Lecture 2b - Molecular Dot Structures
Summary
TLDRThis lecture delves into molecular dot structures, essential for understanding molecular bonding and reactivity. It outlines a step-by-step process to draw dot structures, emphasizing the importance of order. The lecture explains how to calculate valence electrons, determine the central atom, and distribute electrons to achieve octets. It introduces the concept of resonance, where electrons are delocalized, and the use of formal charge to predict molecular structure. Exceptions to the octet rule and expanded octets are also discussed, providing a comprehensive foundation for predicting chemical behavior.
Takeaways
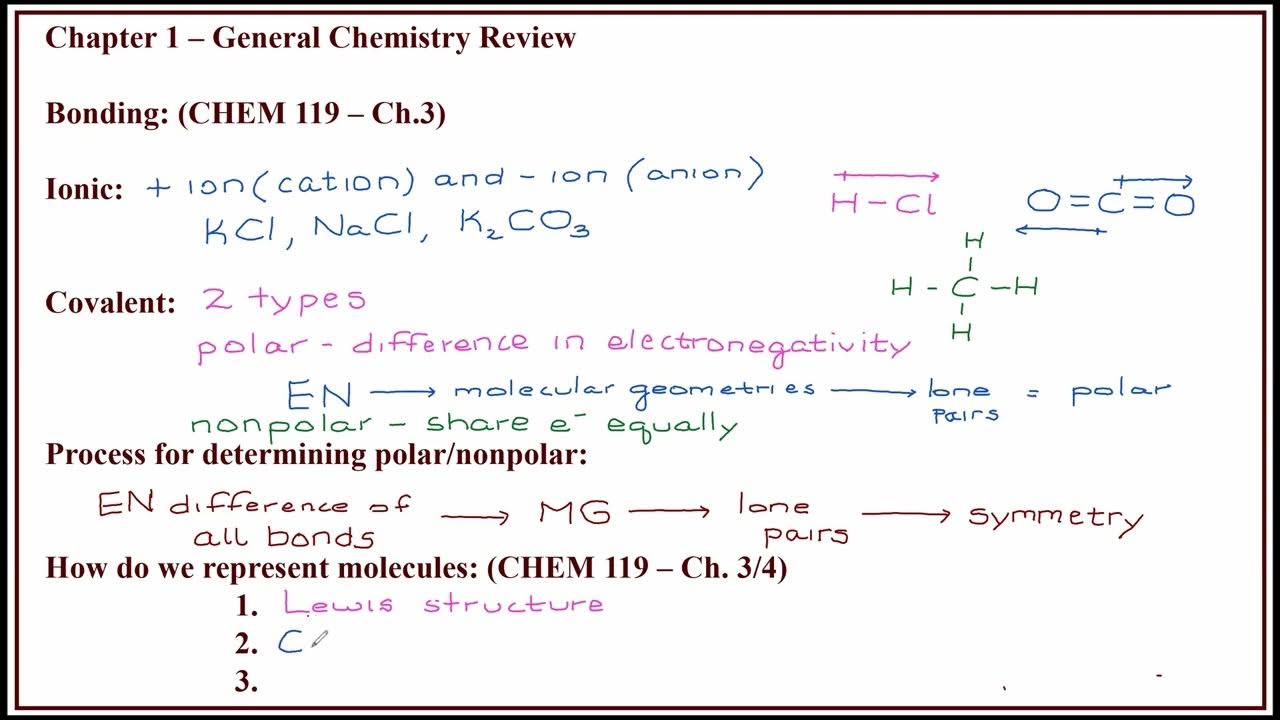
- 🔬 Dot structures for molecules are crucial for understanding bonding and predicting reactivity and chemical behavior.
- 🧩 The process of drawing dot structures involves a series of steps that must be followed in a specific order to ensure accuracy.
- 💡 The first step in creating a dot structure is calculating the total number of valence electrons available from all atoms in the molecule.
- 🚫 Hydrogen is an exception in dot structures; it only needs two electrons to achieve a stable configuration, similar to helium.
- 🔑 The central atom in a molecule is typically the first non-hydrogen atom listed in the chemical formula, around which other atoms are bonded.
- ✅ Single bonds are used initially to connect atoms to the central atom, with each bond representing two electrons.
- 🔄 After initial bonding, lone pairs are added to outer atoms first to complete their octets before considering the central atom.
- 🔄 If there are leftover electrons after outer atoms' octets are filled, they are added as pairs to the central atom.
- 🔁 Resonance structures occur when there is more than one valid way to distribute electrons, especially in molecules with delocalized bonding.
- ⚖️ Formal charge calculations help determine the most stable resonance structure by identifying which atom can best handle a multiple bond.
- 💥 Expanded octets are exceptions to the octet rule, where certain elements, like phosphorus and sulfur, can have more than eight electrons around them.
Q & A
What is the primary purpose of creating dot structures for molecules?
-Dot structures for molecules are primarily used to determine the bonding present in a molecule, which in turn helps in predicting its reactivity, where reactions will occur, and how they will happen.
How does shape prediction in chemistry relate to molecular dot structures?
-Shape prediction in chemistry is related to molecular dot structures because the shape of molecules, influenced by their bonding patterns, is crucial for understanding chemical behavior, such as drug interactions within the body, which are based on the 'lock and key' model of molecular shapes.
What is the significance of the order in which the steps for drawing dot structures are performed?
-The order of the steps for drawing dot structures is significant because changing the order can lead to incorrect dot structures and incorrect predictions about the molecule's bonding and reactivity.
Why is the total number of valence electrons calculated first when drawing dot structures?
-The total number of valence electrons is calculated first to determine the total number of electrons available to fill the octets of all the atoms in the molecule.
Why is hydrogen treated differently when considering valence electrons in covalent bonds?
-Hydrogen is treated differently because when it forms a covalent bond, it is considered to have two electrons around it, resembling a noble gas configuration, and thus it is satisfied with just one bond rather than needing to achieve an octet.
What is the general rule for identifying the central atom in a molecule for dot structure drawing?
-The central atom in a molecule for dot structure drawing is generally the first non-hydrogen atom listed in the chemical formula when read from left to right.
How are lone pairs added to atoms in a dot structure, and in what order?
-Lone pairs are added to complete the octets of the outer atoms first, followed by the central atom if there are electrons remaining. The order is important to ensure that all atoms achieve a stable electron configuration.
What is resonance in the context of molecular dot structures, and why is it important?
-Resonance refers to the phenomenon where a molecule can be represented by more than one valid dot structure due to delocalized electrons. It is important because it reflects the actual bonding situation in a molecule more accurately than a single dot structure and influences the molecule's stability and reactivity.
How does formal charge help in determining preferred resonance structures?
-Formal charge helps in determining preferred resonance structures by indicating which atom can best handle a multiple bond, with the preferred structure having formal charges closest to zero for all atoms.
What is an expanded octet, and which elements are known for forming them?
-An expanded octet is a situation where an atom has more than eight electrons in its valence shell, typically seen with non-metals later in the periodic table, such as phosphorus and sulfur.
Why might the sum of formal charges not equal the overall charge on a molecule if calculated incorrectly?
-If the sum of formal charges does not equal the overall charge on a molecule, it indicates an error in the calculation of formal charges, which can lead to incorrect predictions about the molecule's structure and properties.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

An Introduction to Inorganic Chemistry- Lecture 2

Química Orgânica II – Aula 01 – Aldeídos e cetonas – estrutura e propriedades
CHEM 257 - Fall 2024 - Lecture 1 - Video 2

Full !! Pembahasan Soal Ikatan Kimia Kelas 10

Class 11 Chemistry | Chemical Bonding and Molecular Str. in 15 Minutes | Rapid Revision by BP Sir

Lewis Dot Structures
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
