How An Oil Tanker Works And Designed
Summary
TLDRThis video provides an in-depth look at oil tankers, focusing on ultra-large crude carriers. It explains the two main types—crude tankers for transporting unrefined oil and product tankers for refined products—and highlights their key components, including cargo tanks, ballast tanks, pump and engine rooms, and crew accommodations. The video emphasizes stability mechanisms like multiple cargo tanks to prevent free surface effects, double hulls for environmental safety, and proper weight distribution during loading. It also covers oil loading procedures, heating coils, and offshore transfer methods, offering viewers a comprehensive understanding of how these massive vessels operate safely and efficiently on the high seas.
Takeaways
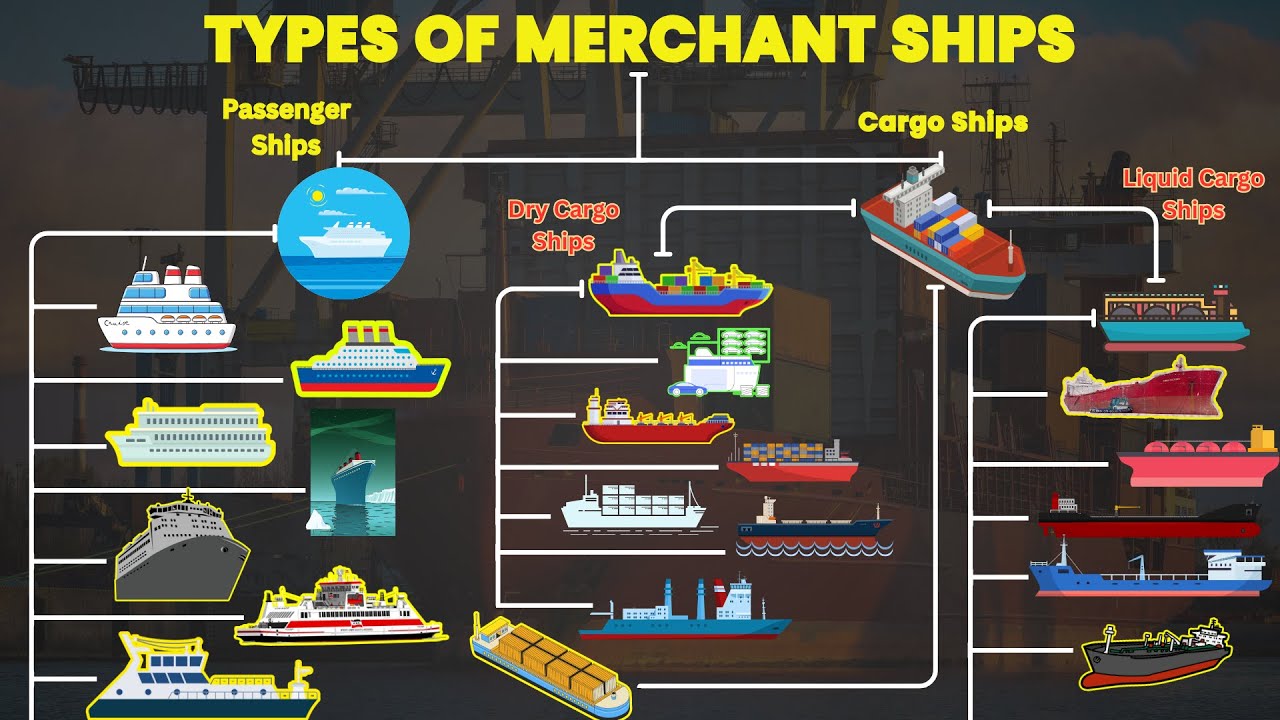
- 🛳️ Oil tankers are ships designed for transporting crude oil and its products, with two main types: crude tankers and product tankers.
- ⚓ Crude tankers carry unrefined oil from extraction points to refineries, while product tankers move refined products to consumer markets.
- 📏 Tanker sizes vary from inland/coastal vessels to ultra-large crude carriers, with the video focusing on the latter.
- 🛠️ Key components of a tanker include pipelines, cranes, helicopter pads, cargo tank mast risers, accommodation areas, control rooms, and emergency escape boats.
- 🛢️ Inside the hull, there are oil cargo tanks, water ballast tanks, fuel tanks, sludge tanks, fresh water tanks, cofferdams, pump rooms, and engine rooms.
- 🌊 Multiple smaller cargo tanks prevent free surface effects, improving vessel stability in rough seas.
- 🛡️ Double hull designs protect oil cargo tanks from external damage, reducing the risk of oil spills and environmental pollution.
- 💧 Water ballast tanks maintain stability when the ship is not fully loaded with oil, and water treatment systems prevent the spread of harmful microorganisms.
- 🧱 Cofferdams separate different liquid tanks to prevent cross-contamination in case of leaks or cracks.
- ⚖️ Proper weight distribution during oil loading is critical for vessel stability, with oil loaded evenly into multiple tanks.
- 🔥 Oil cargo tanks have heating coils to reduce viscosity for easier pumping, and tankers may use loading arms or offshore transfer methods for loading and unloading oil.
- ⛴️ Extremely large tankers may transfer oil to smaller vessels if they cannot approach a dock directly.
Q & A
What are the two basic types of oil tankers?
-The two basic types of oil tankers are crude tankers, which transport unrefined crude oil to refineries, and product tankers, which transport refined oil products from refineries to consuming markets.
What is the primary focus of the video script regarding oil tankers?
-The primary focus is on ultra-large crude carriers (ULCCs), which are very large crude oil tankers designed to transport massive quantities of crude oil.
What are some of the main parts of an oil tanker described in the script?
-Main parts include pipeline systems, a helicopter landing pad, cranes, mast risers, accommodation areas for crew, the control room, emergency escape boats, oil cargo tanks, water ballast tanks, fuel tanks, sludge tanks, fresh water tanks, cofferdams, engine room, and pump room.
Why do large crude oil tankers have multiple oil cargo tanks?
-Multiple tanks help avoid the free surface effect, where the movement of liquid in a single large tank could generate forces strong enough to destabilize or capsize the ship. Dividing the liquid into smaller tanks reduces this risk and provides greater stability.
What is the purpose of the double hull design in oil tankers?
-The double hull protects the oil cargo tanks from external damage. In a single-hull ship, a hull breach could result in oil leakage into the ocean, causing environmental pollution and endangering marine life.
How do water ballast tanks contribute to the stability of an oil tanker?
-Water ballast tanks provide weight and stability when the ship is not carrying oil. By adjusting the amount of water in these tanks, the vessel can remain stable and submerged properly, ensuring safe operation for the crew.
What is a cofferdam and why is it important?
-A cofferdam is an empty space separating different types of liquid tanks. It prevents mixing of liquids if a leak occurs and provides space to fix leaks without contaminating other tanks.
How is oil loaded into cargo tanks to ensure safety?
-Oil is loaded evenly across multiple tanks to maintain weight distribution and balance. Pipelines, pumps, and manifolds are used to direct oil into designated tanks, often grouped to distribute weight evenly across the ship.
Why do oil cargo tanks have heating coils?
-Heating coils reduce the viscosity of crude oil, making it easier to pump in and out of the tanks during loading and unloading operations.
What are the different methods oil tankers use to receive oil from offshore sources?
-Oil tankers can receive oil directly from subsea pipelines using a buoy and floating hoses, or, if the tanker is too large to approach a dock, transfer oil to smaller tankers that can carry it to the dock.
Why is a water treatment system necessary on oil tankers?
-A water treatment system ensures that ballast water discharged into new locations does not carry harmful microorganisms or bacteria from previous locations, protecting marine ecosystems.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)