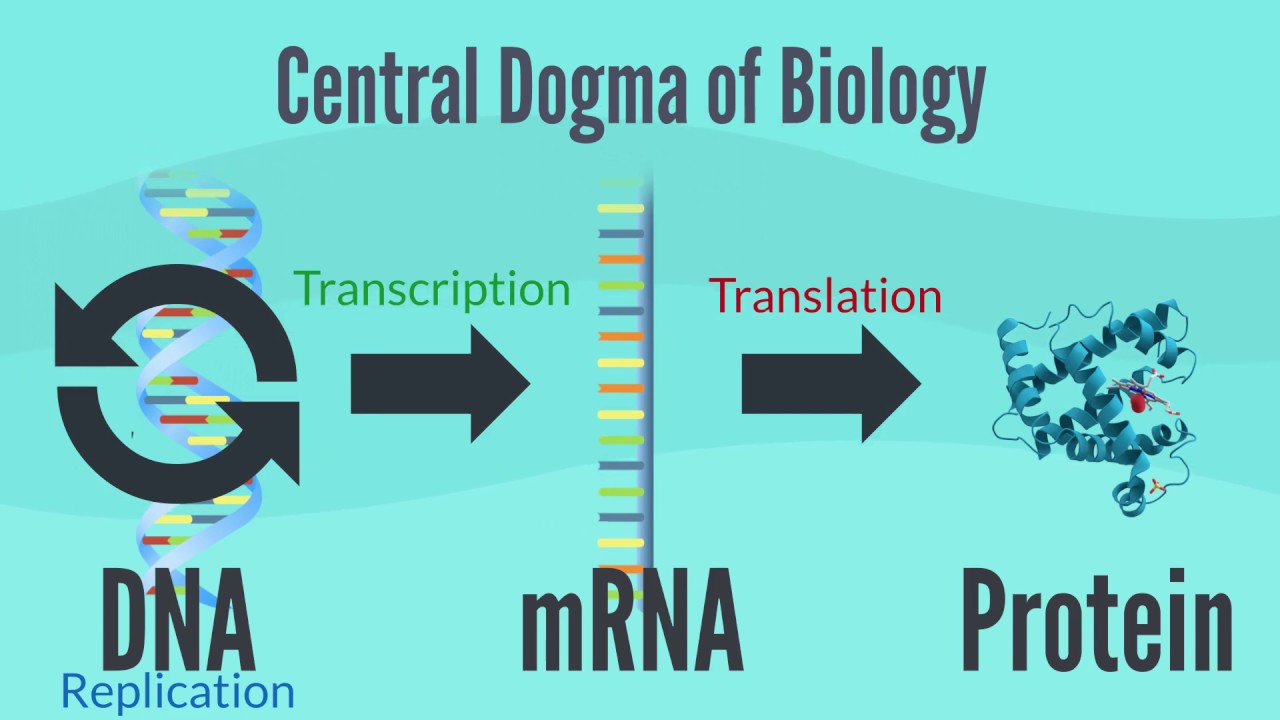
The Central Dogma of Biology
Summary
TLDRThis script describes the intricate process of gene expression from DNA to protein. It begins with the transcription of DNA, where a gene's information is copied into RNA by enzymes that unzip the double helix. The RNA then undergoes splicing, a critical editing phase where non-coding sections called introns are removed, leaving only the protein-coding exons. The spliced RNA exits the nucleus and enters the cytoplasm, where it is translated by ribosomes into a chain of amino acids, which fold into a functional protein. The process is visualized with vivid imagery, illustrating the molecular machinery at work within a living cell.
Takeaways
- 🧬 The DNA double helix is composed of two sequences with the letters A, C, G, and T, which carry genetic instructions.
- 🔬 Transcription begins with the assembly of factors at the start of a gene to read off the DNA information needed for protein synthesis.
- 🔑 The blue molecule unzips the DNA helix and copies one strand, which is then used to create RNA, a DNA chemical cousin.
- 🔄 The RNA undergoes editing through a process called splicing, which removes non-coding regions called introns.
- 🌐 Splicing is guided by factors at intron/exon borders that form a splicing machine known as the spliceosome.
- ⏰ The spliceosome cuts and rejoins RNA, removing introns and leaving only the protein-coding exons.
- 🔁 This splicing process is repeated for every intron, ensuring the RNA contains only exons with complete protein instructions.
- 🐍 The edited RNA moves to the cell's outer part, where it is translated into a protein by the ribosome, a molecular factory.
- 🔠 The ribosome translates the RNA's genetic code into a sequence of amino acids, which are the building blocks of proteins.
- 🔄 Special transfer molecules bring amino acids to the ribosome, where they are matched to the RNA code and added to the growing protein chain.
Q & A
What is the significance of the DNA double helix containing the letters A, C, G, and T?
-The letters A, C, G, and T represent the nucleotide bases adenine, cytosine, guanine, and thymine, which are the building blocks of DNA. They carry the genetic code necessary for the production of proteins.
How does transcription of DNA initiate?
-Transcription begins with a collection of factors assembling at the start of a gene to read off the information needed to make a protein.
What is the role of the blue molecule in the transcription process?
-The blue molecule is responsible for unzipping the DNA double helix and copying one of the strands to create a complementary RNA molecule.
What is the chemical relationship between DNA and RNA?
-RNA is a close chemical cousin of DNA, with uracil (U) replacing thymine (T) in RNA, and it plays a crucial role in protein synthesis by carrying the genetic information from DNA.
How are the building blocks of RNA matched to the DNA during transcription?
-The building blocks, or nucleotides, are matched to the DNA strand letter by letter to copy the gene sequence into RNA.
What is the purpose of RNA editing through splicing?
-RNA editing through splicing removes non-coding regions called introns, leaving only the protein-coding regions called exons, which are essential for protein synthesis.
What is a spliceosome and how does it function?
-A spliceosome is a molecular machine that assembles at intron/exon borders to remove introns from the RNA. It cuts and rejoins the RNA, ensuring that only exons remain.
How does the spliceosome prepare the RNA for cutting and joining?
-The spliceosome brings the exons on either side of the intron close together, cuts one end of the intron, forms a loop, and then cuts the RNA to release the loop and join the exons.
What happens to the RNA after all introns have been removed?
-After all introns are removed, the edited RNA, which now contains only exons, moves to the cell's outer part where it will be translated into a protein.
How is the genetic information in RNA translated into a protein?
-The RNA is translated into a protein by a ribosome, which reads the RNA sequence three letters at a time (codons) and matches them to transfer molecules carrying amino acids.
What are the roles of transfer molecules and amino acids in protein synthesis?
-Transfer molecules, also known as tRNAs, bring specific amino acids to the ribosome. The amino acids are then added to the growing protein chain according to the codons on the RNA.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenant5.0 / 5 (0 votes)