KUPAS TUNTAS: Apakah Perbedaan Statistik Inferensial dengan Statistik Deskriptif ?
Summary
TLDRThis script discusses the differences between inferential and descriptive statistics. Inferential statistics uses sample data to make inferences about a larger population, while descriptive statistics merely describe the data without generalizing. The video explores concepts like population, sample, parameters, and estimators, emphasizing the importance of representative samples for accurate statistical inferences. It also touches on the use of descriptive statistics to describe data trends and characteristics without making broader conclusions.
Takeaways
- 😀 Statistics is the science or art of collecting, organizing, analyzing, interpreting, and drawing conclusions from data.
- 🔍 Inferential statistics involves making generalizations from a sample to a larger population, whereas descriptive statistics focuses on describing the data without generalizing to a larger population.
- 📊 Inferential statistics uses probability theory to estimate or predict about a population, while descriptive statistics uses visual representations like bar charts, histograms, and pie charts to describe data.
- 📈 Descriptive statistics is concerned with measuring and describing the data, such as its spread, variability, mean, median, and mode.
- 🌐 The term 'population' refers to the entire group or set of items under study, which can be anything from people to objects or even abstract concepts like languages.
- 📐 A 'sample' is a subset of the population that is studied to make inferences about the population due to the impracticality of studying the entire population.
- 🔗 The relationship between population and sample is crucial; a good sample should be representative of the population to ensure that conclusions drawn from the sample can be generalized to the population.
- 📋 Parameters are the characteristics or measurements of a population, which are often estimated from sample statistics.
- 📊 Descriptive statistics can be presented in various forms such as pie charts, bar graphs, and line graphs to illustrate trends and distributions without making predictions or generalizations.
- 🔮 Inferential statistics is often used to test policies or methods to determine their effectiveness for a specific group and to assess if they can be applied more broadly.
Q & A
What is statistics?
-Statistics is the science or art of collecting, organizing, analyzing, interpreting, and drawing conclusions from data obtained through observation, surveys, and other means.
What is the difference between inferential and descriptive statistics?
-Inferential statistics uses sample data to make inferences about a larger population, while descriptive statistics merely describe the data without making inferences.
What is the purpose of inferential statistics?
-The purpose of inferential statistics is to generalize findings from a sample to a larger population, estimate population parameters, and make predictions based on sample data.
How does descriptive statistics differ from inferential statistics?
-Descriptive statistics focuses on summarizing and organizing data to describe its main features, such as central tendency, variability, and shape, without generalizing to a larger population.
What role does probability theory play in inferential statistics?
-Probability theory is used in inferential statistics to estimate and predict characteristics of a population and to make inferences based on the likelihood of certain outcomes.
Why is it impractical to study an entire population in statistics?
-It is impractical to study an entire population due to the vast scope, which can be limited by time, resources, and budget constraints.
What is a sample in the context of statistics?
-A sample is a subset of a population that is studied to represent the larger group, allowing for more manageable and cost-effective data collection.
What is the importance of representativeness in a sample?
-Representativeness ensures that the sample accurately reflects the characteristics of the population, allowing for valid inferences and generalizations to be made.
What is a parameter in statistics?
-A parameter is a characteristic or measurement that is associated with an entire population, such as the mean, variance, or proportion.
How does a statistic differ from a parameter?
-A statistic is a measurement derived from a sample, like the sample mean or variance, while a parameter is a measurement of the entire population.
What is the role of generalization in inferential statistics?
-In inferential statistics, generalization is the process of extending the conclusions drawn from a sample to the broader population to make predictions or estimates.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

KUPAS TUNTAS: Apakah Perbedaan Statistik Inferensial dengan Statistik Deskriptif ?
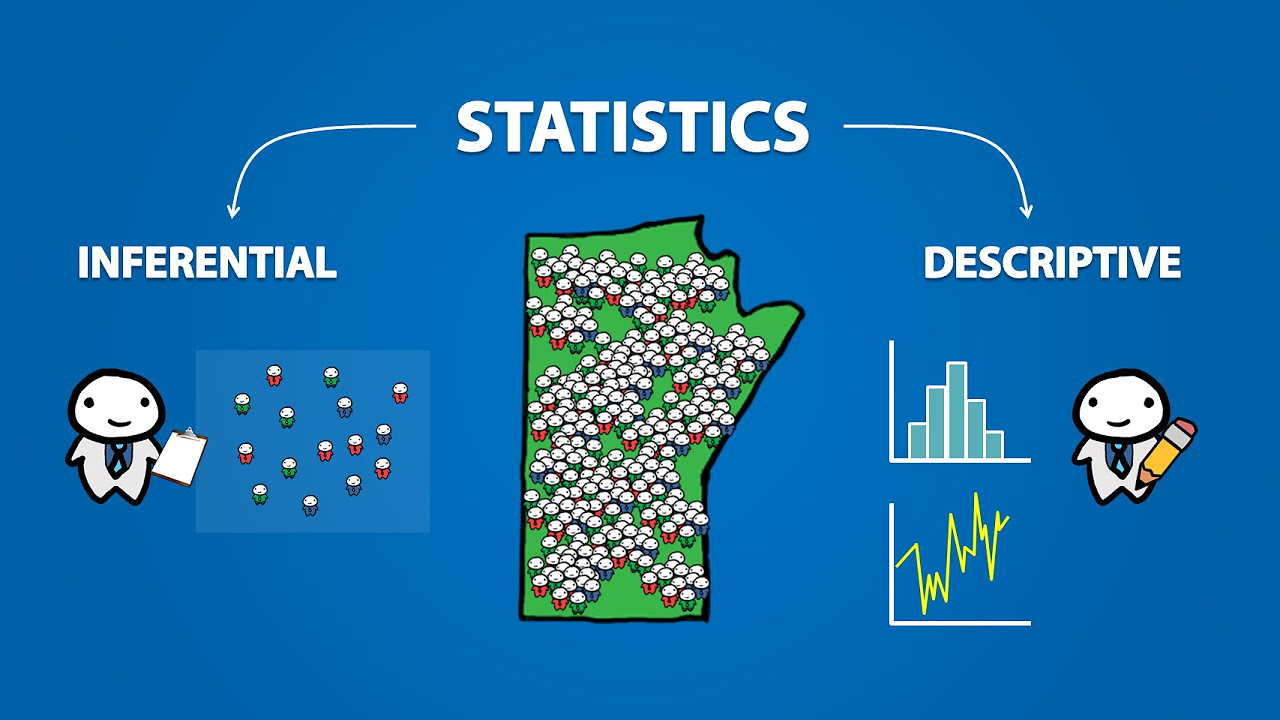
Introduction to Statistics (1.1)
Descriptive Statistics vs Inferential Statistics | Measure of Central Tendency | Types of Statistics

Descriptive Statistics vs Inferential Statistics

Statistik Inferensial & Hipotesis
What is the difference between Descriptive Statistics and Inferential Statistics?
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
