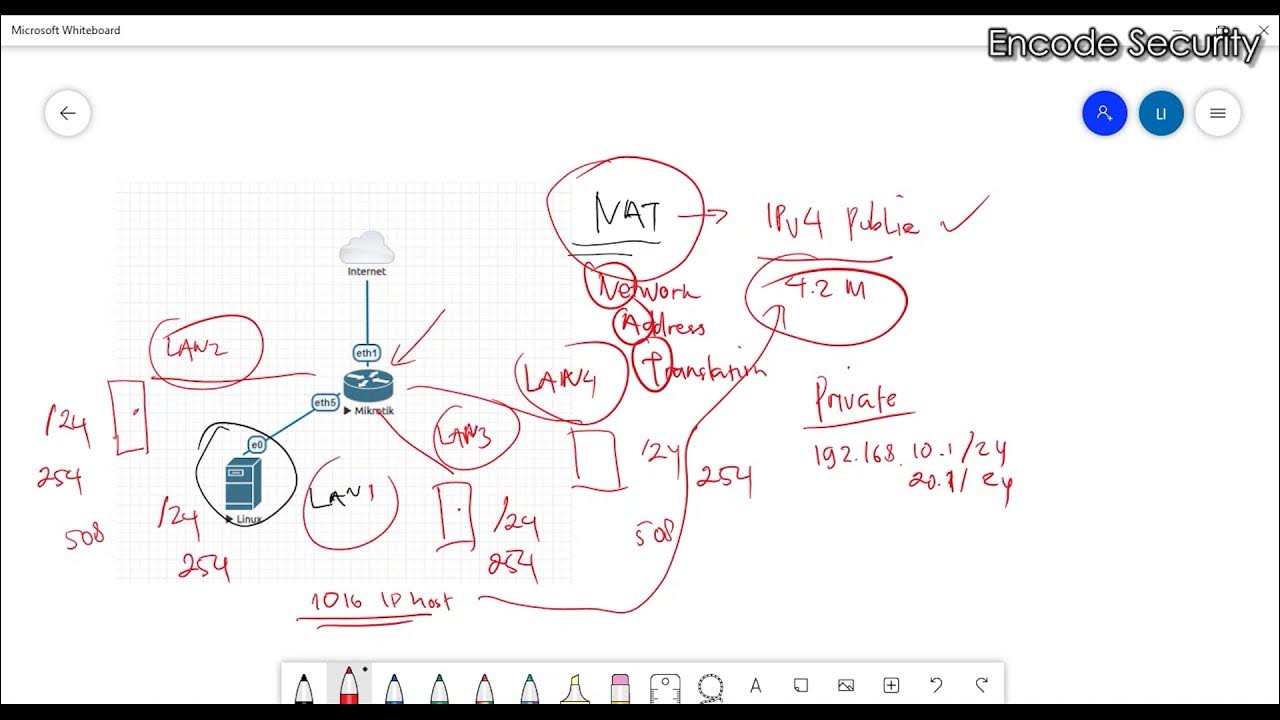
Apa itu NAT (Network Address Translation)?
Summary
TLDRThis video explains Network Address Translation (NAT), a service used in routers to translate one set of IP addresses to another. It helps preserve limited public IP addresses by assigning private IP addresses to devices within a network. The video covers the difference between public and private IP addresses, the role of NAT in translating these addresses, and the future of IP addressing with IPv6, which will eliminate the need for NAT due to an abundance of available IP addresses. The tutorial emphasizes the importance of NAT in today's internet usage and its role in managing IP address scarcity.
Takeaways
- 😀 NAT (Network Address Translation) is used in routers to translate one set of IP addresses into another set.
- 😀 NAT helps conserve the limited number of public IPv4 addresses by using private IP addresses for internal networks.
- 😀 IPv4 originally provided over 4 billion IP addresses, but engineers underestimated the rapid growth of the internet.
- 😀 Public IP addresses are registered on the internet and are required for devices to access the internet.
- 😀 Private IP addresses are used internally within networks (homes or workplaces) and cannot directly access the internet.
- 😀 Routers assign private IP addresses to devices within a network and handle the translation to public IP addresses for internet access.
- 😀 NAT translates private IP addresses to public ones when devices need to access the internet, and vice versa.
- 😀 In the future, with IPv6, NAT and private IP addresses will no longer be necessary due to the abundance of available IPv6 addresses.
- 😀 IPv6 offers more than 340 undecillion unique IP addresses, which ensures we will never run out of IP addresses.
- 😀 The widespread adoption of IPv6 will eliminate the need for NAT as each device will have its own public IP address.
- 😀 NAT is a vital service for efficient IP address management in the current IPv4 internet infrastructure.
Q & A
What is NAT (Network Address Translation)?
-NAT is a service used in routers to translate one set of IP addresses to another. Its main purpose is to help preserve the limited number of public IPv4 addresses available worldwide.
Why was NAT developed?
-NAT was developed to address the shortage of public IPv4 addresses. Initially, engineers did not anticipate the rapid growth of the internet and the demand for more IP addresses.
What is the difference between public and private IP addresses?
-Public IP addresses are registered on the internet and are required for internet access, while private IP addresses are used internally within a network and are not directly accessible on the internet.
Can devices with private IP addresses access the internet?
-No, devices with private IP addresses cannot directly access the internet. They require NAT to translate their private IP addresses into public ones assigned by an ISP.
Why is it expensive and inefficient to give every device a public IP address?
-Providing every device with a public IP address would be costly and inefficient, especially since public IP addresses are limited. This would also waste available public IP addresses, which are already in short supply.
How does NAT help manage IP address usage in a home or workplace?
-NAT allows routers to assign private IP addresses to multiple devices within a network. When these devices need to access the internet, NAT translates their private IP addresses to a public IP address provided by the ISP.
Does NAT only translate private IP addresses to public ones?
-No, NAT also translates public IP addresses back to private IP addresses. This is necessary when a device on a public network wants to communicate with a device on a private network.
What is the difference between IPv4 and IPv6?
-IPv4 is the current version of IP addresses, which is limited to about 4 billion addresses. IPv6, however, offers an immense number of addresses (340 undecillion), eliminating the need for NAT as each device can have its own unique public IP address.
What is the future of NAT with the introduction of IPv6?
-With IPv6, NAT will no longer be necessary because each device will have its own public IP address, effectively eliminating the shortage of IP addresses and the need for address translation.
What is the total number of IP addresses that IPv6 can generate?
-IPv6 can generate more than 340 undecillion IP addresses, which is represented by the number 340 followed by 36 zeros.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahora5.0 / 5 (0 votes)