What is Proteinuria and how to diagnose it? | Lecturio Pediatrics
Summary
TLDRThis lecture discusses proteinuria and nephrotic syndrome, using a case study of a 7-year-old girl with asymptomatic proteinuria. It explains the technical definition of proteinuria and its detection methods, including dipstick tests and the protein-creatinine ratio. The lecture differentiates between benign transient proteinuria, tubular proteinuria, and glomerular proteinuria, highlighting the importance of understanding the underlying cause for appropriate treatment.
Takeaways
- 👧 A 7-year-old girl with dysuria and suspected vaginitis was found to have +3 protein on her urine dipstick.
- 🔍 Proteinuria is defined as more than 100 mg/m² per day or +3 to +4 on the dipstick.
- 📉 Around 10% of children may test positive for urine protein, but only 0.1% have true proteinuria.
- 🔬 +3 or +4 protein on a dipstick typically indicates more than 1 gram of protein loss per day, which is usually pathologic.
- 📏 A 24-hour urine protein test is difficult for children, so a protein-creatinine ratio is preferred.
- 👶 In children under 2 years old, a protein-creatinine ratio over 0.5 is abnormal; over 2 years, more than 0.2 is abnormal.
- ⚠️ Protein-creatinine ratio values above 2 often indicate nephrotic syndrome.
- 🧠 Proteinuria can be classified into benign transient, tubular, or glomerular causes.
- 🌡️ Transient proteinuria can occur in children due to fever, stress, dehydration, or heavy exercise.
- 🏃 Orthostatic proteinuria is common in school-aged children and is benign, with no protein found in the first morning void.
Q & A
What is the definition of proteinuria?
-Proteinuria is defined as having more than 100 mg of protein per square meter per day in the urine, which can be challenging to calculate. On a dipstick test, this roughly correlates to a +3 or +4 reading.
How common is proteinuria in children?
-Around 10% of children will have a positive dipstick for protein in their urine, but only 0.1% of children have true proteinuria.
What does a +3 or +4 reading on a urine dipstick indicate?
-+3 and +4 on the urine dipstick typically indicate more than 1 gram of protein lost per day, which is usually a sign of pathology.
Why is a 24-hour urine protein collection not practical for children?
-Collecting a 24-hour urine protein sample is not practical for children because it can be difficult for them to consistently collect their urine, especially if they are at school or forget to use the collection cup.
What test is preferred over a 24-hour urine collection for children?
-A protein-to-creatinine ratio is preferred over a 24-hour urine collection for children because it adjusts for urine concentration and is easier to obtain.
What is considered an abnormal protein-to-creatinine ratio in children?
-In children under two years of age, an abnormal protein-to-creatinine ratio is more than 0.5. In children over two, a ratio greater than 0.2 is considered abnormal.
What protein-to-creatinine ratio suggests nephrotic syndrome?
-A protein-to-creatinine ratio greater than 2 is usually indicative of nephrotic syndrome, suggesting significant kidney dysfunction.
What are the three major categories of proteinuria?
-The three major categories of proteinuria are benign transient proteinuria, tubular proteinuria, and glomerular proteinuria.
What are some causes of benign transient proteinuria?
-Benign transient proteinuria can be caused by fever, seizures, stress, dehydration, or excessive exercise, and it usually resolves once the underlying stressor is addressed.
What is orthostatic proteinuria and how is it diagnosed?
-Orthostatic proteinuria is a form of benign proteinuria seen in school-aged children, where protein is only present in the urine after standing. It is diagnosed by checking the first morning void, which will not contain protein.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

Nephrotic Syndrome - Overview (Sign and symptoms, pathophysiology)

This Vitamin Stops Proteinuria Fast And Repair KIDNEY Quickly!
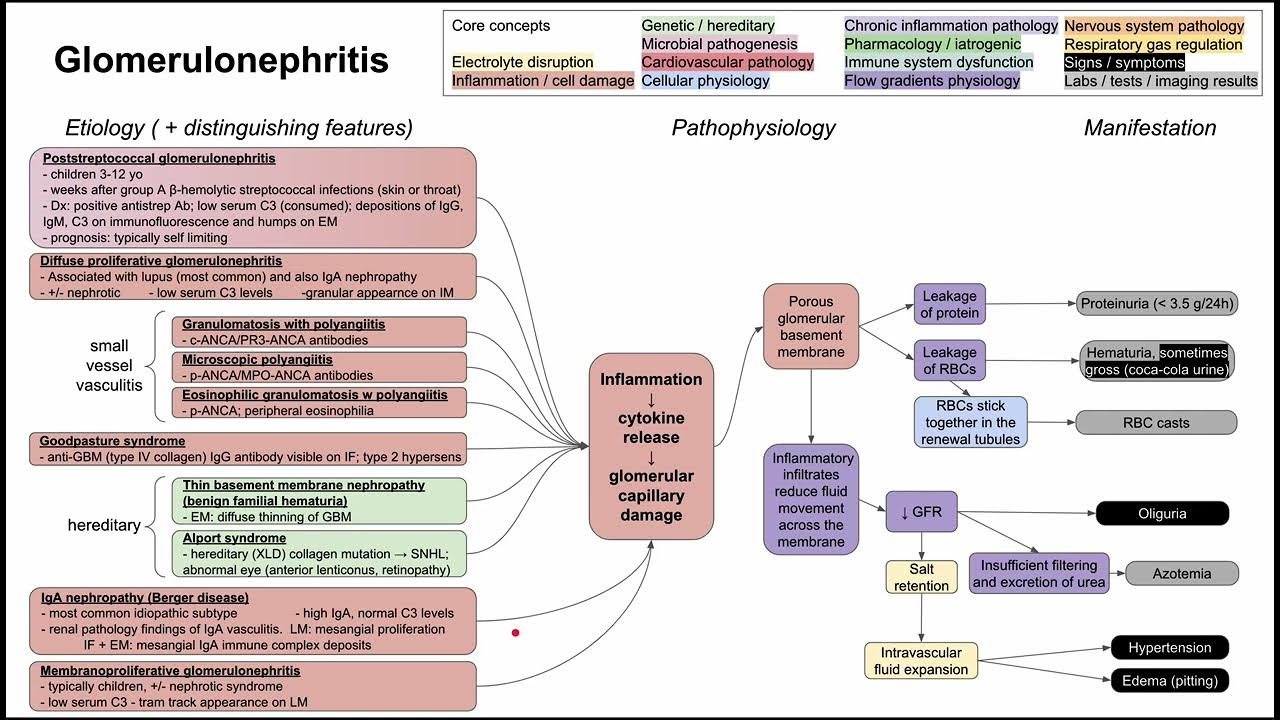
Glomerulonephritis (mechanism of disease)

Collaboration Across Professions Improves Patient Outcomes

BREAKING NEWS! Polres Jakarta Selatan Rilis Penahanan Vadel Badjideh Atas Kasus Tindak Asusila

Top 3 Vitamins That Help Stop Proteinuria and Heal Your Kidneys
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
