Evolution of Atomic Model 400 BC - 2020 | History of the atom Timeline, Atomic Theories
Summary
TLDRThis educational video traces the evolution of the atomic model from Democritus' spherical atoms in 400 BC to the modern atomic theory. It covers Aristotle's four elements, Dalton's indivisible atoms, Thompson's plum pudding model, Rutherford's nuclear model, Bohr's quantum theory, Schrödinger's mathematical model, Heisenberg's uncertainty principle, and Chadwick's discovery of neutrons. The video concludes with the 21st-century understanding of isotopes and the role of atomic structure in nuclear power and weaponry.
Takeaways
- 📚 All matter is composed of atoms, a fundamental concept in chemistry.
- 🔬 Over a century ago, scientists were still debating the structure of atoms.
- 🏛️ Democritus proposed the first atomic model in 400 BC, envisioning atoms as indivisible spheres.
- 🌐 Aristotle's theory of the four elements (fire, air, earth, water) influenced early thoughts on matter's composition.
- 🔬 John Dalton's modern atomic theory in 1803 introduced the idea of atoms as the smallest units of elements, indivisible and indestructible.
- 🍇 J.J. Thomson's 'plum pudding' model in 1897 depicted atoms with electrons scattered within a positive 'soup'.
- 💥 Ernest Rutherford's gold foil experiment in 1911 led to the discovery of a small, dense atomic nucleus.
- 🌌 Niels Bohr's model in 1913 introduced electron orbits around the nucleus, refining the atomic structure understanding.
- 🧮 Erwin Schrödinger's 1926 quantum mechanical model provided a mathematical framework for electron distribution within atoms.
- 🌐 Werner Heisenberg's uncertainty principle in 1927 highlighted the limits of precision in measuring electrons' position and momentum.
- 🌀 James Chadwick's discovery of the neutron in 1932 completed the picture of the atomic nucleus, distinct from protons.
- ⚛️ Modern atomic theory recognizes isotopes and the diversity of atomic structures across different elements.
Q & A
Who is credited with creating the first atomic model?
-Democritus is credited with creating the first atomic model in 400 BC.
What were the key features of Democritus' atomic model?
-Democritus' atomic model featured a round sphere with no electrons, protons, or neutrons.
What was Aristotle's contribution to the early understanding of elements?
-Aristotle developed a theory based on four elements: fire, air, earth, and water, and believed these elements had four qualities: dryness, hotness, coldness, and moistness.
What are the five factors that John Dalton proposed in his modern theory of the atom?
-John Dalton proposed that matter is made of indivisible and indestructible atoms, all atoms of an element are identical, atoms of different elements have different weights and chemical properties, atoms combine in simple whole numbers to form compounds, and atoms cannot be created or destroyed.
Who discovered the electron and proposed the plum pudding model of the atom?
-J.J. Thomson discovered the electron and proposed the plum pudding model of the atom in 1897.
What was Ernest Rutherford's contribution to the atomic model?
-Ernest Rutherford theorized that atoms have their positive charge concentrated in a very small nucleus, leading to the Rutherford model of the atom.
What significant experiment did Rutherford perform that supported his atomic model?
-Rutherford performed the gold foil experiment, which involved bombarding gold foil with alpha particles, leading to his discovery of the atomic nucleus.
How did Niels Bohr's atomic model differ from Rutherford's?
-Niels Bohr's model built upon Rutherford's by introducing the concept of electrons orbiting the nucleus in quantized energy levels.
What was Erwin Schrödinger's contribution to the understanding of electron distribution in an atom?
-Erwin Schrödinger developed a mathematical model for the distribution of electrons in an atom, which led to the concept of quantum numbers describing the location of electrons.
What is the uncertainty principle, and who introduced it?
-The uncertainty principle, introduced by Werner Heisenberg, states that the more precisely the position of an electron is determined, the less precisely its momentum is known, and vice versa.
Who discovered the neutron, and what was the significance of this discovery?
-James Chadwick discovered the neutron in 1932, which led to a better understanding of the atomic nucleus and was crucial for the development of nuclear power and weapons.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Struktur Atom (1) | Perkembangan Teori Atom | Kimia Kelas 10
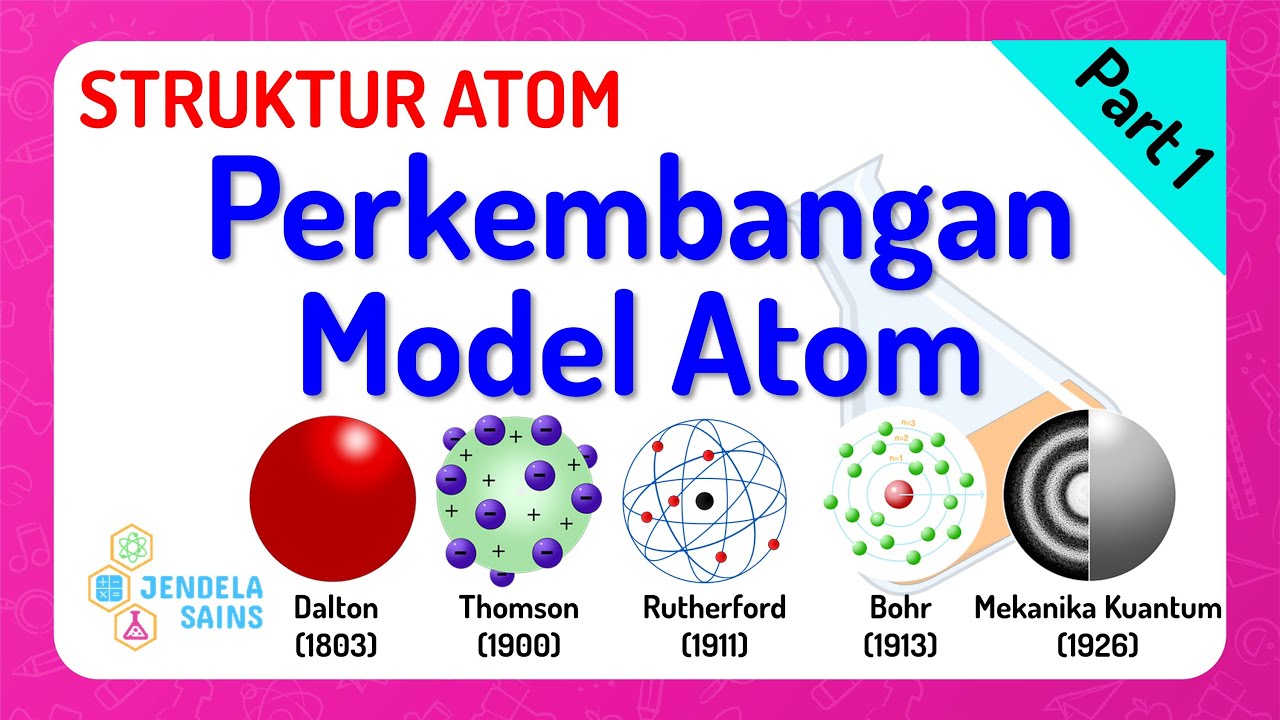
Struktur Atom • Part 1: Perkembangan Model Atom

Models of the Atom Timeline

Kimia X - Struktur Atom #3 | Perkembangan Teori dan Model Atom

Partikel Penyusun Benda dan Makhluk Hidup (Part-1) Teori Atom dan Lambang Atom

STRUKTUR ATOM DAN SISTEM PERIODIK UNSUR : Struktur Atom - Materi KIMIA SMA Kelas 10, TKA SMA |Part 1
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)