanical model of the atom?
-The modern quantum mechanical model, developed by scientists like Louis de Broglie, Werner Heisenberg, and Erwin Schrödinger, describes electrons in terms of probability clouds or orbitals, indicating where they are most likely to be found rather than fixed orbits.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Evolution of Atomic Model 400 BC - 2020 | History of the atom Timeline, Atomic Theories
Struktur Atom • Part 1: Perkembangan Model Atom

Kimia X - Struktur Atom #3 | Perkembangan Teori dan Model Atom

Teoría atómica (Leucipo y Demócrito) VS Teoría de los cuatro elementos (Aristóteles)

Modelos de Dalton e Thomson [Módulo 02 - Aula 01]

PERKEMBANGAN TEORI ATOM | Dalton, Thomson, Rutherford, Bohr, Heisenberg, Erwin Schrodinger,
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)