Havo 5 | DNA | Basisstof 4 Genexpressie
Summary
TLDRThis video explains gene expression and regulation, detailing their critical roles in protein synthesis and development. It compares gene regulation mechanisms in prokaryotes, like E. coli, which utilize operons and repressors, with the more complex regulation found in eukaryotes. The video also discusses the importance of stem cells in differentiation, highlighting how embryonic stem cells can develop into various cell types. Finally, it covers epigenetic regulation, such as DNA methylation, which affects gene accessibility and is inherited during cell division, underscoring the intricate interplay between genetics and development.
Takeaways
- 😀 Gene expression is the process of turning genes on or off, leading to protein synthesis through transcription and translation.
- 🔄 Gene regulation ensures that the correct genes are active at the right time, influenced by various internal and external factors.
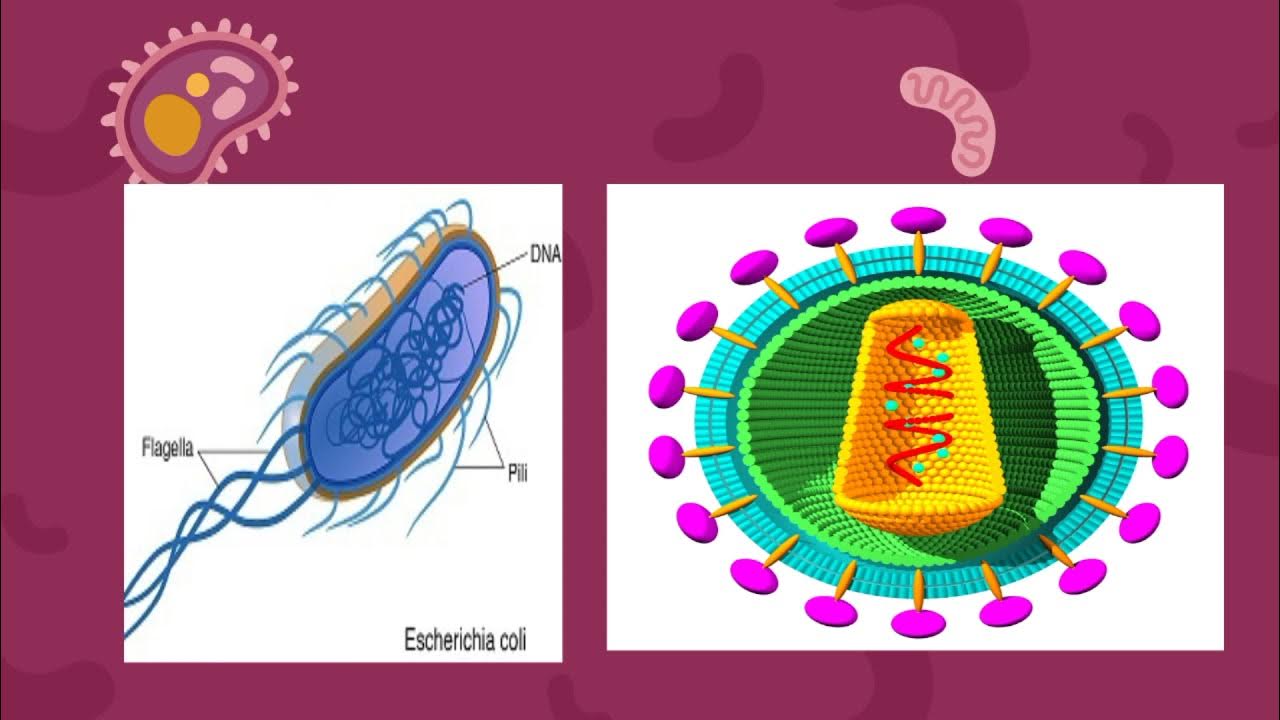
- 🦠 Prokaryotic gene regulation involves repressors that inhibit transcription, as demonstrated by E. coli's response to lactose.
- 🧬 In the absence of lactose, E. coli synthesizes a repressor that prevents RNA polymerase from transcribing the gene for beta-galactosidase.
- 🥛 When lactose is present, it binds to the repressor, allowing RNA polymerase to initiate transcription and produce the enzyme.
- 🌱 Eukaryotic gene regulation is more complex, involving enhancers, silencers, and a diverse range of regulatory proteins.
- 👶 Human development includes approximately 220 cell types, all arising from stem cells through differentiation processes.
- 🔗 Cell differentiation results from a chain of gene regulation and expression, allowing cells to acquire specific functions.
- 🧪 DNA packaging around histones affects gene accessibility for transcription, influencing which genes are expressed.
- 🧬 DNA methylation can render certain DNA regions unreadable, serving as a crucial mechanism for regulating gene expression.
Q & A
What is gene expression?
-Gene expression refers to the process of turning genes on or off, leading to the synthesis of proteins through transcription and translation.
How do gene regulators function?
-Gene regulators are proteins that ensure the right genes are active at the right times, influenced by various internal and external factors.
What are the differences in gene regulation between prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
-In prokaryotes, gene regulation primarily occurs through repressors, while in eukaryotes, it involves both repressive and stimulating proteins.
What role do operons play in prokaryotic gene regulation?
-Operons consist of a regulatory gene, a promoter, and structural genes, allowing the coordinated regulation of gene expression in prokaryotes.
How does lactose affect the regulation of beta-galactosidase synthesis in E. coli?
-In the absence of lactose, the repressor binds to the operator, preventing RNA polymerase from transcribing the gene for beta-galactosidase. When lactose is present, it binds to the repressor, allowing transcription to occur.
What are stem cells and how do they relate to cellular differentiation?
-Stem cells are undifferentiated cells that can develop into various cell types. They are crucial in the process of cellular differentiation as they give rise to specialized cells in the body.
What is the significance of epigenetics in gene expression?
-Epigenetics involves changes in gene expression without altering the DNA sequence, often through mechanisms like DNA methylation, which can affect cellular development and differentiation.
What happens during transcription and translation in gene expression?
-During transcription, DNA is copied into RNA, and during translation, the RNA is used to synthesize proteins based on the genetic code.
How do histones influence gene regulation in eukaryotic cells?
-Histones are proteins that package DNA into a compact form. The degree of DNA winding around histones can affect whether a gene is accessible for transcription.
What is the outcome of DNA methylation on gene expression?
-DNA methylation can inhibit gene expression by preventing transcription factors from accessing the DNA, thus silencing certain genes.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

What is microRNA? (miRNA)
Mikrobiologi | Genetika Mikroorganisme

SINTESIS POLIPEPTIDA ; Cara Tubuh Menghasilkan Protein

[Module 2] Lesson 2 Central Dogma (Part 2)

Non coding RNA types, features and function. miRNA, siRNA, lncRNA, piRNA, snRNA, snoRNA, rRNA, tRNA.

Post-transcriptional regulation | Biomolecules | MCAT | Khan Academy
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)