What is a SYNCHRONOUS MOTOR and how does it work? - Rotating magnetic field - Synchronism speed
Summary
TLDRThis video explains how synchronous motors operate, detailing their design and unique features. The motor's rotation speed is synchronized with the frequency of alternating current, offering high precision in various fields. It covers how the stator and rotor interact through magnetic fields, how motors operate at constant speed, and their use in applications like electric and hybrid cars. Additionally, the video discusses innovations, such as squirrel cages for smooth startup, and the role of electronics in controlling speed, providing a comprehensive understanding of synchronous motors.
Takeaways
- 😀 Synchronous motors are electric motors that operate at a speed synchronized with the frequency of the alternating current (AC).
- 😀 These motors are used in applications where high precision is necessary.
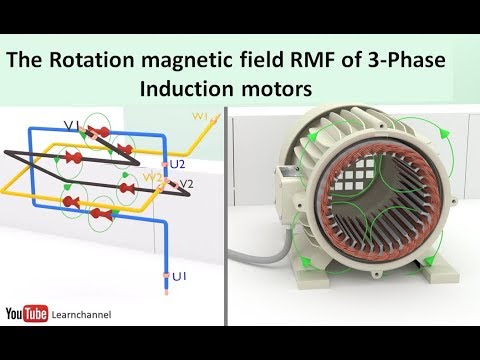
- 😀 The stator (stationary part) is powered by three-phase alternating current to create a rotating magnetic field.
- 😀 The rotor (rotating part) is powered by direct current, creating alternating magnetic fields similar to magnets.
- 😀 The rotor and stator interact through attractive and repulsive magnetic forces, which causes the rotor to rotate at the same speed as the stator's rotating magnetic field.
- 😀 Synchronous motors operate at a constant speed based on the electrical frequency and the number of rotor pole pairs.
- 😀 Motors with more rotor and stator coils have lower speeds but develop higher mechanical torque.
- 😀 Synchronous motors cannot accelerate or decelerate easily and will stop if there is a disruption in synchronization.
- 😀 To improve motor performance, a squirrel cage was introduced above the rotor to assist in the starting phase.
- 😀 Synchronous motors are used in electric and hybrid vehicles, functioning as both a motor and alternator for regenerative braking.
- 😀 Advances in electronics have simplified starting electric cars by enabling inverters to modify frequency and voltage, allowing smoother acceleration from a standstill.
Q & A
What is a synchronous motor?
-A synchronous motor is an electric motor whose rotational speed is synchronized with the electric frequency of the alternating current (AC). It is used in applications where high precision is required.
How does a synchronous motor work?
-In a synchronous motor, the stator is powered by three-phase alternating current, creating a rotating magnetic field. The rotor is powered by direct current (DC) and produces alternating magnetic fields, which interact with the stator’s magnetic field to make the rotor rotate at the same speed.
What makes the rotor rotate in a synchronous motor?
-The opposite poles of the stator and rotor attract each other, causing the rotor to rotate at the same speed as the rotating magnetic field of the stator.
Why are synchronous motors unable to accelerate or decelerate?
-Synchronous motors operate at a constant speed dictated by the electrical frequency of the AC power supply and the number of rotor poles. They cannot accelerate or decelerate easily because their speed is locked to the frequency of the power supply.
What happens if a synchronous motor is accelerated or braked by external forces?
-If external forces accelerate or decelerate the motor, the rotor will fall out of synchronization with the stator’s magnetic field, causing the rotor to stop.
What is the issue with starting a synchronous motor from a stationary position?
-If the rotor is stationary, the alternating magnetic fields of the stator will alternate too quickly for the rotor to start, preventing the motor from functioning until it reaches synchronous speed.
How is a squirrel cage used to improve the synchronous motor?
-A squirrel cage is added above the rotor coils. During startup, the rotor coils are not energized, but the rotating magnetic field induces electricity into the squirrel cage, allowing the motor to start like an induction motor. Once the motor reaches synchronous speed, the rotor coils are energized and the motor operates as a synchronous motor.
What is the role of synchronous motors in electric and hybrid cars?
-Synchronous motors in electric and hybrid cars can function both as a motor to drive the wheels and as an alternator in the regenerative braking phase, converting kinetic energy back into electrical energy to recharge the battery.
How has electronic advancement impacted the operation of synchronous motors in vehicles?
-With advancements in electronics, it is now easier to control the speed of synchronous motors in vehicles. Inverters can modify the frequency and voltage of the power supply, enabling the motor to accelerate from a standstill and operate efficiently.
What is the importance of inverters in controlling synchronous motors?
-Inverters are crucial for controlling synchronous motors as they allow the modification of both the frequency and the voltage of the power supply. This enables precise control over the motor’s speed, including the ability to start from zero speed.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

Synchronous Motor vs Asynchronous Motor | Synchronous vs Induction Motor | Come4Concepts

How alternating current motors work?

permanent magnet synchronous motor | pmsm motor | pmsm motor working principle | in hindi |animation
Induction Motor animation I: The Rotating Magnetic Field RMF
Types of Motors used in EV | Single, Dual, Three & Four Motor Configuration in EV

SynRM | Raksasa baru dunia kelistrikan
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
