1. Berkenalan Dengan Kerja Perangkat Kontrol PLC
Summary
TLDRThis video introduces the concept and functionality of Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs), highlighting their crucial role in modern industrial automation. PLCs are versatile devices that replace complex relay systems, offering a compact, flexible solution for controlling machinery. The video explains how PLCs receive input signals, process them through programmed logic, and activate outputs to control actuators like motors or lights. Key components such as input modules, CPUs, and output modules are covered, alongside practical applications like conveyor systems and HVAC controls. The video emphasizes the benefits of using PLCs, including simplified wiring, space efficiency, and reliability.
Takeaways
- 😀 PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) is a critical component in modern automation systems, used to control machinery and industrial processes efficiently.
- 😀 PLC functions like a mini personal computer, processing input signals and outputting control commands to actuators based on programmed logic.
- 😀 Before PLC technology, industrial control relied on complex relay systems, which were bulky, space-consuming, and difficult to troubleshoot.
- 😀 PLCs simplify control systems by using logic programming and electronic components, replacing traditional relay-based systems and reducing wiring complexity.
- 😀 The three main parts of a PLC are the input module (receiving signals), the CPU (processing the signals), and the output module (controlling actuators).
- 😀 Input signals can be digital (on/off) or analog (continuous range), with analog inputs requiring additional processing to convert to digital signals.
- 😀 PLCs offer precise control, such as controlling conveyor belts, heating systems, and pumps based on pre-programmed logic and sensor inputs.
- 😀 A common application of PLCs is in automated systems, like baggage handling in airports, where a sensor scans barcodes and controls the conveyor system based on the destination.
- 😀 The PLC's CPU interprets input signals, executes programmed instructions, and manages communication with external devices like sensors and actuators.
- 😀 The use of PLCs greatly reduces the need for physical space and wiring, simplifies troubleshooting, and allows for more flexible, scalable automation systems.
- 😀 PLCs enable efficient energy management and process control, such as adjusting heating or cooling in buildings, optimizing operations based on schedules and real-time conditions.
Q & A
What is a PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) and how is it used in modern automation systems?
-A PLC is a device used to control automated systems in industries. It receives inputs from sensors, processes these inputs based on a pre-programmed logic, and then sends outputs to actuators, controlling various devices like motors, lights, or valves. PLCs are used in various automation tasks to enhance efficiency and simplify operations.
What are the main components of a PLC?
-The main components of a PLC are the Input Module (which receives signals from external devices), the CPU (which processes these inputs according to the programmed logic), and the Output Module (which sends signals to actuators based on the processed input).
How does a PLC process input signals?
-A PLC processes input signals by first reading them from external devices, such as sensors or switches. These signals can be either digital (on/off) or analog (ranging values). The PLC then converts these signals into a form that the CPU can process, applies the programmed logic, and generates corresponding output signals.
Why is PLC considered more efficient than older control systems using relays?
-PLCs are more efficient because they replace complex relay systems that require intricate wiring and physical space with a software-based control system. This reduces the need for large amounts of wiring, simplifies troubleshooting, and allows for easier reprogramming and scalability.
What are the advantages of using a PLC in industrial automation?
-PLCs offer several advantages: they allow for easy program modifications, reduce physical wiring needs, have built-in troubleshooting capabilities, can store multiple programs, and can be expanded by adding more input/output modules. They are also reliable, as they can continue operating during power failures.
Can you give an example of how a PLC is used in real-world applications?
-One example is in airport baggage handling systems. When a passenger's baggage is scanned with a barcode, the PLC processes the information, determines the destination (domestic or international), and automatically sorts the baggage to the correct gate based on the programmed logic.
How does a PLC work with sensors to control heating or cooling systems in buildings?
-A PLC can control heating and cooling systems by processing data from sensors such as temperature sensors. For instance, if the temperature in a room is too high or low, the PLC will execute a program that adjusts the HVAC system accordingly, such as turning on heating or cooling to maintain a desired room temperature.
What is the role of the CPU in a PLC system?
-The CPU is the core of the PLC, responsible for executing the programmed instructions. It processes input signals, applies the necessary logic or calculations, and then sends appropriate commands to the output modules to control actuators and devices in the system.
How does a PLC handle analog inputs?
-PLCs can handle analog inputs, such as temperature or pressure sensors, by converting the analog signals (which can have a range of values) into digital values that the CPU can process. This allows the PLC to control actuators with precision, based on the continuous data received from the sensors.
What are some specific advantages of using a PLC over traditional relay-based systems?
-PLCs provide several advantages over relay-based systems, including simplified wiring, faster troubleshooting, the ability to easily update or change control logic, and a smaller physical footprint. PLCs also allow for more complex control processes that can be programmed and adjusted easily, reducing the need for manual intervention.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Belajar PLC | Pengenalan Programmable Logic Controller #1

AWAL BELAJAR Ngobrol Santai Tentang PLC (Programmable Logic Controller)

What is a PLC?...and a PAC?!?
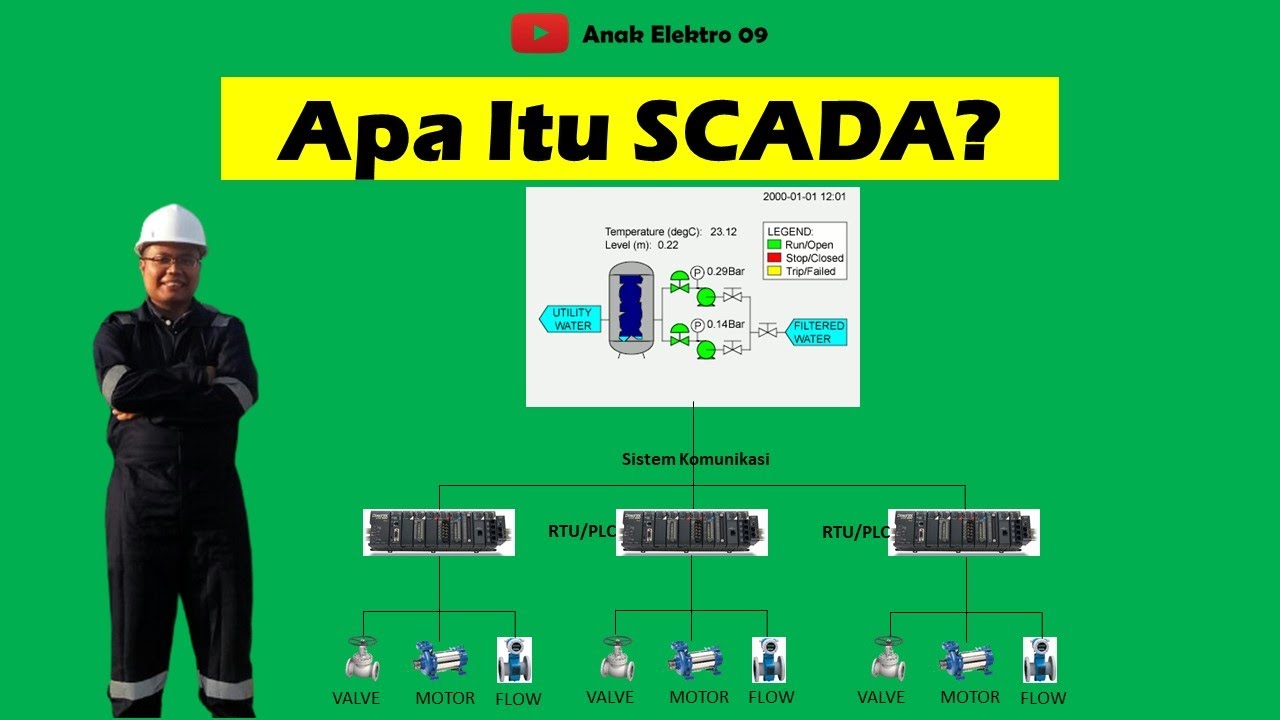
Pengenalan SCADA (Supervisory Control And Data Acquisition)

Introduction to Industrial Automation | Introduction and History

Electrical Review - PLC Basics Part 1
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)