Sifat Koligatif Larutan -Kimia SMA kelas 12 semester 1
Summary
TLDRThis video tutorial explains the concept of colligative properties of solutions, particularly focusing on their significance in various real-life scenarios, like boiling water and the use of saline infusions in medicine. It covers key topics such as vapor pressure lowering, boiling point elevation, freezing point depression, and osmotic pressure. Additionally, it introduces essential concepts like mol fraction and molality, providing formulas for calculations. The video also includes practical examples, such as the calculation of boiling point elevation in a glucose solution, making the material accessible for students in their chemistry studies.
Takeaways
- 😀 The video introduces the topic of colligative properties of solutions, which are taught in 12th-grade chemistry.
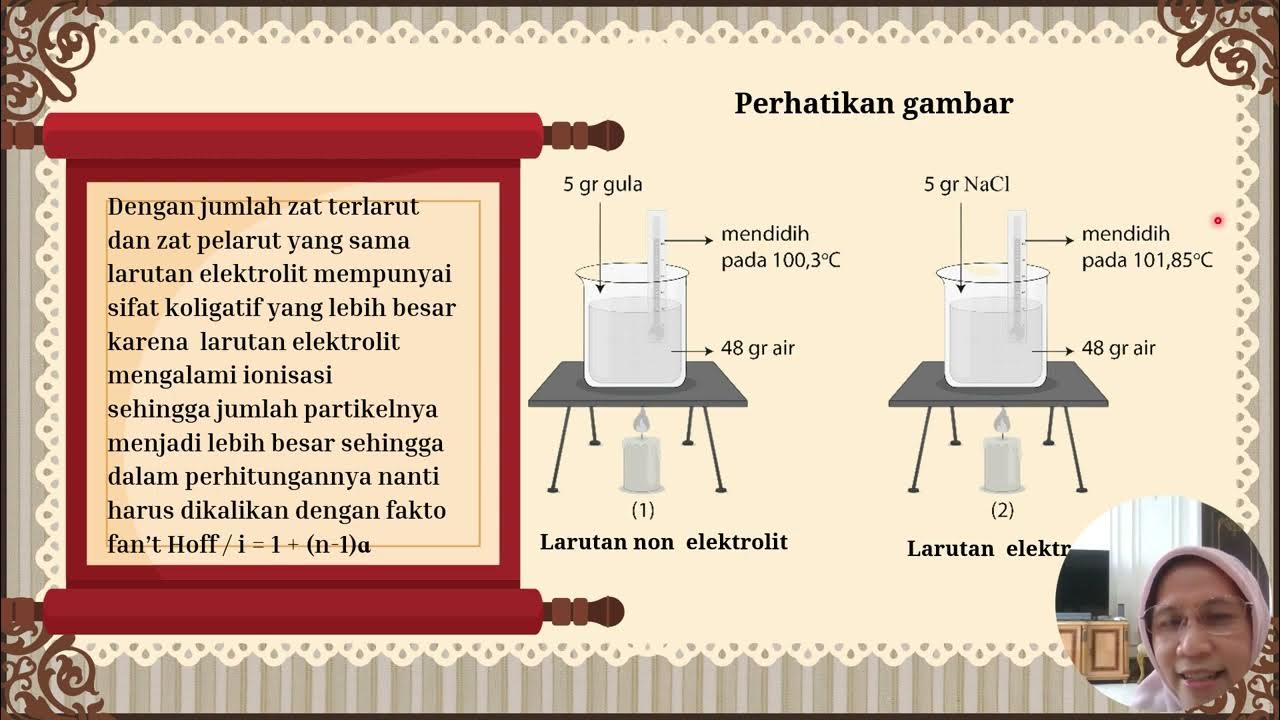
- 😀 Colligative properties depend on the number of particles in a solution, not the type of solute.
- 😀 When sugar is added to boiling water, the bubbles (vapor pressure) decrease due to a phenomenon called vapor pressure lowering.
- 😀 Infusion solutions must be isotonic with the body fluids to avoid harmful effects like cell shrinkage (hypertonic) or cell rupture (hypotonic).
- 😀 Mol fraction and molality are essential concepts for understanding colligative properties. Mol fraction represents the ratio of the number of moles of solute or solvent to total moles.
- 😀 Molality (m) is different from molarity and is calculated using the mass of the solute and the mass of the solvent.
- 😀 The four types of colligative properties are: vapor pressure lowering, boiling point elevation, freezing point depression, and osmotic pressure.
- 😀 Boiling point elevation occurs when a solute is added to a solvent, causing the boiling point of the solution to rise compared to the pure solvent.
- 😀 Freezing point depression occurs when the freezing point of a solution is lower than the pure solvent due to the presence of solute particles.
- 😀 Osmotic pressure is the pressure exerted by a solution to prevent the flow of solvent, and it is influenced by the number of dissolved particles in the solution.
Q & A
What is the definition of colligative properties of solutions?
-Colligative properties of solutions are properties that depend on the number of solute particles in a solution, rather than the type of solute particles.
What is the effect of adding sugar to boiling water?
-When sugar is added to boiling water, the bubbles formed by boiling water decrease or disappear. This happens because the sugar reduces the vapor pressure of the water, which is an example of a colligative property called vapor pressure lowering.
What is the relationship between infusions and colligative properties?
-Infusions must be isotonic with the body’s fluids. If the osmotic pressure of the infusion is different from the body’s fluids, it can lead to either cell shrinkage (hypertonic) or cell rupture (hypotonic), both of which are undesirable effects.
What is molar fraction and how is it calculated?
-Molar fraction (represented as x) is the ratio of the amount of a substance (solute or solvent) to the total amount of substances in a solution. For solute, it’s the ratio of moles of solute to total moles (solute + solvent). For solvent, it’s the ratio of moles of solvent to the total moles.
How does molality differ from molarity?
-Molality (symbolized as m) is a measure of the amount of solute in a given mass of solvent. It is calculated as the number of moles of solute divided by the mass of the solvent in kilograms. Molarity, on the other hand, is the number of moles of solute per liter of solution.
What is vapor pressure lowering?
-Vapor pressure lowering occurs when a non-volatile solute is added to a solvent, reducing the solvent's vapor pressure. This is a colligative property, which depends on the number of solute particles.
How is boiling point elevation calculated?
-Boiling point elevation (ΔTb) can be calculated using the formula ΔTb = m × Kb, where m is the molality of the solution, and Kb is the ebullioscopic constant of the solvent.
What is freezing point depression?
-Freezing point depression (ΔTf) is the lowering of the freezing point of a solvent when a non-volatile solute is added. It can be calculated using the formula ΔTf = m × Kf, where m is the molality of the solution and Kf is the cryoscopic constant of the solvent.
What is osmotic pressure and how is it calculated?
-Osmotic pressure is the pressure exerted by a solution to stop osmosis. It can be calculated using the formula π = M × R × T, where M is the molarity of the solution, R is the gas constant, and T is the temperature in Kelvin.
What is Van't Hoff factor and how does it affect colligative properties?
-The Van't Hoff factor (i) is used for electrolyte solutions and represents the number of particles into which a solute dissociates in solution. It affects colligative properties by modifying the number of particles that contribute to the solution's properties, such as osmotic pressure and boiling point elevation.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)