Struktur Bumi | Geografi | Alternatifa
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the host introduces the foundational concepts of Earth's structure, beginning with the *litosfer* (crust), *mantel bumi* (mantle), and *inti bumi* (core). Using a boiled egg analogy, the video explains how the Earth's layers function, from the outer crust that supports life to the deep, liquid outer core generating the magnetic field. The host also highlights the importance of understanding these layers for grasping phenomena like earthquakes and volcanic eruptions, as well as their influence on human activities and natural resources. The video ends with a teaser on tectonic plate movements.
Takeaways
- 😀 Earth's structure is crucial in geography because it affects everything from landscape to human activities.
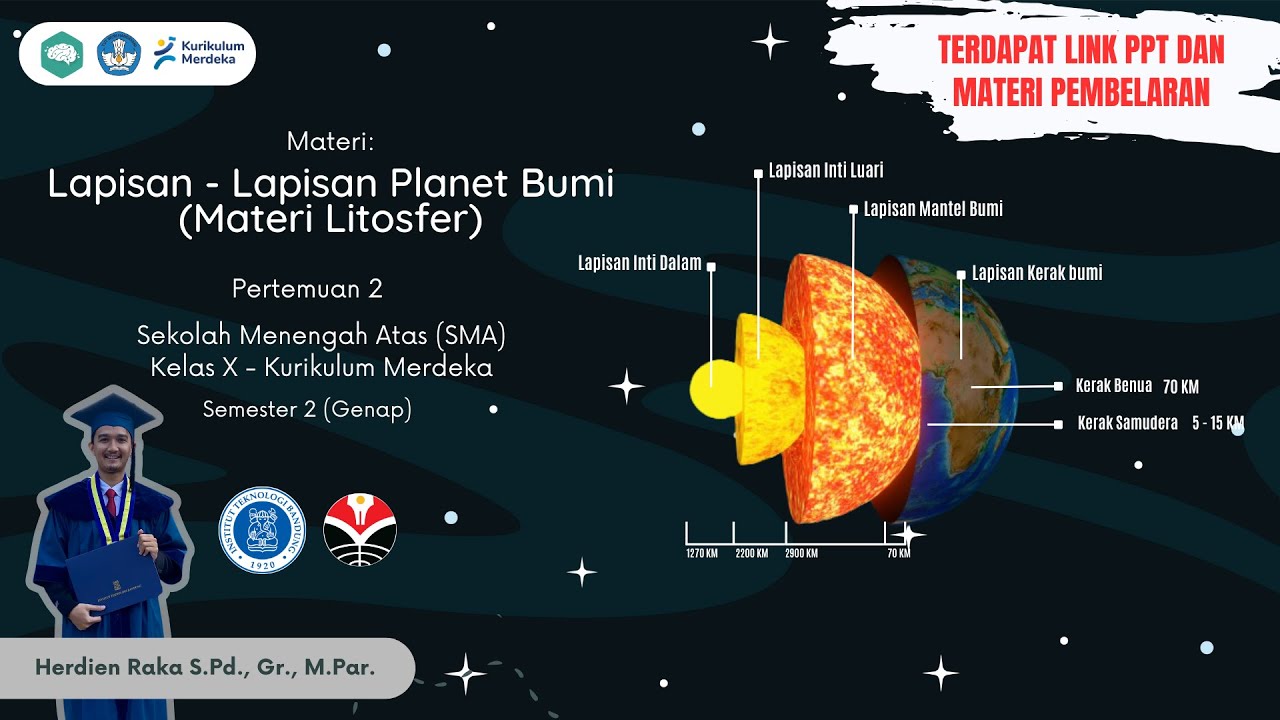
- 🌍 The Earth is made up of three main layers: the core, mantle, and crust (lithosphere).
- 🥚 The boiled egg analogy is used to explain Earth's structure, comparing the shell to the crust, the white to the mantle, and the yolk to the core.
- 🌍 The Earth's crust is the thinnest layer, ranging from 40-60 km thick, with the thickest sections found in mountainous regions.
- 🔥 The mantle, which lies beneath the crust, is about 2,900 km thick and contains magma responsible for seismic activity like earthquakes and volcanic eruptions.
- 🌊 The core of the Earth is divided into two parts: the outer core (liquid) and the inner core (solid), both made mostly of iron and nickel.
- 🧲 The movement of the molten material in the outer core generates Earth's magnetic field.
- 🌋 Seismic activity in the mantle causes natural disasters such as earthquakes, volcanoes, and tsunamis.
- 🌍 The structure of Earth influences agriculture, human settlements, and natural resource distribution.
- ⚡ The lithosphere is the largest layer in terms of surface area, and it's where life exists, from bacteria to humans.
Q & A
What are the three main layers of the Earth mentioned in the video?
-The three main layers of the Earth are the crust (litosfer), the mantle, and the core (inti bumi).
How is the structure of the Earth similar to a boiled egg?
-The structure of the Earth is compared to a boiled egg: the shell represents the crust (litosfer), the white represents the mantle, and the yolk represents the core.
What is the primary function of the lithosphere (crust) in relation to Earth's surface?
-The lithosphere, or Earth's crust, plays a crucial role in shaping the surface of the Earth, influencing landforms, agriculture, culture, and resource distribution.
What makes the continental crust thicker than the oceanic crust?
-The continental crust is thicker, ranging up to 60 km, especially in mountainous regions, due to the pressure and geological activity in those areas. In contrast, the oceanic crust is thinner, typically 5-10 km thick.
What is the significance of the mantle in the Earth's structure?
-The mantle is the thickest layer of the Earth, about 2900 km thick, and is made up of semi-solid magma. It plays a key role in seismic activity, causing earthquakes, volcanoes, and tsunamis.
How is the core of the Earth structured?
-The core is divided into two parts: the outer core, which is liquid, and the inner core, which is solid. The outer core is responsible for generating the Earth's magnetic field.
Why does the outer core of the Earth remain liquid while the inner core is solid?
-The outer core remains liquid due to lower pressure, while the inner core is solid because of the immense pressure at that depth, causing metals like iron and nickel to solidify.
What percentage of the Earth's mass is found in the mantle?
-The mantle makes up approximately 67% of Earth's total mass.
How does seismic activity in the mantle affect the Earth's surface?
-Seismic activity in the mantle leads to phenomena such as earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and tsunamis, which significantly impact the Earth's surface.
Why is understanding the structure of the Earth fundamental for studying geography?
-Understanding Earth's structure is fundamental because it helps explain how geological processes shape the planet's surface, influence natural resources, and affect human activity such as agriculture and settlement.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Day-8 || BA 1st semester geography Unit-1 ( Interior of Earth 🌍) by Mukul Sir #geography #earth

Geologia: Formação do Planeta Terra - Brasil Escola
LITOSFER : LAPISAN - LAPISAN PLANET BUMI

LITOSFER 1

A estrutura da Terra | Parte I

Materi Dinamika Litosfer (Lapisan Bumi) : Materi Geografi SMA dan SIMAK UI | Part 1
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)