What’s behind the South China Sea dispute? | Start Here
Summary
TLDRThe South China Sea dispute is a complex issue driven by rich resources and strategic shipping lanes. China's historical claim, marked by the nine-dash line, faces opposition from ASEAN nations and the US, who protect trade routes and regional stability. China's naval expansion and militarization of islands have heightened tensions, while international law and ASEAN's Code of Conduct attempts to mediate the conflict. The region's future hinges on navigating these competing interests without escalating to war.
Takeaways
- 🌏 The South China Sea is a region rich in resources such as oil, gas, and fisheries, and it hosts some of the world's busiest shipping lanes.
- 🇨🇳 China claims control over the South China Sea to secure its trade routes and access to resources necessary for its economy, aiming to be a naval force in the Indian and Pacific Oceans.
- 🏝️ Multiple countries, including Taiwan, Vietnam, the Philippines, Malaysia, Brunei, and Indonesia, claim rights to parts of the South China Sea, leading to territorial disputes.
- 🛳️ The US has a vested interest in the region due to the significant value of trade that passes through its shipping lanes, amounting to hundreds of billions of dollars.
- 📜 China's historical claim is based on the 'nine-dash line' drawn in 1929, which was later expanded in 2013 to include Taiwan, indicating an increasing territorial appetite.
- 🚢 Around 40% of the world's liquefied natural gas and $3 trillion worth of annual trade pass through the South China Sea, highlighting its strategic importance.
- ⚖️ The Philippines took China to court over territorial claims, and in 2016, an international tribunal ruled China's nine-dash line claim invalid.
- 🛡️ China has been militarizing the region by building outposts and military bases on contested islands to strengthen its territorial claims.
- 🇺🇸 The US asserts its navigational rights and presence in the South China Sea through naval patrols and military exercises with allies.
- 🤝 ASEAN countries have been attempting to establish a Code of Conduct for the South China Sea to manage territorial disputes, but progress has been slow due to China's influence and differing interests among member states.
- 🕊️ Despite the potential for conflict, the South China Sea dispute often remains under the radar, with China viewing it as essential to its survival and playing a long-term strategy in the region.
Q & A
Why is the South China Sea a point of contention among various countries?
-The South China Sea is rich in oil and gas, has abundant fish stocks, and features some of the busiest shipping lanes in the world, making it a strategic and economically significant area.
What is China's strategic interest in the South China Sea?
-China seeks to be a naval force across the Indian and Pacific Oceans to ensure its trade with the world and access to oil and gas to drive its economy, thus it wants to control the South China Sea.
What are the 'nine dash line' and 'tenth line' mentioned in the script?
-The 'nine dash line' is a territorial claim by China based on old British sailing charts from 1929, which they used to outline their borders around the South China Sea. The 'tenth line' was added in 2013 to include Taiwan in China's territorial claims.
What is the significance of the South China Sea to global trade?
-Approximately 40% of the world's liquefied natural gas passes through the South China Sea, and the trade that sails through there is worth $3 trillion a year, representing one-third of the global total.
How has China been asserting its territorial claims in the South China Sea?
-China has been planting its flag on contested islands, building outposts in the Paracels, and reclaiming over 13 square kilometers of land in the Spratlys since 2013 to turn them into military bases.
What is the role of the United States in the South China Sea disputes?
-The U.S. aims to protect valuable shipping lanes and assert navigational rights and freedoms by having its navy sail through the South China Sea and conducting military exercises in the region with allies.
What was the outcome of the Philippines' case against China at The Hague?
-The international tribunal at The Hague ruled in favor of the Philippines, concluding that China's territorial claim based on the nine dash line is invalid and that it had no right to the Scarborough Shoal.
What is the UN Convention on the Law of the Sea and how does it relate to the South China Sea disputes?
-The UN Convention on the Law of the Sea establishes exclusive economic zones extending 200 nautical miles from a country's coastline. China has signed up to this law, but its claims in the South China Sea have been challenged for not adhering to it.
What is the ASEAN's attempt to address the South China Sea disputes?
-Since the 1990s, ASEAN has been trying to develop a Code of Conduct for the South China Sea to control China's ambitions and manage disputes among member states, although progress has been slow.
Why has the dispute over the South China Sea remained unresolved?
-The dispute remains unresolved due to the vastness of the area, high stakes involved, heavily armed nations defending their interests, and China's long-term strategic approach to the issue.
How does China view the South China Sea in terms of its national interests?
-China sees the South China Sea as essential to its survival and national interests, which is why it has been persistent in its claims and actions in the region.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

What is the South China Sea dispute?
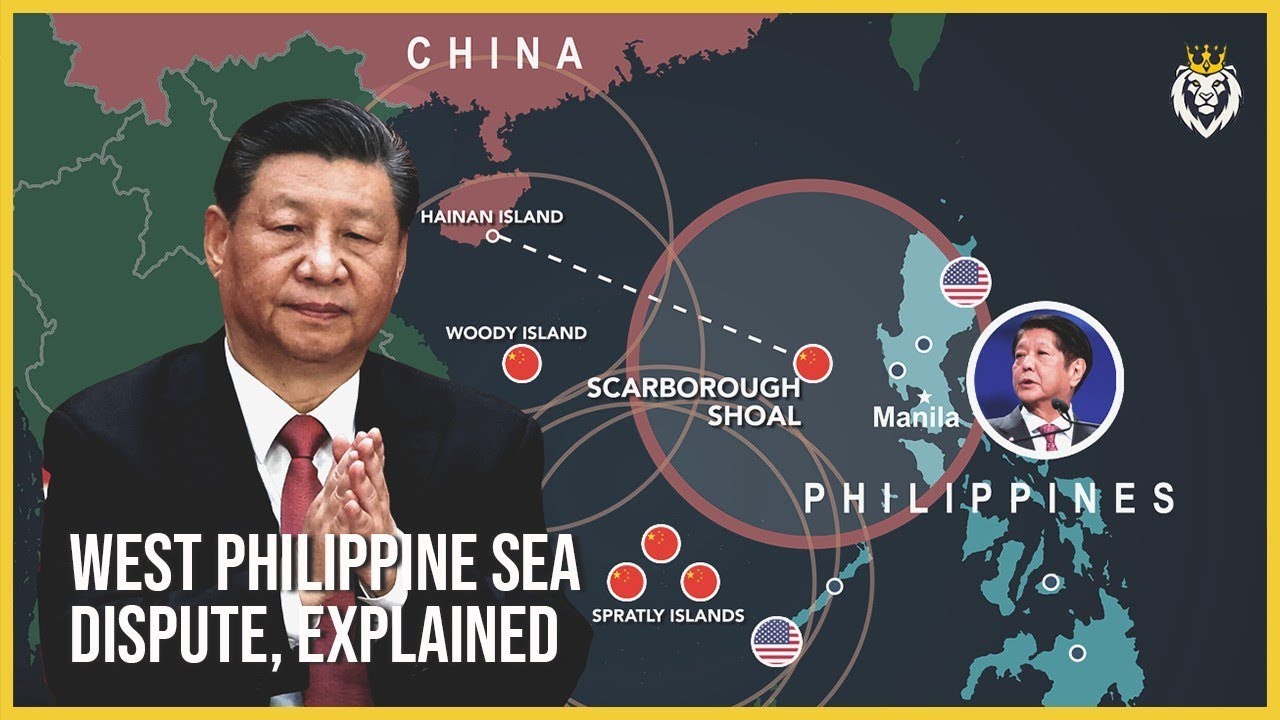
The West Philippine Sea Dispute, Explained

Mengenal Lebih Dekat Kabupaten Natuna, dan kenapa China ingin Mengakuinya?

WEST PHILIPPINE SEA: Territorial Waters of the Philippines but Controlled by China?

Chinese Ship Rams into Filipino Vessel: Latest West Philippine Sea Clash | Vantage with Palki Sharma

SENGKETA PULAU NATUNA
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
