Basic configurations #1 - Wheatstone bridge
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the creator explains the basics of the Wheatstone Bridge, a common circuit used to measure small resistance changes. The Wheatstone Bridge consists of four resistors arranged in a diamond shape, where three values are known, and the fourth is variable. When the circuit is balanced, the voltage between two points is zero. This configuration is ideal for sensor applications, such as strain gauges, light-dependent resistors, or thermistors, as it separates the effects of temperature changes. The video demonstrates this concept through a practical example with a breadboard setup, showcasing its use in measuring temperature and other variables.
Takeaways
- 😀 The Wheatstone Bridge is a simple circuit used to measure resistance changes, often applied in sensor technology.
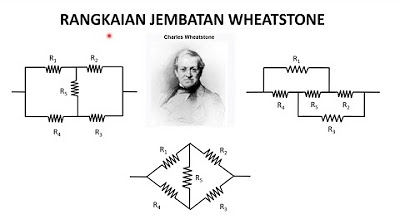
- 😀 It consists of four resistors arranged in a diamond configuration, with three resistors known and one unknown.
- 😀 The voltage difference between points C and D in the Wheatstone Bridge helps detect small changes in resistance.
- 😀 The formula for voltage dividers in the Wheatstone Bridge helps calculate the voltages at points C and D.
- 😀 A balanced bridge occurs when the voltage difference between points C and D equals zero, allowing accurate resistance measurement.
- 😀 By adjusting the value of the known resistors (R1 and R2) and measuring changes in R3, the unknown resistance (Rx) can be calculated.
- 😀 The Wheatstone Bridge is especially useful for measuring small resistance changes, such as those from strain gauges.
- 😀 Strain gauges detect changes in resistance when force is applied, and the Wheatstone Bridge helps measure these small changes with high accuracy.
- 😀 The Wheatstone Bridge setup also compensates for environmental factors like temperature, which would otherwise affect the accuracy of sensor readings.
- 😀 The Wheatstone Bridge can be used with different sensors such as strain gauges, thermistors, or light-dependent resistors (LDRs) to measure force, temperature, or light.
- 😀 The output voltage from the Wheatstone Bridge is proportional to the resistance change, which can be used for precise measurements in various applications.
Q & A
What is the main purpose of a Wheatstone bridge?
-The main purpose of a Wheatstone bridge is to measure small resistance changes by converting these changes into measurable voltage changes, often used in sensor applications.
How does the Wheatstone bridge work?
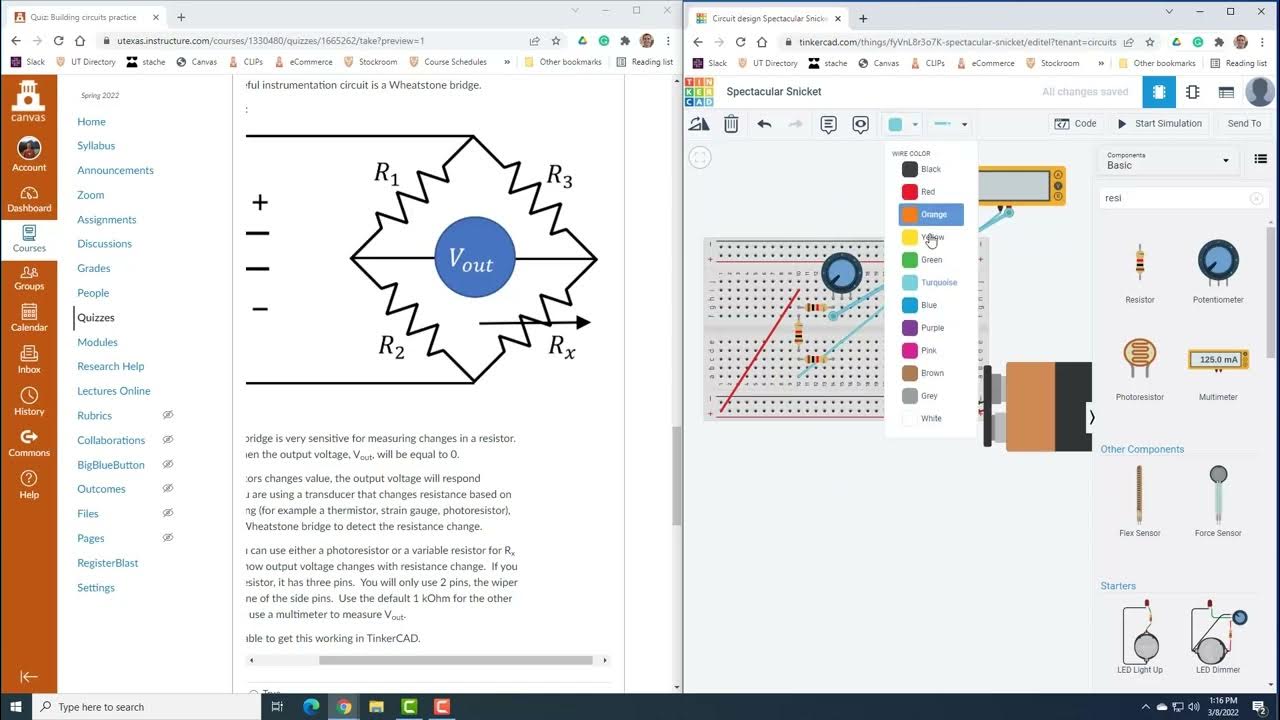
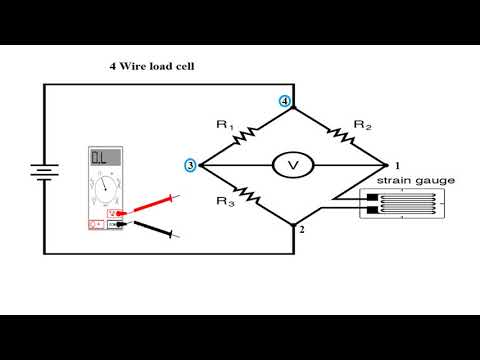
-The Wheatstone bridge works by using four resistors arranged in a diamond shape. Three resistors have known values, and one is unknown. A supply voltage is applied across points A and B, and the voltage drop between points C and D is measured. The bridge is balanced when the voltage difference between C and D is zero.
Why is the Wheatstone bridge important for sensor applications?
-The Wheatstone bridge is crucial for sensor applications because it can detect very small resistance changes and convert them into measurable voltage changes. This is especially useful for sensors like strain gauges, thermistors, and light-dependent resistors (LDRs).
What does it mean for the Wheatstone bridge to be 'balanced'?
-A balanced Wheatstone bridge occurs when the voltage difference between points C and D is zero. This happens when the resistances in the bridge produce equal voltage dividers, allowing for precise measurement of the unknown resistance.
How is the unknown resistance (RX) calculated in a Wheatstone bridge?
-The unknown resistance RX is calculated using the equation RX = R3 * (R2 / R1), where R1 and R2 are known resistances, and R3 is the variable resistor. By adjusting R3, the bridge is balanced, and RX can be determined.
What happens if the Wheatstone bridge is not balanced?
-If the Wheatstone bridge is not balanced, the voltage drop between points C and D will not be zero, indicating that the resistances are not equal, which prevents accurate measurement of the unknown resistance.
How does temperature affect sensor readings in a Wheatstone bridge?
-Temperature can affect sensor readings by causing changes in the resistance of components like strain gauges. However, by using a Wheatstone bridge, the temperature-induced changes in resistance can affect all resistors in the bridge, thus minimizing their impact on the measurement of the sensor's resistance change due to force or other factors.
Why not just use a voltage divider with sensors instead of a Wheatstone bridge?
-Using a voltage divider with sensors directly can lead to unreliable measurements due to temperature fluctuations affecting the sensor's resistance. The Wheatstone bridge setup helps separate the temperature error from the actual sensor reading, ensuring more accurate measurements.
Can the Wheatstone bridge be used with different types of sensors?
-Yes, the Wheatstone bridge can be used with various types of sensors, such as strain gauges, thermistors, and light-dependent resistors (LDRs), to measure changes in resistance caused by force, temperature, or light.
What was demonstrated in the video as an example of using a Wheatstone bridge?
-The video demonstrates using a Wheatstone bridge with two resistors of 100 kOhms, a variable resistor of 200 kOhms, and a thermistor. The voltage across points C and D is adjusted until the bridge is balanced, and then the thermistor is heated to show how temperature changes the voltage measurement.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)