Lisossomo
Summary
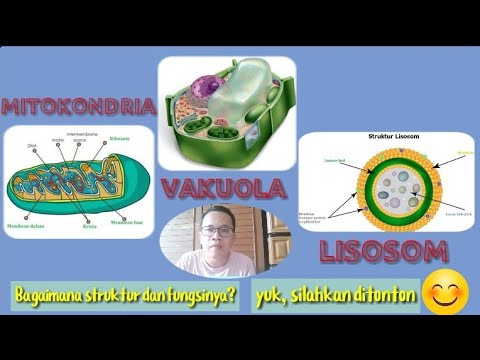
TLDRLysosomes are organelles packed with enzymes that carry out intracellular digestion. Produced in the rough endoplasmic reticulum and packaged in the Golgi complex, they play a key role in breaking down organic matter in unicellular organisms and some animal cells. Unlike animals, plant cells use digestive enzymes from the cellular juice vacuole instead of lysosomes. The enzymes inside lysosomes, called acid hydrolases, break down food molecules in an acidic environment, aiding in digestion with water molecules.
Takeaways
- 😀 Lysosomes are organelles filled with enzymes that perform intracellular digestion.
- 😀 The enzymes in lysosomes are produced in the rough endoplasmic reticulum (ER).
- 😀 Lysosomes are packaged and formed in the Golgi complex.
- 😀 Unicellular organisms, such as protozoa, and specialized cells in animals have lysosomes.
- 😀 Lysosomes allow organisms and cells to capture and digest small organic matter fragments.
- 😀 Fungi and plant cells lack lysosomes and instead perform digestion with digestive enzymes from the cellular juice vacuole.
- 😀 Lysosomal enzymes are known as acid hydrolases due to their acidic environment and their function in breaking down food molecules with water molecules.
- 😀 The interior of lysosomes is acidic, which is essential for their digestion process.
- 😀 The breakdown of food in lysosomes involves the use of water molecules.
- 😀 The video emphasizes that learning biology in 90 seconds helps fit complex concepts into a short, accessible format.
Q & A
What are lysosomes and what is their primary function?
-Lysosomes are organelles filled with enzymes that are responsible for intracellular digestion. Their primary function is to break down and digest cellular waste, organic matter, and foreign invaders.
Where are the enzymes in lysosomes produced?
-The enzymes in lysosomes are produced in the rough endoplasmic reticulum.
How are lysosomes formed?
-Lysosomes are formed when the enzymes produced in the rough endoplasmic reticulum are packaged in the Golgi complex.
Which types of organisms have lysosomes?
-Lysosomes are found in unicellular organisms like protozoa and in some specialized cells of animals.
What role do lysosomes play in unicellular organisms?
-In unicellular organisms, lysosomes capture and digest small fragments of organic matter, helping to break down and process food.
Do fungi and plant cells have lysosomes?
-No, fungi and plant cells do not have lysosomes. Instead, they use digestive enzymes within the cellular vacuole to perform digestion.
What are the enzymes in lysosomes called, and why are they named this way?
-The enzymes in lysosomes are called acid hydrolases because they break down food molecules by adding water molecules in an acidic environment.
Why is the interior of lysosomes acidic?
-The interior of lysosomes is acidic to provide an optimal environment for the acid hydrolases to effectively carry out their digestive functions.
How do lysosomes differ from vacuoles in plant cells?
-Lysosomes are involved in digestion within certain animal and unicellular organisms' cells, while in plant cells, digestion is carried out by digestive enzymes in vacuoles rather than lysosomes.
What is the significance of lysosomes in cellular maintenance?
-Lysosomes play a crucial role in cellular maintenance by digesting damaged organelles, waste materials, and pathogens, helping maintain a clean and functional cell environment.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级5.0 / 5 (0 votes)