Apa itu NAT ? Bagaimana NAT Bekerja ?
Summary
TLDRThis tutorial video explains the concept and configuration of Network Address Translation (NAT) on MikroTik routers. It covers the importance of NAT in enabling private IP networks to access the internet, especially given the limited availability of public IP addresses. The tutorial walks through various types of NAT configurations, such as Masquerade and Source NAT, showing their differences and applications. It also demonstrates practical steps for setting up NAT in a MikroTik router to ensure seamless internet connectivity for devices on a local network. The video is ideal for network practitioners and MikroTik users looking to understand NAT functionality.
Takeaways
- 😀 Network Address Translation (NAT) is an essential tool for enabling multiple devices in a local network to access the internet using a single public IP address.
- 😀 NAT helps overcome the limitations of IPv4 address space by allowing multiple private IP addresses to share a single public IP.
- 😀 The growing number of internet users highlighted the need for NAT, as the limited IPv4 address space was insufficient for the increasing demand.
- 😀 NAT allows devices on private IP addresses, such as 192.168.x.x or 10.x.x.x, to communicate with external servers that only recognize public IP addresses.
- 😀 There are two main methods for configuring NAT on MikroTik routers: Masquerade and Source NAT (Src-NAT).
- 😀 Masquerade is commonly used when the public IP is dynamic and assigned by an ISP. It is the preferred method for most dynamic public IP configurations.
- 😀 Source NAT (Src-NAT) is useful when a static public IP is used, and requires additional parameters to specify which public IP address should be used for translation.
- 😀 In a typical NAT process, private IP addresses from client devices are mapped to a public IP address when they send requests to access the internet.
- 😀 The router processes the NAT translation, ensuring that the response from the internet is sent back to the correct private IP address by looking up the source of the original request.
- 😀 The tutorial provides practical steps to configure NAT on MikroTik routers using both Masquerade and Source NAT methods to enable private IP addresses to access the internet.
Q & A
What is Network Address Translation (NAT)?
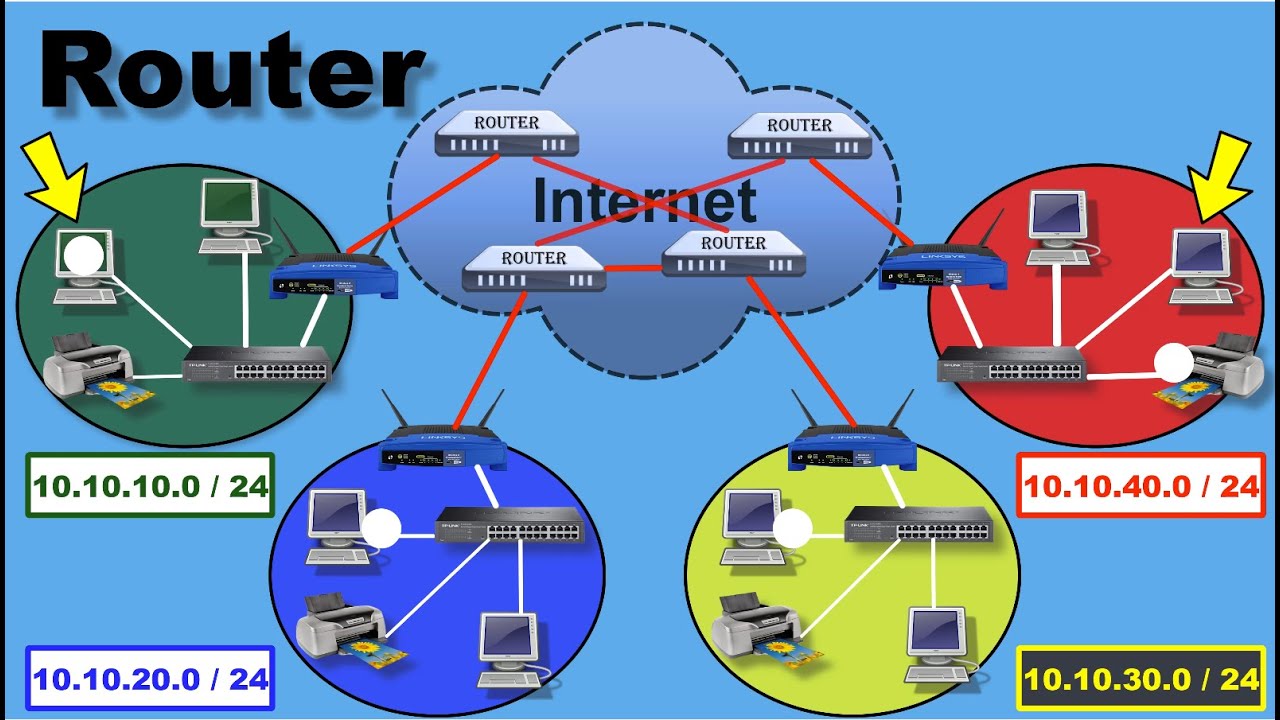
-Network Address Translation (NAT) is a method used in networking to translate private IP addresses within a local network to a public IP address when accessing the internet. This allows multiple devices within a private network to share a single public IP address.
Why is NAT important in networking?
-NAT is crucial because it helps manage the limited number of available public IPv4 addresses. By using private IP addresses internally and translating them to a public address for internet access, NAT ensures that more devices can connect to the internet without consuming a separate public IP for each one.
What is the primary difference between public and private IP addresses?
-Public IP addresses are routable over the internet and are globally unique, whereas private IP addresses are used within internal networks and are not directly accessible from the internet.
How many public IPv4 addresses are available, and why does it matter?
-There are approximately 4.2 billion public IPv4 addresses. This limited supply is one of the main reasons NAT was developed, as it allows multiple devices to use the same public IP address while still maintaining unique private addresses within local networks.
How does NAT allow multiple devices with private IP addresses to access the internet?
-NAT enables multiple devices to access the internet using a single public IP address by translating their private IP addresses to the public address. The router keeps track of which internal device made the request, ensuring that responses are correctly routed back to the right device.
What are the two common methods of NAT used in MikroTik routers?
-The two common methods of NAT used in MikroTik routers are Masquerade NAT and Source NAT. Masquerade NAT is often used with dynamic public IP addresses, while Source NAT is used when a static public IP address is required.
What is Masquerade NAT, and when is it typically used?
-Masquerade NAT is used when the public IP address is dynamically assigned by an Internet Service Provider (ISP). It allows multiple devices on a local network to access the internet using a single public IP address.
What is Source NAT, and how is it different from Masquerade NAT?
-Source NAT is used when a static public IP address is assigned to a network. Unlike Masquerade NAT, which automatically uses the router's public IP, Source NAT requires explicit configuration of the public IP to be used for translation.
What happens during the NAT translation process when a device sends a request to the internet?
-When a device in the LAN sends a request to the internet, the router translates the private IP address to the public IP address. The request is then forwarded to the destination server (e.g., Google). The server responds to the public IP, and the router translates it back to the private IP of the requesting device, completing the connection.
What configuration steps are necessary to implement NAT on a MikroTik router?
-To configure NAT on a MikroTik router, you must define a NAT rule with the correct source address, specify the outbound interface connected to the internet, and choose the appropriate NAT action (Masquerade or Source NAT) based on the type of public IP address you're using.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)