How To Solve The Wheatstone Bridge Circuit
Summary
TLDRThis script explains the Wheatstone bridge circuit, a tool for measuring low resistance values. It demonstrates how to calculate unknown resistor values when the bridge is balanced, using the principle that the potential at two points must be equal. The script also covers how to calculate the voltage reading of a voltmeter in an unbalanced circuit, highlighting the importance of understanding circuit balance and using voltage divider formulas to find the potential at specific points, ultimately determining the voltmeter's reading.
Takeaways
- 🔍 The video discusses solving problems related to Wheatstone Bridge circuits, which are used for measuring low resistance values.
- 🌐 When the ammeter shows zero amps, it indicates a balanced Wheatstone Bridge, where the potential at points C and D are the same.
- ⚖️ The balance condition in a Wheatstone Bridge implies that the resistors on the left are proportional to those on the right.
- 📐 The missing resistor value (X) can be calculated by multiplying one of the known resistors by a factor derived from the other resistors' values.
- 🔧 Ohm's Law is used to relate the voltage across resistors to the current flowing through them in the circuit.
- 🔄 The voltage across resistors in parallel (such as R2 and RX) is the same, which is a key point in calculating the unknown resistor value.
- 📉 The script provides a formula to find the unknown resistor value by rearranging the voltage ratio across known resistors.
- 📚 The script includes a practice problem to reinforce the concept of calculating the missing resistor in a Wheatstone Bridge.
- 🔌 The video also covers how to calculate the voltage reading of a voltmeter in an unbalanced Wheatstone Bridge circuit.
- 🔋 A voltmeter is considered to have a very high resistance, effectively disconnecting the points it measures from the rest of the circuit.
- ⚡ The voltage across a resistor in a voltage divider can be calculated using the formula involving the resistor's value and the source voltage.
- 📉 The script explains how to determine the potential at different points in the circuit to find the voltmeter's reading, especially in an unbalanced condition.
Q & A
What is a Wheatstone bridge and why is it used?
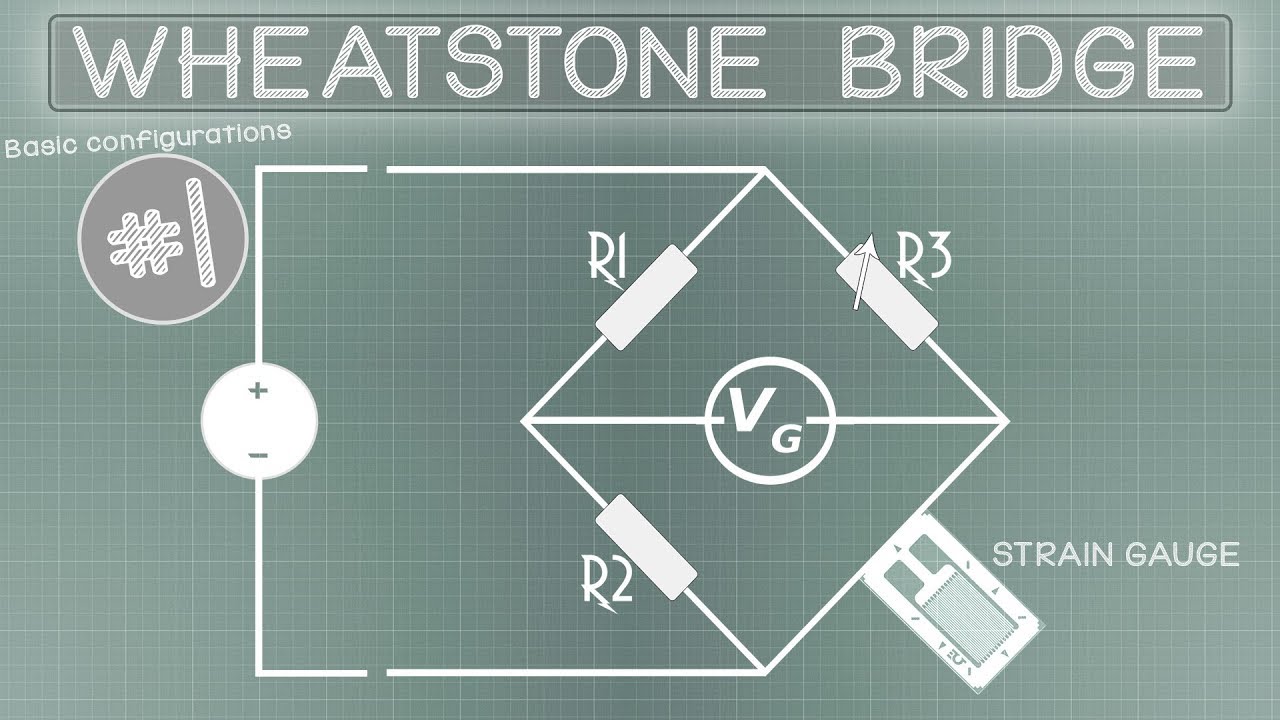
-A Wheatstone bridge is a circuit used to measure electrical resistance or to divide a voltage by using a balanced ratio of resistors. It is particularly useful for measuring very low values of resistance with precision.
How can you determine if a Wheatstone bridge is balanced?
-A Wheatstone bridge is balanced when the potential at two specific points (commonly referred to as points C and D in the script) is the same, resulting in no current flowing through the ammeter placed in the bridge circuit.
What is the significance of the current through the ammeter being zero amps in the context of the Wheatstone bridge?
-When the current through the ammeter is zero amps, it indicates that the Wheatstone bridge is balanced, meaning the resistors on either side of the bridge are in the correct proportion to each other.
How does the script calculate the missing resistor value (Rx) in a balanced Wheatstone bridge?
-The script calculates the missing resistor value (Rx) by using the proportion of the known resistors. Since R1 to R3 is in a 1:2 ratio, R2 to Rx should also be in a 1:2 ratio, leading to the calculation Rx = (R2 * 2) / R1.
What is Ohm's law and how is it applied in the script?
-Ohm's law states that the voltage across a resistor is equal to the current through it times the resistance (V = I * R). In the script, it is used to establish that the voltage across resistors R1 and R3 (or R2 and Rx) is the same when the current through them is the same.
How does the script confirm the calculated value of Rx using a formula?
-The script confirms the calculated value of Rx by using the formula derived from the voltage ratios across the resistors, which is Rx = (R2 / R1) * R3.
What is a voltage divider and how is it related to the Wheatstone bridge in the script?
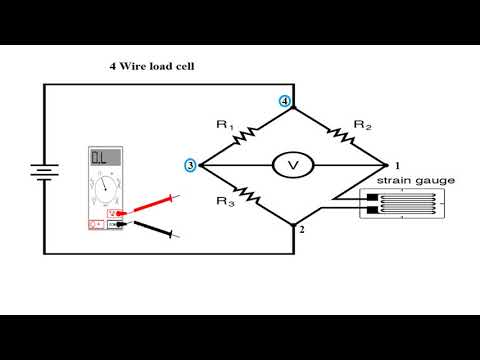
-A voltage divider is a passive linear circuit that produces an output voltage proportional to an input voltage. In the script, the voltage divider concept is used to calculate the potential at points C and D in an unbalanced Wheatstone bridge circuit.
How does the script determine if the Wheatstone bridge circuit is balanced or unbalanced?
-The script determines the balance by comparing the ratios of the resistors. If the ratio of R1 to R2 is not the same as the ratio of R3 to R4, the circuit is unbalanced.
What is the formula used to calculate the voltage across a resistor in a voltage divider?
-The formula used to calculate the voltage across a resistor (Vr) in a voltage divider is Vr = (Resistor value) / (Sum of resistor values) * Source voltage.
How does the script calculate the voltage reading of the voltmeter in an unbalanced Wheatstone bridge circuit?
-The script calculates the voltage reading by determining the potential difference between points C and D, which are calculated using the voltage divider formula for the respective branches of the unbalanced bridge.
What is the final voltage reading that the voltmeter would show in the example given in the script?
-The final voltage reading that the voltmeter would show is 8 volts, which is the potential difference between points C (36 volts) and D (28 volts).
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآن5.0 / 5 (0 votes)