13.2 Colligative Properties of Solutions (1/2)
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the concept of colligative properties of solutions, which depend on the concentration of solute, not the type of solute itself. It covers the lowering of vapor pressure, freezing point depression, and boiling point elevation. The video illustrates how solute presence reduces vapor pressure, lowers the freezing point, and raises the boiling point of a solution. Practical examples are provided, including how to calculate changes in freezing and boiling points using constants like Kf and Kb. The importance of molality in these calculations is emphasized for better understanding of colligative properties.
Takeaways
- 😀 Colligative properties depend on the concentration of solute, not the type of solute.
- 😀 Vapor pressure is lowered when solute is added to a solvent, as fewer solvent molecules can escape into the gas phase.
- 😀 Colligative properties, including vapor pressure lowering, apply to all solutions, such as saltwater and sugar solutions.
- 😀 The vapor pressure of a solution is always lower than that of the pure solvent, like water in a saltwater solution.
- 😀 The lowering of vapor pressure is the same for different solutes (e.g., sucrose and glucose) as long as the molality is the same.
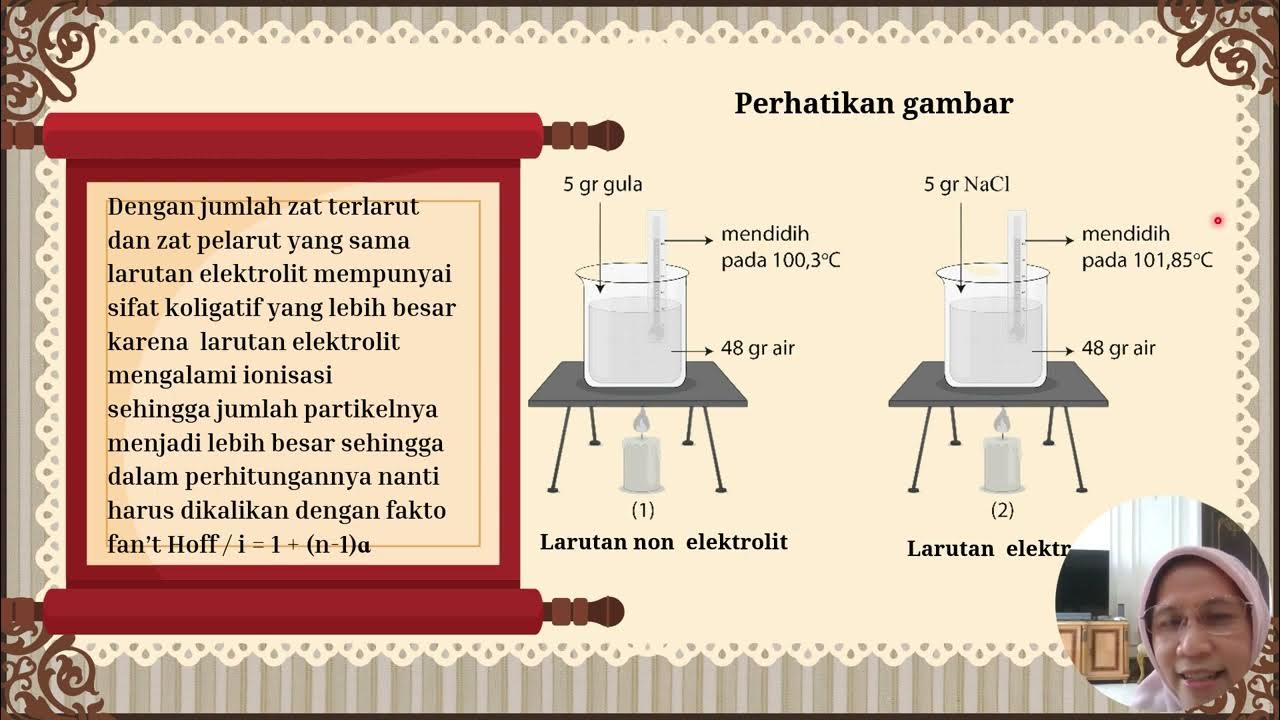
- 😀 Freezing point depression occurs when a solute is added to a solvent, with the freezing point dropping by 1.86°C per mole of solute per kilogram of solvent.
- 😀 For non-electrolyte solutes, such as sucrose, one mole results in a 1.86°C decrease in freezing point.
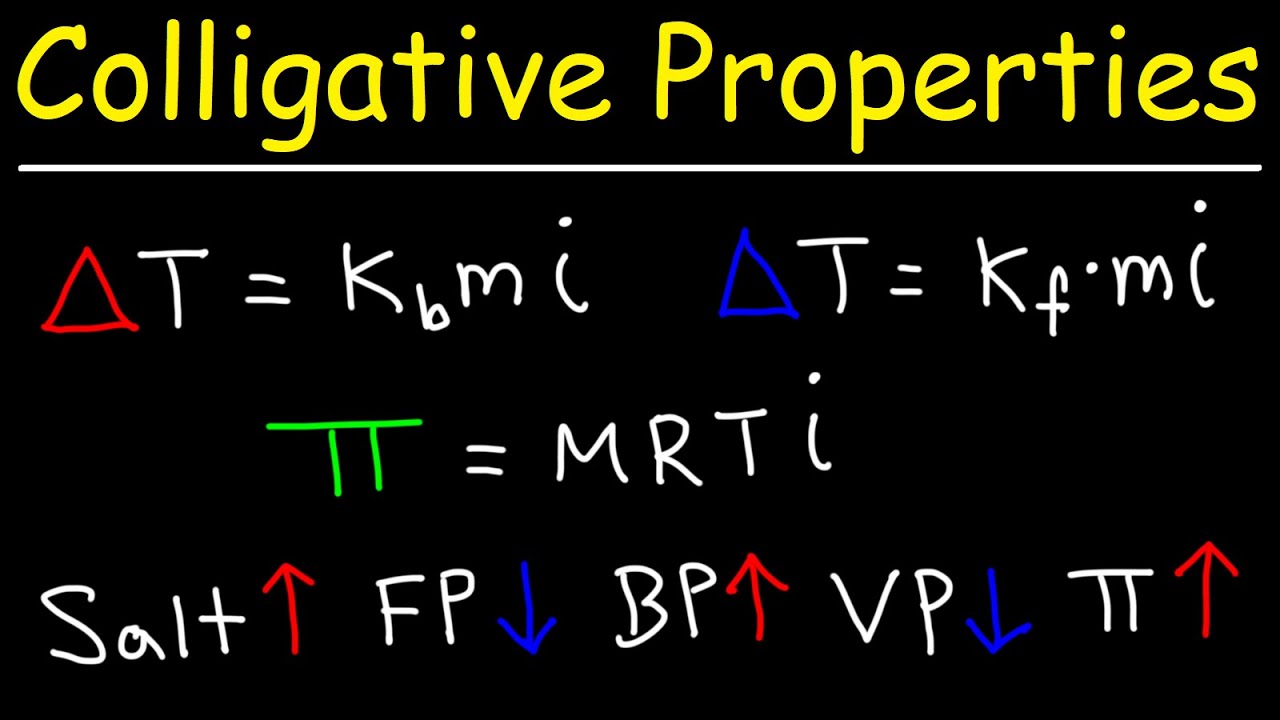
- 😀 The formula to calculate freezing point depression is ΔT = Kf × molality, where Kf is the freezing point constant.
- 😀 To calculate the change in freezing point, the molality of a solution must be determined by dividing moles of solute by kilograms of solvent.
- 😀 Boiling point elevation occurs when solute is added to a solvent, requiring more thermal energy to match atmospheric pressure, raising the boiling point by 0.51°C per mole of solute per kilogram of solvent.
Q & A
What are colligative properties of solutions?
-Colligative properties are properties of a solution that depend on the concentration of solute, usually expressed in molality (moles per kilogram of solvent), and not on the nature of the solute itself.
What is molality?
-Molality is defined as the number of moles of solute per kilogram of solvent. It is used to express the concentration of a solution.
How do colligative properties differ based on the solute?
-Colligative properties do not depend on the type of solute. Whether the solute is salt, sugar, or glucose, its concentration (molality) determines the effect on the solution's properties like vapor pressure, freezing point, and boiling point.
What causes the lowering of vapor pressure in a solution?
-The addition of solute to a solvent reduces the surface area available for solvent molecules to evaporate, leading to fewer solvent molecules in the gas phase. As a result, the vapor pressure of the solution is lower than that of the pure solvent.
Why does the presence of solute lower the vapor pressure?
-Because solute molecules occupy space at the surface of the liquid, preventing solvent molecules from escaping into the gas phase. Since fewer solvent molecules can vaporize, the vapor pressure decreases.
What is freezing point depression?
-Freezing point depression refers to the lowering of the freezing point of a solvent when a solute is added. This effect is proportional to the molality of the solution.
How is the freezing point depression calculated?
-Freezing point depression is calculated by multiplying the molality of the solution by the freezing point depression constant (kf). The formula is: change in temperature = kf × molality.
How does adding solute affect the boiling point of a solution?
-Adding solute to a solvent raises the boiling point of the solution. This is because the solute reduces the vapor pressure of the solvent, requiring more heat (thermal energy) to reach the boiling point.
What is the boiling point elevation constant?
-The boiling point elevation constant (kb) is a proportionality constant that relates the change in boiling point to the molality of the solution. For water, the constant is 0.51 °C·kg/mol.
How do you calculate the change in boiling point?
-To calculate the change in boiling point, multiply the molality of the solution by the boiling point elevation constant (kb). The formula is: change in temperature = kb × molality.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

SIFAT KOLIGATIF LARUTAN : PENURUNAN TEKANAN UAP
Sifat Koligatif 2Penurunan Tekanan Uap
Colligative Properties - Boiling Point Elevation, Freezing Point Depression & Osmotic Pressure

ruangbelajar - Kimia XII SMA - Pendahuluan Sifat Koligatif

SIFAT KOLIGATIF LARUTAN - KIMIA - MATERI UTBK SBMPTN DAN SIMAK UI

3 1 1 Penurunan Tekanan Uap, XII MIPA
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)