[Updated] LAYERS OF THE EARTH (Filipino) | Earth and Life Science
Summary
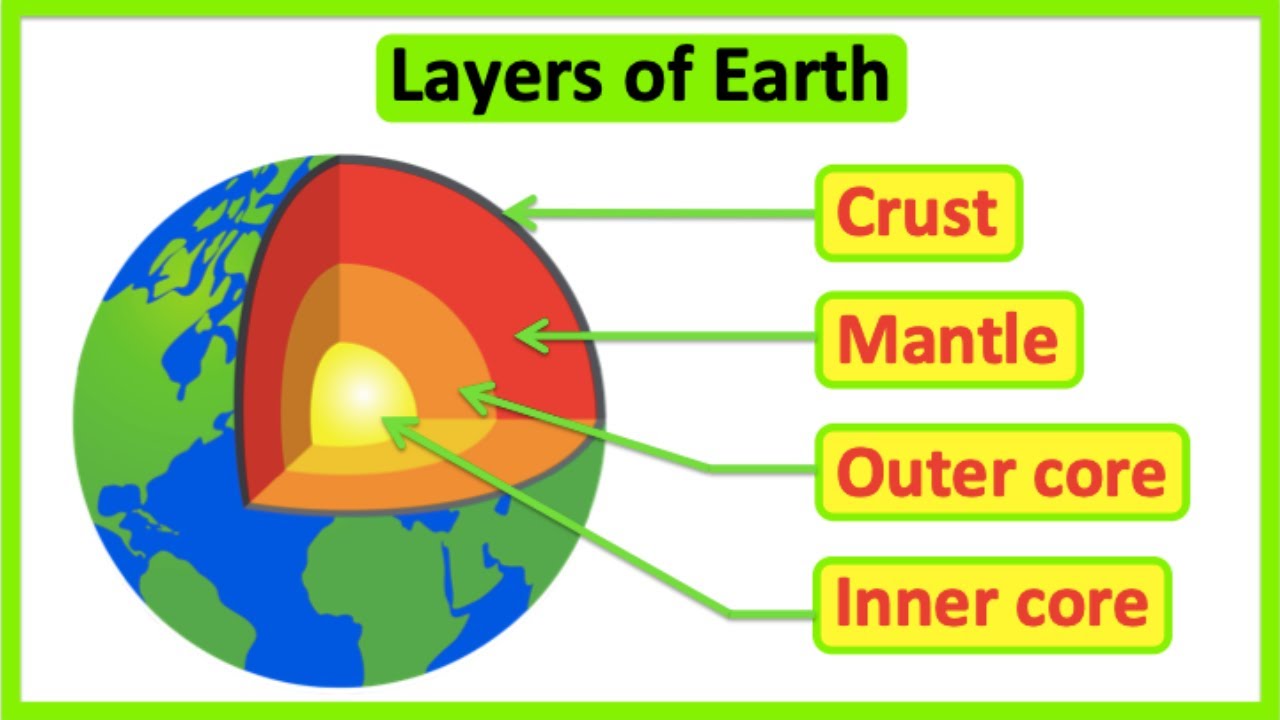
TLDRThis educational script explains Earth's layers using a boiled egg analogy: the yolk as the inner core, the white as the mantle, and the shell as the crust. It details the inner core's discovery by Ingle Lehmann in 1936, its solid crystalline iron form under extreme pressure, and high temperatures reaching 5,000 Kelvin. The outer core, discovered by Beno Gutenberg in 1913, is liquid, composed mainly of iron and nickel, and responsible for Earth's magnetic field. The mantle, the planet's largest layer, drives geological activities and is made of silicate materials, with the upper mantle being solid and malleable, and the lower mantle being softer and partially molten. The crust, Earth's outermost and lightest layer, is composed of silicate materials, with continental crust being granitic and older than the oceanic crust, which is basaltic and continuously formed and destroyed.
Takeaways
- 🌐 The Earth is layered, with the innermost layer being the inner core, discovered by Inge Lehmann in 1936.
- 🔥 The inner core is extremely hot, with temperatures ranging from 3,000 to 5,000 Kelvin, and is believed to be composed mainly of iron and possibly some nickel.
- 🌋 Seismic waves are crucial for understanding the Earth's layers, as they travel through these layers and provide data about the Earth's interior.
- 🌎 The Earth's magnetic field is generated by the outer core, which is also composed mainly of iron and nickel but is in a liquid state.
- 🌡 The outer core has a temperature range from 3,000 to 8,000 Kelvin, with the outer part being cooler and the inner part hotter.
- 🌍 The mantle is responsible for many geological activities, such as plate tectonics, volcanic activities, earthquakes, and mountain formation.
- 📏 The mantle is the largest layer of the Earth, making up 84% of its volume and is about 2,900 km thick.
- 🗻 The upper mantle is solid and malleable, while the lower mantle is softer and made of molten rocks.
- 🌌 Mantle convection, driven by heat transfer, is a key process that leads to the movement of tectonic plates.
- 🏔 The crust is the outermost and lightest layer of the Earth, composed mainly of silicate materials and divided into continental and oceanic crust.
Q & A
What is the innermost layer of the Earth called?
-The innermost layer of the Earth is called the inner core.
Who discovered the inner core and when was it discovered?
-The inner core was discovered by Inge Lehmann in 1936.
What is the temperature range of the inner core?
-The temperature of the inner core ranges from 3,000 to 5,000 Kelvin.
How do scientists gather information about the inner core since they don't have direct samples?
-Scientists gather information about the inner core from seismic waves that travel through the Earth's layers.
What is the composition of the outer core?
-The outer core is believed to consist mainly of iron and nickel.
What is the difference between the inner core and the outer core?
-The main difference is that the outer core is liquid, while the inner core is solid.
What is the role of the outer core in relation to Earth's magnetic field?
-The outer core, with its flowing liquid metal, generates Earth's magnetic field, which helps protect us from the solar wind.
What is the thickness of the outer core?
-The outer core is approximately 2,400 km thick.
What geological activities is the mantle responsible for?
-The mantle is responsible for plate tectonics, volcanic activities, earthquakes, and mountain formation.
What percentage of Earth's volume does the mantle make up?
-The mantle makes up about 84% of Earth's volume.
What is the composition of the mantle?
-The mantle is composed of silicate materials, which are made of silicon and oxygen.
What is the temperature range of the mantle?
-The temperature of the mantle ranges from 1,300 Kelvin in the upper portion to 4,000 Kelvin in the lower portion.
How are the crust and mantle connected?
-The crust is part of the upper mantle, with the lithosphere including both the crust and the uppermost mantle.
What are the two types of crust and how do they differ?
-There are two types of crust: continental crust, which is granitic and rich in silica and aluminum, and oceanic crust, which is basaltic and rich in magnesium and silica.
What is the average age of the oceanic crust?
-The age of the oceanic crust increases with distance from mid-ocean ridges, with the oldest crust found at the deepest parts.
What are the boundaries between the Earth's layers called?
-The boundaries are called the Bullen discontinuity (inner core and outer core), Gutenberg discontinuity (outer core and mantle), and Mohorovičić discontinuity (mantle and crust). The boundary between oceanic and continental crust is called the Conrad discontinuity.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

Bagaimana Struktur Bumi kita?

Struktur Bumi | Geografi | Alternatifa

Earth Structure and Its Development | Science Material Class 8 Merdeka Curriculum

ข้อมูลในการศึกษาและแบ่งชั้นโครงสร้างโลก (โลกและอวกาศ ม.6 บทที่ 5)
Layers of the Earth | Structure of the Earth | Educational Science Lesson

Layers of The Earth
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
