Programable Logic Controller Basics Explained - automation engineering
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the automation of mechanical and electrical systems in commercial and industrial settings, focusing on programmable logic controllers (PLCs). Sponsored by TeleControls, it explains how PLCs, acting as small computers, control systems with minimal manual intervention based on pre-programmed outputs and inputs. The video covers the components of PLCs, their basic operation, and advantages, including easier reprogramming and fault-finding. It also provides practical examples of PLC applications in scenarios like airport baggage handling and building temperature control.
Takeaways
- 🏢 Automation of mechanical and electrical systems in commercial and industrial facilities is increasing with the construction of larger, smarter, and more complex buildings.
- 🔗 Telecontrols, a leading manufacturer in the automation industry since 1963, offers technology compatible with all PLCs, HMIs, and controllers, reducing programming time and saving storage space.
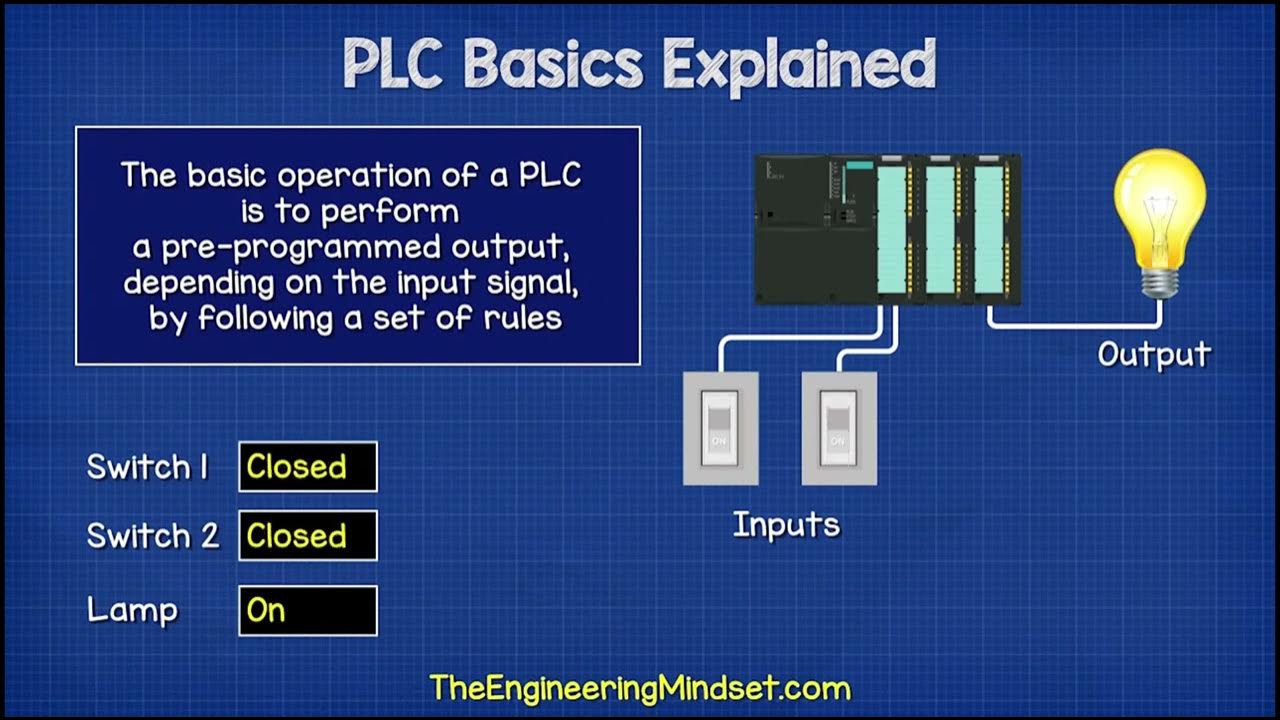
- 🤖 PLCs, or Programmable Logic Controllers, are small computers that execute pre-programmed outputs based on inputs and specific rules, with minimal or no manual intervention.
- 🔄 Before PLCs, control was managed by banks of relays which were large, complex, and required physical rewiring to change operations.
- 🔌 PLCs monitor inputs, make decisions based on stored rules, and output commands to automate processes, often in combination with relays for more efficient task handling.
- 🛂 Input modules of PLCs connect to field sensors and perform tasks such as sensing signals, converting signal voltage, isolating fluctuations, and sending corrected signals to the CPU.
- 🧠 The CPU, or Central Processing Unit, is the brain of the PLC, holding the program that decides output requirements by applying rules to input signals.
- 🔩 Output modules interface with field output devices, such as indicator lights, solenoid valves, motor starters, and variable frequency drives, providing signals to control these devices.
- 🔄 Basic PLC operation involves input scanning, program scanning, executing program logic, updating outputs, and housekeeping tasks like self-diagnostics and communication updates.
- 🌡️ Analog inputs, such as those from a thermistor, take longer to process than digital inputs, affecting the scan time which can vary from milliseconds to hundreds of milliseconds depending on the application.
- 🛠️ PLCs offer advantages like local control software storage, software-based connections instead of physical wires, smaller installations, easier reprogramming, and faster fault finding.
Q & A
What is the primary purpose of automation in commercial and industrial facilities?
-The primary purpose of automation in commercial and industrial facilities is to control mechanical and electrical systems efficiently, reducing the need for manual intervention and enhancing the operation of larger, smarter, and more complex systems.
Who is Telecontrols and what is their role in the automation industry?
-Telecontrols is one of the leading manufacturers in the automation industry since 1963. They produce technology compatible with every PLC, HMI, and controller on the market, which helps reduce PLC programming time and saves storage by handling smaller automation tasks directly.
What does PLC stand for and what is its basic function?
-PLC stands for Programmable Logic Controller. Its basic function is to act as a small computer that carries out pre-programmed outputs based on inputs and a set of specific rules, used to control systems with minimal or no manual intervention.
How did control systems operate before the advent of PLCs?
-Before PLCs, control systems operated via banks of relays, which controlled dedicated inputs and outputs based on physical wiring. Changing the operation required altering the physical connections, making the system large, complex, and difficult to modify or troubleshoot.
What are the main components of a PLC system?
-The main components of a PLC system include input modules, a central processing unit (CPU), output modules, a battery for power failure backup, a user interface, a time clock and calendar, and a power supply for low voltage needs.
How do input modules in a PLC system function?
-Input modules in a PLC system sense when a signal is received, convert the signal voltage into the correct format for the CPU, isolate the PLC from fluctuations in input voltage or current, and send the corrected signal to the CPU.
What is the role of the CPU in a PLC system?
-The CPU, or central processing unit, is the brain of the PLC system. It holds the program or software that decides what outputs are required by applying rules to the input signals. It typically consists of a microprocessor, a memory chip for storing the program and data, and integrated circuits for communication and other functions.
What is the basic operation process of a PLC?
-The basic operation process of a PLC includes an input scan to detect the state of inputs, a program scan to determine actions, execution of program logic, updating outputs to operate devices, and housekeeping for self-diagnostics, communications, and reporting.
What is the advantage of using a PLC over traditional relays in controlling a heating system?
-A PLC offers advantages such as the ability to incorporate time functions, easier reprogramming, and the capacity to handle more complex control strategies like PID loops and optimizers. It also simplifies fault finding and allows for more compact installations compared to traditional relays.
Can you provide an example of a complex control strategy mentioned in the script?
-An example of a complex control strategy mentioned in the script is the use of an optimizer in heating or cooling systems of commercial buildings. This optimizer learns the building's heating and cooling dynamics over time and starts the system at the optimal time to ensure the building is at the desired temperature when occupied.
What are some of the main advantages of using PLCs in industrial applications?
-Some main advantages of using PLCs include local storage of control software for continued operation during system failures, software-based connections reducing the need for physical wiring, smaller installations compared to relay banks, ease of reprogramming, faster fault finding, and the ability to expand inputs and outputs with additional cards.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

What is a PLC?...and a PAC?!?

Electrical Review - PLC Basics Part 1

AWAL BELAJAR Ngobrol Santai Tentang PLC (Programmable Logic Controller)
1. Berkenalan Dengan Kerja Perangkat Kontrol PLC

Belajar PLC | Pengenalan Programmable Logic Controller #1
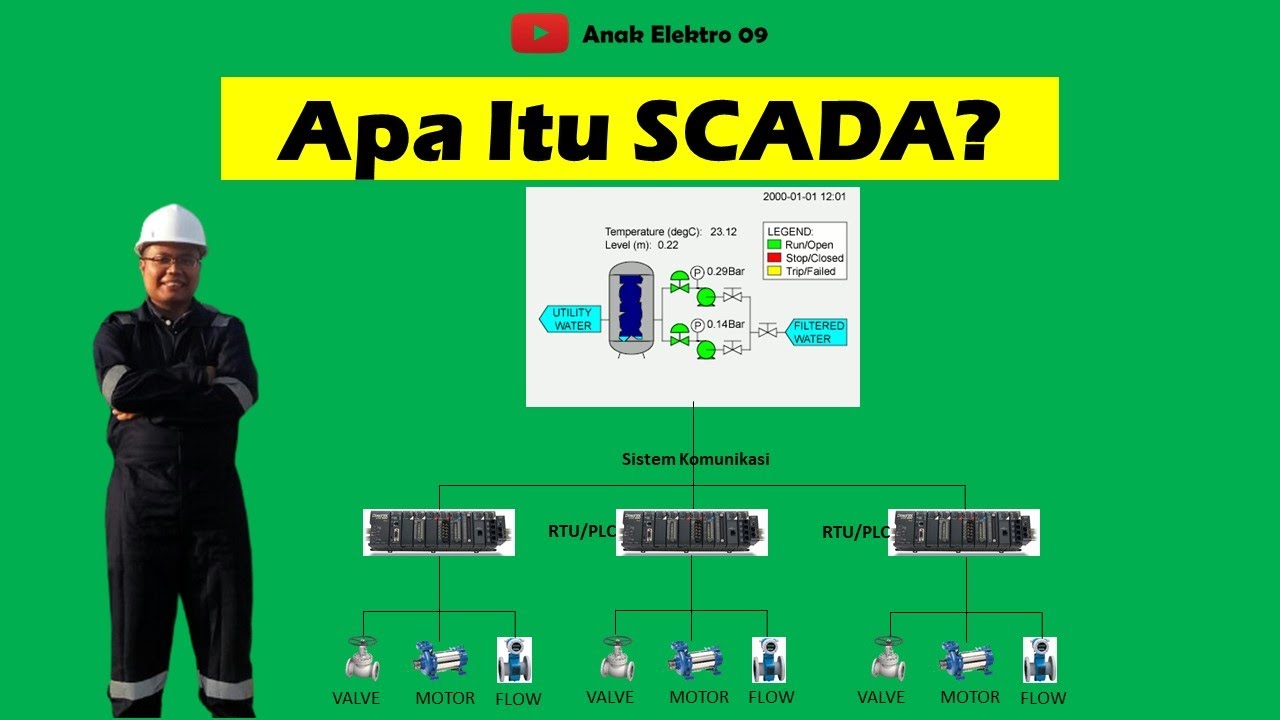
Pengenalan SCADA (Supervisory Control And Data Acquisition)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
