Class 11 Chemistry | Chemical Bonding and Molecular Str. in 15 Minutes | Rapid Revision by BP Sir
Summary
TLDRThe script is a chemistry lecture focusing on chemical bonding and molecular structure for 11th-grade students. It covers crucial topics like atomic bonding, the octet rule, Lewis symbols, and different types of bonds including ionic, covalent, and coordinate bonds. The lecture also delves into bond parameters, bond energy, and theories like VSEPR and hybridization to predict molecular geometry. Concepts of polar and nonpolar molecules, dipole moments, and hydrogen bonding are also discussed, providing a comprehensive understanding of the subject.
Takeaways
- 😀 The video is an educational lecture aimed at 11th-grade students, focusing on the crucial chemistry topics of Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure.
- 🎓 The lecturer, India Panchaali, emphasizes the importance of understanding concepts such as chemical bonding, which involves the forces that hold atoms together in different species.
- 🔬 The Octet Rule is discussed, stating that atoms tend to combine in such a way that their valence (outermost) shell has eight electrons, leading to stable structures.
- 🏫 The lecture introduces Lewis symbols, which represent the valence electrons of atoms using dots and crosses, aiding in visualizing chemical bonding.
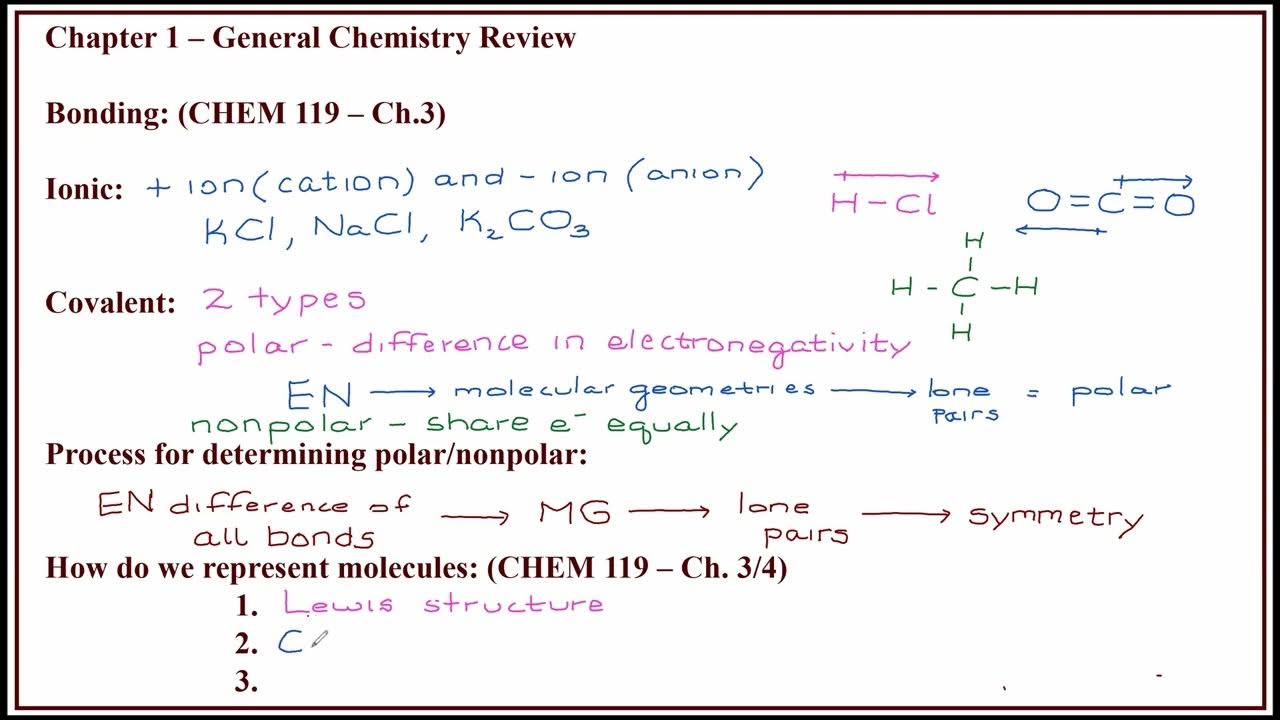
- ⚛️ Different types of chemical bonds are explained, including ionic bonds formed by the transfer of electrons and covalent bonds resulting from the sharing of electrons between atoms.
- 🔗 The concept of coordinate covalent bonds is introduced, where one atom donates a lone pair of electrons to another atom to form a bond.
- 📚 The lecture touches on bond parameters such as bond angle, bond length, and bond energy, which are essential for understanding molecular geometry.
- 📐 VSEPR theory is discussed, which predicts the shape of molecules based on the repulsion between electron pairs around the central atom.
- 🧬 The concept of hybridization is introduced, explaining how atomic orbitals mix to form new hybrid orbitals that determine the shape of molecules.
- 🔬 Resonance structures are explained as a way to describe molecules where a single Lewis structure cannot fully represent the bonding and electron distribution.
- 🌐 The lecture concludes with a discussion on polar and nonpolar molecules, explaining how the distribution of charge affects the molecule's polarity.
Q & A
What is the main topic discussed in the video?
-The main topic discussed in the video is Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure, specifically for 11th-grade students.
What is the Octet Rule mentioned in the video?
-The Octet Rule states that atoms are more stable when they have eight electrons in their valence shell, and they tend to combine with other atoms to achieve this stable configuration.
What does Lewis Symbol represent?
-Lewis Symbol represents the valence electrons of an atom using dots and crosses, where single dots represent unpaired electrons and double dots represent paired electrons.
What are the different types of chemical bonds discussed?
-The video discusses various types of chemical bonds including ionic bonds, covalent bonds, and coordinate bonds.
What is a coordinate bond?
-A coordinate bond is a type of covalent bond where one atom donates both electrons to form the bond, rather than sharing electrons between two atoms.
What is the significance of the valence electrons in determining the type of chemical bond an atom can form?
-The number of valence electrons determines the type of chemical bond an atom can form, as it influences whether an atom will lose, gain, or share electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration.
What is the difference between polar and nonpolar molecules?
-Polar molecules have an uneven distribution of electron density, leading to a net dipole moment, while nonpolar molecules have an even distribution of electron density and no net dipole moment.
What is meant by the term 'hybridization' in the context of the video?
-Hybridization refers to the concept where atomic orbitals mix to form new hybrid orbitals that are used in bonding, which can better explain the molecular geometry observed in molecules.
What is the VSEPR theory and how does it relate to molecular geometry?
-The VSEPR theory (Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion) predicts the shape of molecules by minimizing electron pair repulsions, which helps determine the molecular geometry around a central atom.
What are hydrogen bonds and how do they differ from covalent bonds?
-Hydrogen bonds are a type of intermolecular force that occurs between a hydrogen atom and a more electronegative atom, unlike covalent bonds which involve the sharing of electrons between atoms within a molecule.
How does the video explain the concept of resonance structures?
-The video explains resonance structures as alternative ways of representing the same molecule, where the positions of electrons are drawn differently but represent the same overall molecule.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)