Introduction to Statistics (1.1)
Summary
TLDRThis script introduces the fundamental concepts of statistics, distinguishing between inferential and descriptive statistics. It explains how statistics measure variability in traits like height and preferences, using samples to make inferences about populations. Descriptive statistics summarize data with tools like histograms, while inferential statistics make broader claims. The script also covers key definitions, such as population, sample size, and variables, and differentiates between categorical and quantitative data, including discrete, continuous, ordinal, and nominal types.
Takeaways
- 📊 Statistics is the collection and interpretation of data to measure and analyze variability in characteristics such as height, weight, and preferences.
- 🔍 There are two types of statistics: inferential, which makes judgments about a population based on a sample, and descriptive, which summarizes and explains data.
- 📚 Descriptive statistics is used to provide summaries, like average scores, using tools like histograms and graphs.
- 🧐 Inferential statistics involves using a sample to make broader claims about a population.
- 🌐 A population in statistics refers to the entire set of items or subjects under study, which can be anything from people to vehicles.
- 🔍 A sample is a subset of the population used for study, with the number of items in the sample known as the sample size.
- 📝 Variables are the characteristics being studied and can be measured, counted, or categorized, such as height or hair color.
- 📊 Data can be either categorical, which groups items into categories like hair color, or quantitative, which involves numerical measurements like height.
- 🔢 Quantitative data comes from variables that can be measured numerically and are suitable for arithmetic calculations, such as calculating an average.
- 🗂 Categorical data comes from variables that categorize items, with two types being ordinal, which has a logical order like letter grades, and nominal, which does not, like hair color.
- 🔢 Quantitative variables can be discrete, which can only take certain numbers like the number of pets, or continuous, which can take any numerical value like weight.
Q & A
What is the definition of statistics according to the transcript?
-Statistics can be defined as the collection and interpretation of data, which is used to measure and analyze variability in various aspects such as height, weight, hair color, and food preferences among individuals.
What are the two kinds of statistics mentioned in the transcript?
-The two kinds of statistics are inferential statistics and descriptive statistics.
What does inferential statistics involve?
-Inferential statistics involves taking a sample, analyzing it, and making judgments or claims about a population based on that sample.
How is descriptive statistics different from inferential statistics?
-Descriptive statistics refers to the process of collecting data and summarizing it through means such as histograms and graphs, without making inferences about the larger population.
What is a population in the context of statistics?
-A population in statistics refers to the total amount of things being studied, which can be people, cats, vehicles, houses, or almost anything.
What is a sample and what is its significance in statistics?
-A sample is a small part of the population that is used for study. It is significant because it allows researchers to examine and extract information from a subset of the population.
What is meant by sample size in statistics?
-Sample size in statistics refers to the total number of things or individuals included in a sample.
What is a variable in the context of statistics?
-A variable in statistics is a characteristic of what is being studied, which can be measurable, countable, and categorized, and varies among different individuals.
What is the difference between categorical data and quantitative data?
-Categorical data refers to values that place things into different groups or categories, such as hair color or type of cat. Quantitative data, on the other hand, is measured in numbers and is suitable for arithmetic calculations, such as height or weight.
What are the two types of categorical variables mentioned in the transcript?
-The two types of categorical variables are categorical and ordinal, and categorical and nominal. Categorical and ordinal variables have a logical ordering, like letter grades. Categorical and nominal variables do not have a logical ordering, such as hair color.
What are the two types of quantitative variables and how do they differ?
-The two types of quantitative variables are discrete and continuous. Discrete variables can only be measured in certain numbers, like the number of pets one owns. Continuous variables can take on any numerical value and can be measured in many decimal places, like weight.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Descriptive Statistics vs Inferential Statistics
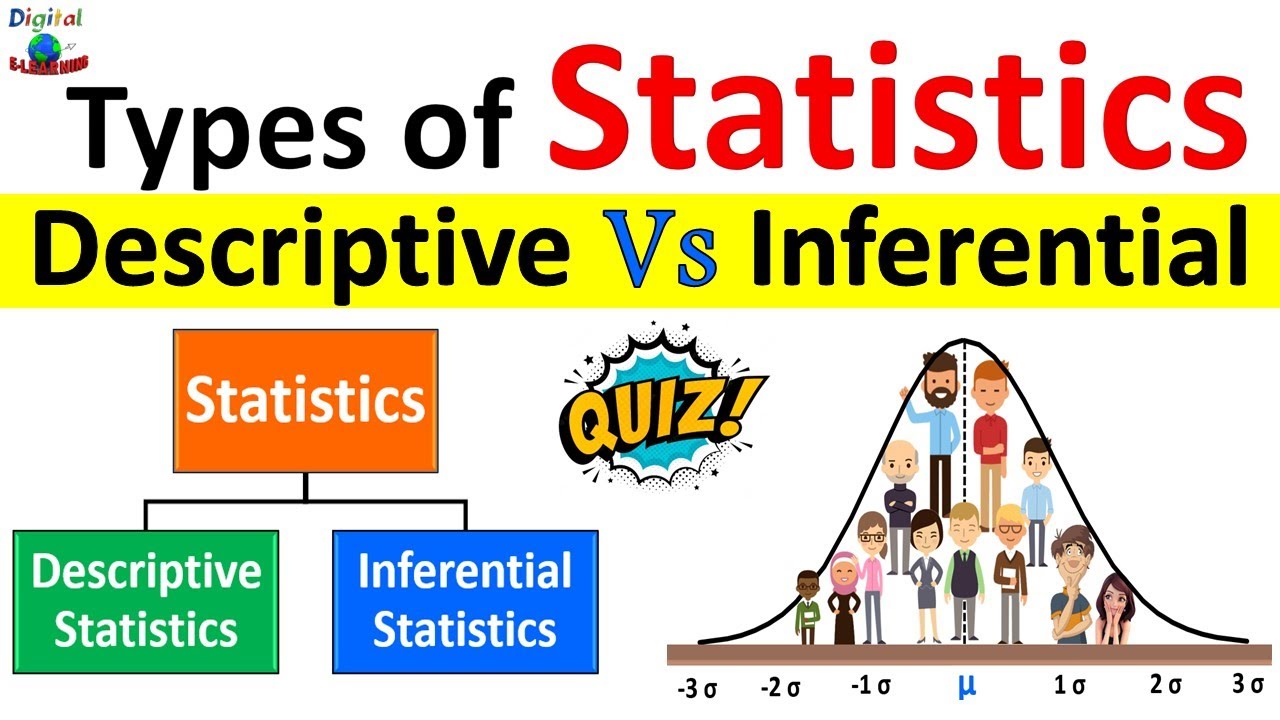
Descriptive Statistics vs Inferential Statistics | Measure of Central Tendency | Types of Statistics

KUPAS TUNTAS: Apakah Perbedaan Statistik Inferensial dengan Statistik Deskriptif ?

Statistik 2: pembagian statistika
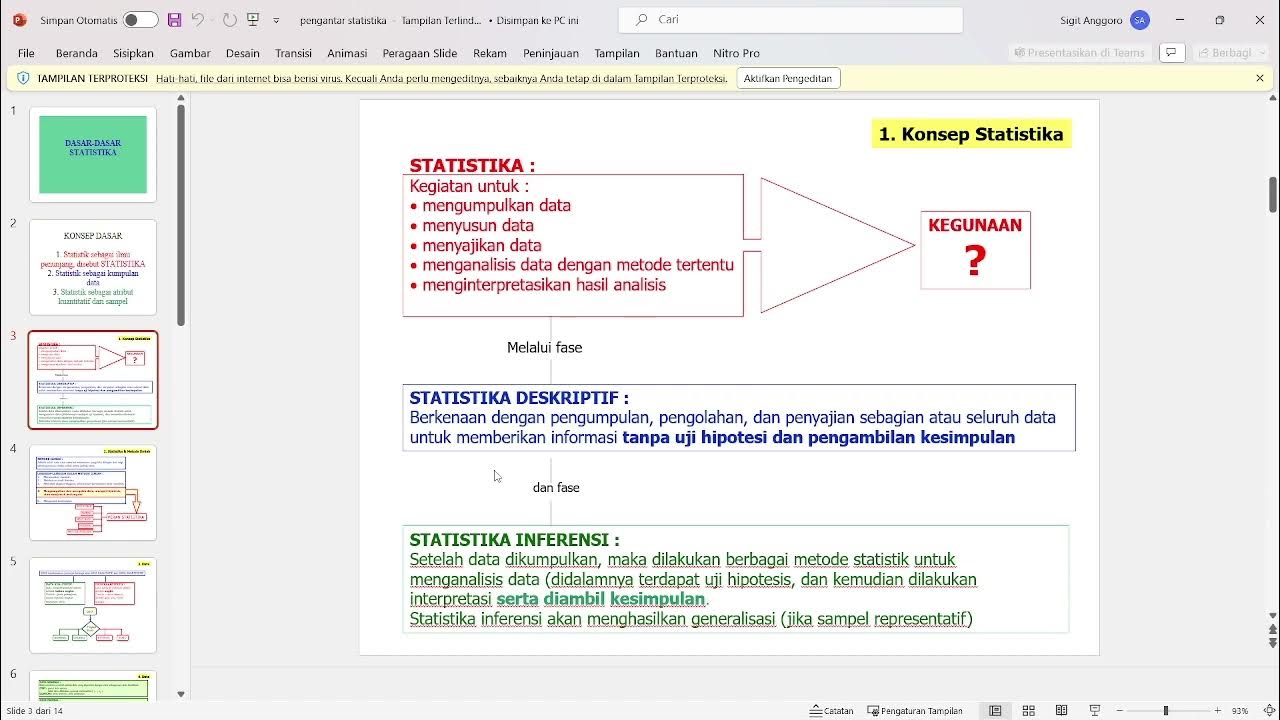
Statisitik ke 3-1

KUPAS TUNTAS: Apakah Perbedaan Statistik Inferensial dengan Statistik Deskriptif ?
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)