Ekonomi Indonesia mulai DEFLASI?
Summary
TLDRThe script discusses the post-COVID imbalance between supply and demand, attributing it to the 'Bullwhip Effect', a phenomenon causing significant fluctuations in supply chain management. It narrates the impact of the pandemic on global economies, particularly the U.S. and China, detailing the economic measures taken to combat the crisis. The speaker also expresses concerns about potential deflation in China and its ripple effects on Indonesia, urging the government to be vigilant and prioritize self-sufficiency, export performance, and a conducive business environment.
Takeaways
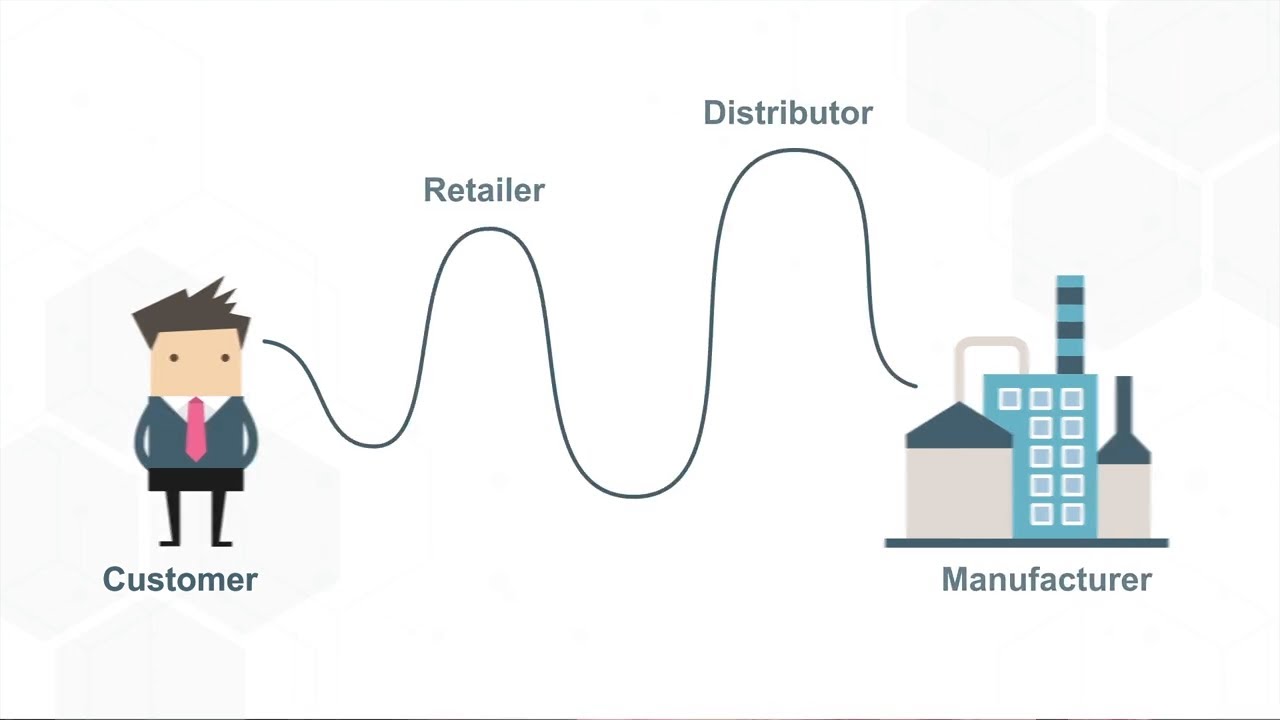
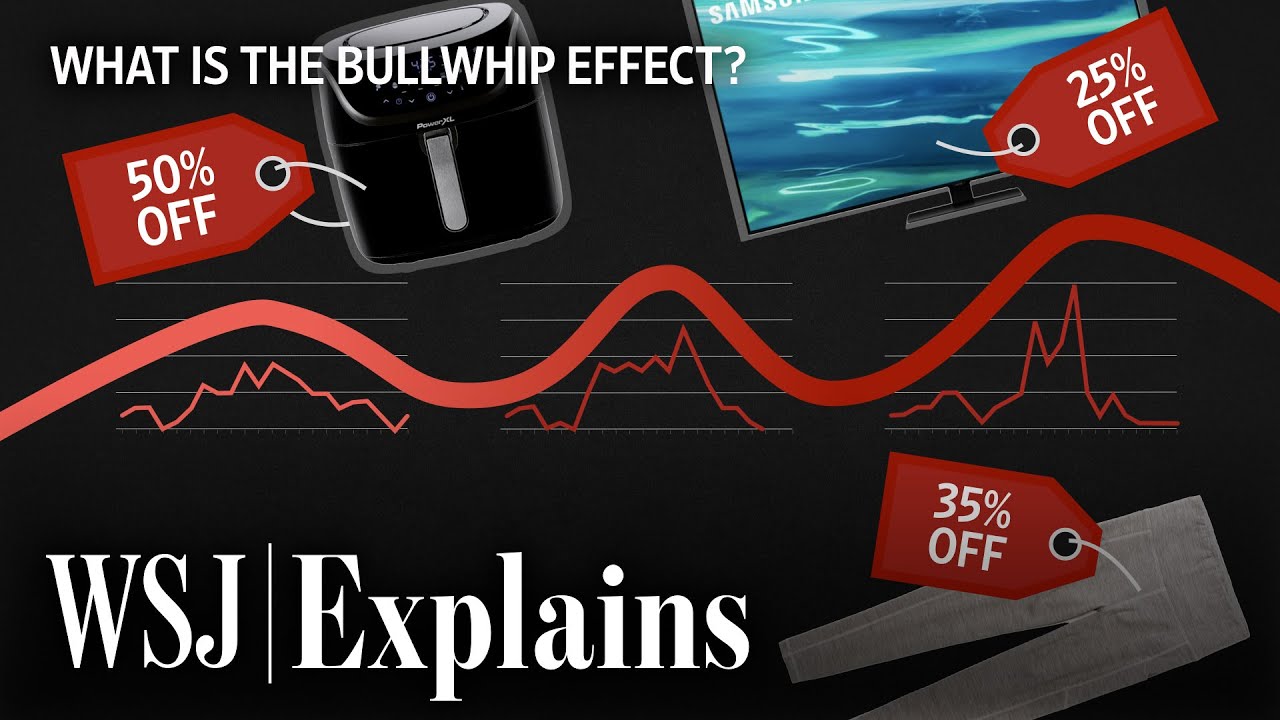
- 📈 The current economic imbalance is primarily due to the Bullwhip Effect, a phenomenon where small fluctuations in consumer demand lead to significant changes upstream in a supply chain.
- 🏫 The concept of the Bullwhip Effect was introduced by Prof. Jay Wright Forrester, a legendary figure known for his contributions to computer systems, engineering, and management science, particularly in the field of supply chain management.
- 🎲 The Beard Distribution Game, created by Prof. Forrester, is a tradition at MIT and illustrates the Bullwhip Effect, showing how demand variability can amplify as it moves up the supply chain.
- 🌐 The script uses the story of a small store in a town called Konoha to explain how a sudden increase in demand can lead to overproduction and overstock, eventually resulting in economic inefficiencies.
- 🔄 The COVID-19 pandemic led to a simultaneous collapse in both supply and demand, causing a global economic freeze, which was addressed by governments through measures like quantitative easing to prevent a complete economic collapse.
- 💵 The U.S. government, under the Trump administration, worked to maintain aggregate demand by injecting money into the economy through the purchase of government bonds, ensuring that people could continue to spend on necessities.
- 📉 The post-pandemic period has seen a recovery in aggregate demand, leading to a resurgence in production and a global Bullwhip Effect as factories, which were previously shut down, ramp up production to meet increased demand.
- 📈 China, being the world's largest manufacturer, faced a surge in demand for its products post-lockdown, which, coupled with its strict zero-COVID policy, created significant supply chain challenges.
- 📉 Inflation in the U.S. and China has been a concern, with China's producer price index (PPI) experiencing deflation in 2023, indicating a decrease in the price level at the producer level.
- 🌍 The script highlights the interconnectedness of global economies, with China's economic policies and conditions having a ripple effect on other countries, including the potential for deflation to spread.
- 📊 The speaker emphasizes the importance of government awareness and preparedness in managing economic policies, especially in increasing self-sufficiency in food, improving export performance, and creating a more conducive business environment.
Q & A
What is the main concept discussed in the video script related to the current economic situation?
-The main concept discussed is the imbalance between aggregate supply and demand, which is attributed to the 'Bullwhip Effect' or 'Forrester Effect', a phenomenon in supply chain management where small fluctuations in consumer demand lead to significant changes in production orders.
What is the 'Bullwhip Effect' and how does it relate to the post-COVID economic scenario?
-The 'Bullwhip Effect' is a phenomenon where small changes in customer demand result in larger changes upstream in the supply chain. In the context of the post-COVID economic scenario, it refers to the global imbalance caused by sudden shifts in demand and supply due to lockdowns and subsequent economic policies, leading to overproduction and overstocking issues.
What is the Beard Distribution Game mentioned in the script?
-The Beard Distribution Game is a tradition at MIT Sloan School of Management, created by Professor Jay Wright Forrester. It is a simulation game designed to illustrate the dynamics of supply chain management and the 'Bullwhip Effect'.
How did the COVID-19 pandemic initially affect the global economy according to the script?
-The COVID-19 pandemic led to a global lockdown, causing a simultaneous collapse in both aggregate demand and supply. This resulted in a 'freeze' of the economy, a surge in unemployment, and fears of a depression worse than the Great American Depression of 1929.
What measures did the U.S. government take to prevent an economic collapse during the pandemic?
-The U.S. government, under the Trump administration, worked to prevent an economic collapse by increasing the money supply through the purchase of government bonds, distributing funds to citizens to maintain consumption, and supporting businesses to keep the aggregate demand from collapsing.
What is the connection between the 'Bullwhip Effect' and the economic activities after the COVID-19 pandemic?
-The 'Bullwhip Effect' is connected to post-pandemic economic activities as the sudden increase in demand for goods and services after the lockdowns led to overproduction and overstocking in the supply chain, similar to the effect described in the theory.
What was the impact of China's Zero COVID Policy on the global supply chain?
-China's Zero COVID Policy resulted in many factories remaining in lockdown, contributing to a global supply chain disruption. This caused a surge in demand for products from China, which was unable to meet the demand due to production limitations, leading to further imbalances in the global economy.
How did the U.S. Federal Reserve respond to the inflationary pressures in 2021?
-The U.S. Federal Reserve responded to inflationary pressures by implementing aggressive interest rate hikes, known as 'front loading', to quickly raise rates and then gradually increase them to reduce aggregate demand and combat inflation.
What is the significance of the Beard Distribution Game in understanding the 'Bullwhip Effect'?
-The Beard Distribution Game is significant as it provides a practical, interactive way to understand the 'Bullwhip Effect' by simulating the dynamics of supply and demand, and the resulting impact on inventory management in a supply chain.
What are the potential consequences of China's deflation for other countries, as mentioned in the script?
-The potential consequences of China's deflation for other countries include increased competition from cheap Chinese products, which could harm local industries and potentially lead to job losses and a decrease in aggregate demand, further exacerbating the deflationary spiral.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahora5.0 / 5 (0 votes)