permanent magnet synchronous motor | pmsm motor | pmsm motor working principle | in hindi |animation
Summary
TLDRThis lecture delves into the construction and operation of Permanent Magnet (PM) Synchronous Motors, highlighting their role in converting electrical energy to mechanical energy. The speaker emphasizes the unique design that excludes commutators and brushes, featuring a rotor with permanent magnets for enhanced efficiency. Key principles such as the generation of a rotating magnetic field through three-phase AC supply are explained. The lecture compares PM motors with induction synchronous motors, noting differences in efficiency and applications. PM Synchronous Motors are showcased as essential in various high-power environments, where they significantly improve performance and power factors.
Takeaways
- 😀 PMSM is a type of synchronous motor that uses permanent magnets on the rotor to improve efficiency.
- 😀 Unlike normal synchronous motors, PMSMs do not require a commutator or brushes for operation.
- 😀 The rotor of a PMSM is made of permanent magnets, which enhance the motor’s performance and efficiency.
- 😀 The stator of the PMSM is made of laminated silicon steel to support the magnetic field lines and improve performance.
- 😀 PMSMs use a rotating magnetic field created by three-phase supply in the stator to drive the rotor.
- 😀 The motor operates at synchronous speed, which is calculated using the formula N_s = 120 × f / P.
- 😀 External control systems like Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs) and servo drives are used to achieve synchronous speed.
- 😀 Once the rotor reaches synchronous speed, the external control system can be disconnected.
- 😀 PMSMs are commonly used in power systems, machine tools, and traction control systems where high efficiency and speed are required.
- 😀 Compared to induction motors, PMSMs are more expensive but offer better efficiency and higher performance at high speeds.
- 😀 The absence of windings and the use of permanent magnets in PMSMs reduce the need for maintenance and improve reliability.
Q & A
What is a PM synchronous motor?
-A PM synchronous motor is a type of synchronous motor that uses permanent magnets to convert electrical energy into mechanical energy.
How does the construction of a PM motor differ from a regular synchronous motor?
-The construction of a PM motor differs as it does not use a commutator or brushes, featuring a rotor that contains permanent magnets instead.
What material is used for the stator in a PM synchronous motor, and why?
-The stator is typically made of laminated silicon steel due to its high permeability, which supports magnetic field lines.
What role do the stator windings play in a PM motor?
-The stator windings supply a three-phase electrical supply that produces a rotating magnetic field, enabling the rotor to spin synchronously.
What is the significance of the synchronous speed in a PM motor?
-Synchronous speed is the speed at which the rotor rotates in sync with the rotating magnetic field produced by the stator, determined by the frequency of the electrical supply and the number of poles.
How is the speed of a PM motor controlled?
-The speed of a PM motor is typically controlled using variable frequency drives (VFDs) and servo drives to maintain synchronous speed.
Why are PM motors considered to have higher efficiency?
-PM motors have higher efficiency due to their design, which eliminates the need for slip in operation and reduces losses associated with brushes and commutators.
In what applications are PM synchronous motors commonly used?
-PM synchronous motors are commonly used in machine tools, traction control systems, and situations where improved leading and lagging power factors are necessary.
How does the cost of PM motors compare to induction motors?
-PM motors are generally more expensive than induction motors, mainly due to their advanced construction and efficiency benefits.
What is the role of the rotor in a PM synchronous motor?
-The rotor in a PM synchronous motor is designed with permanent magnets, creating a magnetic field that interacts with the rotating magnetic field of the stator, causing rotation.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

pmdc motor | pmdc motor working principle | construction and working | permanent magnet dc motor |dc
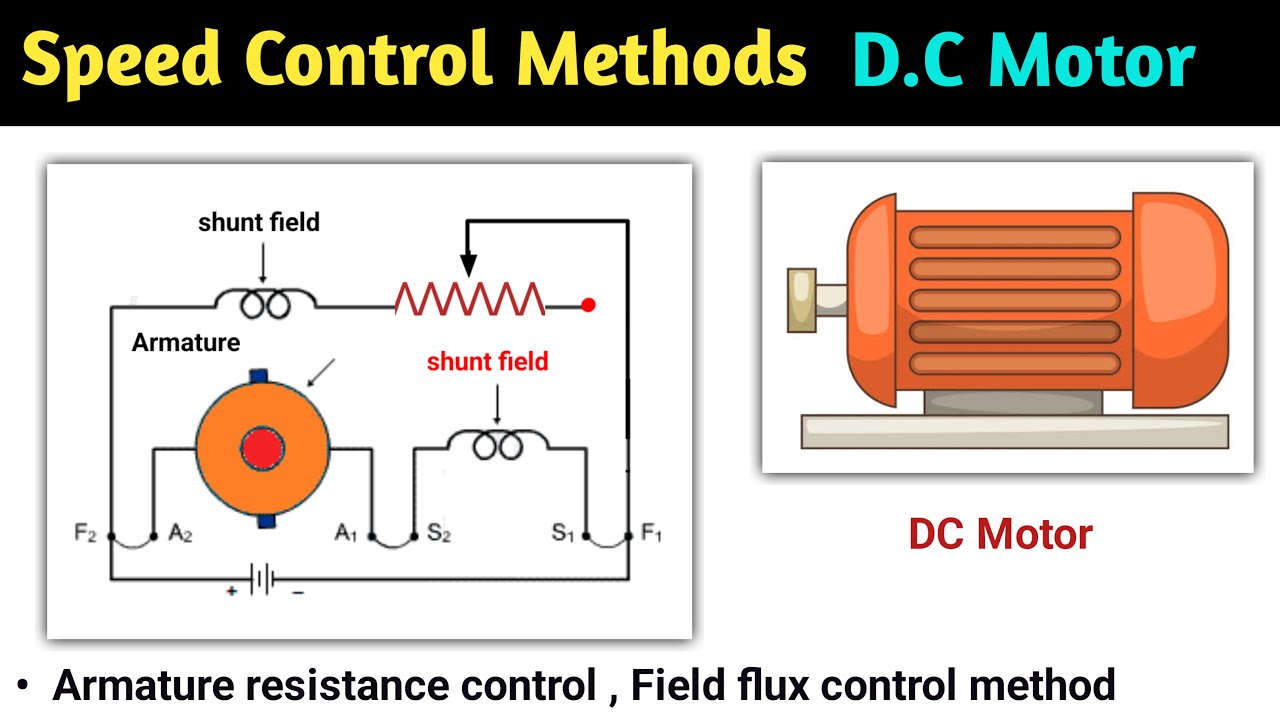
speed control of dc motor | speed control of dc shunt motor | dc motor speed control | series motor
Motor VS Generator VS Alternator || How Generator, Motor And Alternator Works || In Hindi

Synchronous Machines - Introduction (Part1)
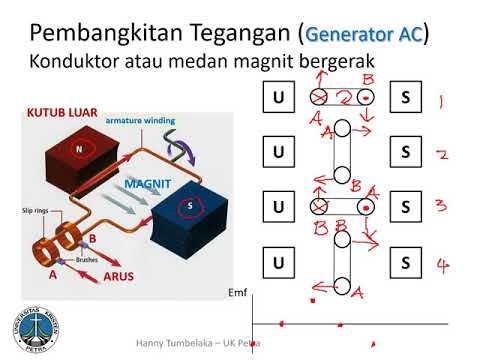
Prinsip Kerja Generator AC

How Stepper Motors Work - Electric motor
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)