SOLVING QUADRATIC EQUATIONS BY COMPLETING THE SQUARE || GRADE 9 MATHEMATICS Q1
Summary
TLDRThis educational video script focuses on the process of expressing square of trinomials as square of binomials and solving quadratic equations by completing the square. It provides step-by-step examples, including converting non-perfect square trinomials into perfect squares and solving the resulting equations by extracting square roots. The script illustrates various examples, demonstrating how to manipulate algebraic expressions to find the values of x in different quadratic equations.
Takeaways
- 📚 The video explains how to express the square of trinomials as the square of binomials.
- 🔍 It demonstrates solving quadratic equations by completing the square, a method involving adding the square of half the coefficient of 'x' to form a perfect square trinomial.
- 📐 The process involves transforming an equation like 'x^2 + bx' into a perfect square trinomial '(x + b/2)^2'.
- 📘 Examples are provided, such as transforming 'x^2 - 8x + 16' into '(x - 4)^2' and 'x^2 + 3x' into '(x + 3/2)^2'.
- 📙 The video also covers converting perfect square trinomials back into the square of binomials, as shown with 'x^2 + 4x + 4' becoming '(x + 2)^2'.
- 📒 The method is applied to solve quadratic equations, such as 'x^2 + 10x = 3', by creating a perfect square trinomial and then isolating it.
- 📕 After forming the perfect square trinomial, the equation is balanced by adding the constant term to both sides, allowing for the extraction of square roots.
- 📗 The video provides step-by-step solutions for equations, including how to handle non-perfect square roots, like in the equation 'x^2 - 3x = 1'.
- 📖 It explains how to simplify the final answer by combining like terms and rationalizing denominators when necessary.
- 📔 The process is illustrated with multiple examples, each showing a different approach to solving quadratic equations by completing the square.
- 📓 The video concludes with a challenging example, '2x^2 - 3x - 9 = 0', which is solved by adjusting the equation, forming a perfect square trinomial, and then extracting the square root.
Q & A
What is the process of completing the square for a quadratic expression?
-Completing the square involves taking a quadratic expression of the form x^2 + bx and adding the square of half the coefficient of x to make it a perfect square trinomial, which is then expressed as (x + b/2)^2.
How do you express a perfect square trinomial as a square of a binomial?
-To express a perfect square trinomial as a square of a binomial, you take the square root of the constant term and add it to x, if the middle term is positive, or subtract it from x, if the middle term is negative, resulting in (x ± √constant term)^2.
What is the first step in solving a quadratic equation by completing the square?
-The first step is to ensure the quadratic equation is in the form x^2 + bx = c, then add the square of half the coefficient of x to both sides of the equation to form a perfect square trinomial.
How do you find the value of 'b' in the context of completing the square?
-The value of 'b' is half the coefficient of the x term in the quadratic expression. For example, if the expression is x^2 - 8x, then b = -8/2 = -4.
What is the purpose of adding and subtracting the same value in the process of completing the square?
-Adding and subtracting the same value helps to create a perfect square trinomial on one side of the equation without changing the equation's balance, which is essential for solving the quadratic equation.
Can you provide an example of a quadratic equation solved by completing the square?
-An example is the equation x^2 - 8x = 16. By completing the square, it becomes x^2 - 8x + 16 = 16 + 16, which simplifies to (x - 4)^2 = 32, and then solving for x gives x = 4 ± √32.
What is the significance of the term 'perfect square trinomial' in the context of completing the square?
-A perfect square trinomial is an expression of the form x^2 + 2bx + b^2, which is the square of the binomial (x + b). It is significant because it allows the quadratic expression to be rewritten in a simpler, squared form that can be easily solved.
How do you determine if a quadratic expression can be expressed as a perfect square trinomial?
-A quadratic expression can be expressed as a perfect square trinomial if the coefficient of the x term is an even number, and the constant term is the square of half the coefficient of the x term.
What is the final step in solving a quadratic equation by completing the square?
-The final step is to take the square root of both sides of the equation to solve for x, which results in x = ±√(c + square of half the coefficient of x).
Can the method of completing the square be used for any quadratic equation?
-The method of completing the square can be used for any quadratic equation, but it is most effective when the quadratic does not factor easily or when the coefficient of the x^2 term is 1.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen

2. Ecuaciones cuadráticas completas, solución por el Método de completar el binomio
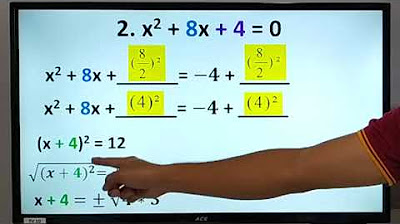
Math8 1G LV4 - Completing the Square and Quadratic Formula

Persamaan Kuadrat Kelas 10 Kurikulum Merdeka

How to Solve Quadratic Equations by Completing the Square? Grade 9 Math

How to Solve Quadratic Equations by Extracting the Square Root? @MathTeacherGon

Solving Quadratic Equations
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
