The Structure & Function of Lysosomes - A Level Biology
Summary
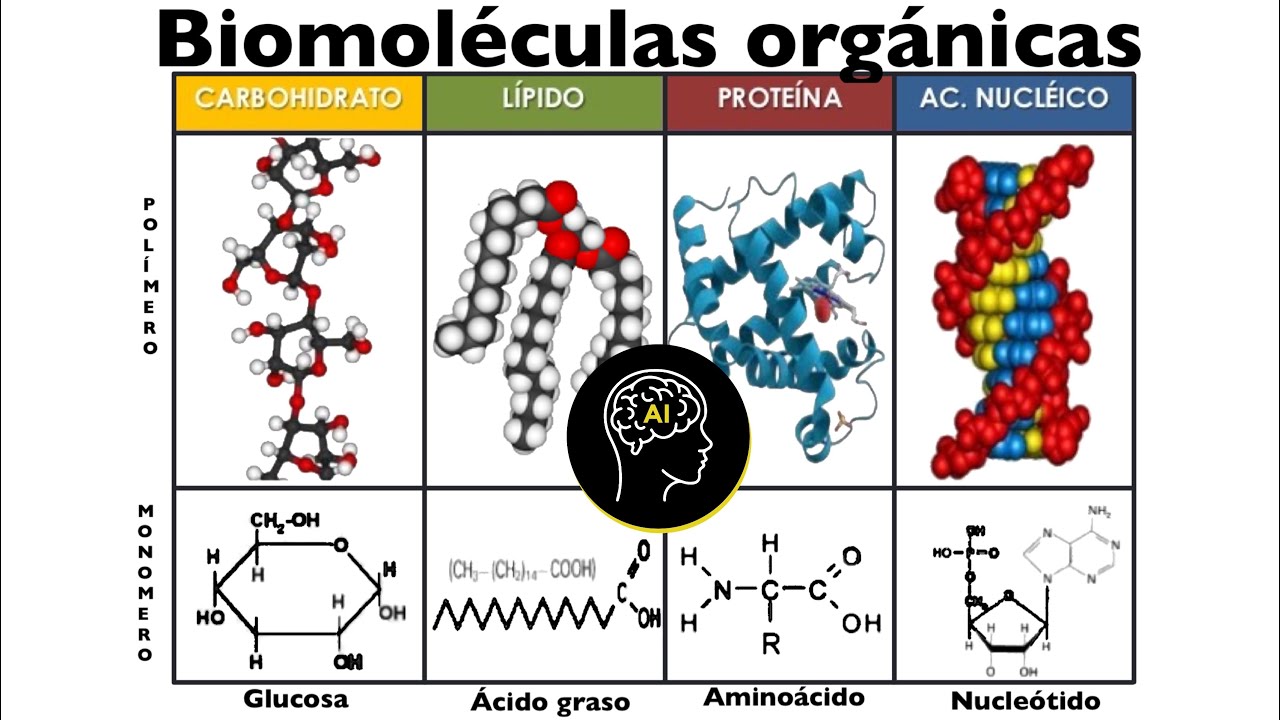
TLDRLysosomes are membrane-bound vesicles containing hydrolytic enzymes that break down proteins, nucleic acids, lipids, and carbohydrates. These enzymes are synthesized in the endoplasmic reticulum and transported to the Golgi apparatus, where the lysosomes are formed. When cells ingest particles like bacteria or viruses via phagocytosis, lysosomes fuse with the phagosome, releasing enzymes to degrade the particles. Lysosomes also help recycle damaged organelles, such as old mitochondria, by breaking them down and aiding in cellular maintenance.
Takeaways
- 😀 Lysosomes are membrane-bound vesicles containing hydrolytic enzymes.
- 😀 Hydrolytic enzymes in lysosomes break down proteins, nucleic acids, lipids, and carbohydrates.
- 😀 Lysosomes are formed in the endoplasmic reticulum.
- 😀 Enzymes are transported to the Golgi apparatus via transport vesicles.
- 😀 Lysosomes originate from the Golgi apparatus.
- 😀 Lysosomes help destroy and recycle cellular components.
- 😀 When viruses or bacteria are ingested by phagocytosis, lysosomes fuse with the phagosomes.
- 😀 Lysosomes deliver hydrolytic enzymes to the phagosomes for degradation of ingested particles.
- 😀 Lysosomes also fuse with organelles such as old mitochondria.
- 😀 The fusion of lysosomes with damaged organelles leads to their destruction and recycling.
Q & A
What are lysosomes?
-Lysosomes are membrane-bound vesicles that contain hydrolytic enzymes responsible for breaking down various biomolecules such as proteins, nucleic acids, lipids, and carbohydrates.
What is the role of hydrolytic enzymes in lysosomes?
-The hydrolytic enzymes in lysosomes degrade biomolecules like proteins, nucleic acids, lipids, and carbohydrates, helping in the breakdown and recycling of cellular components.
Where are lysosomes formed in the cell?
-Lysosomes are formed in the endoplasmic reticulum, and their enzymes are then transported to the Golgi apparatus by transport vesicles.
How do lysosomes get their enzymes?
-Lysosomal enzymes are synthesized in the endoplasmic reticulum and transported to the Golgi apparatus, where they are packaged into vesicles and eventually form lysosomes.
What happens when lysosomes fuse with a phagosome?
-When lysosomes fuse with a phagosome, which contains ingested particles such as viruses or bacteria, the hydrolytic enzymes from the lysosome are delivered to break down and degrade the particles.
What is phagocytosis and how is it related to lysosomes?
-Phagocytosis is the process by which a cell engulfs particles, such as viruses or bacteria. The lysosome then fuses with the vesicle containing the ingested material, releasing its hydrolytic enzymes to degrade the particles.
What other organelles do lysosomes interact with, aside from phagosomes?
-Lysosomes also fuse with organelles like old mitochondria. This fusion leads to the degradation and recycling of these worn-out structures.
Why is the recycling of organelles like mitochondria important?
-The recycling of old organelles, such as mitochondria, ensures that damaged or non-functional components are broken down and their materials are reused, maintaining cellular health.
What is the Golgi apparatus's role in lysosome formation?
-The Golgi apparatus receives enzymes from the endoplasmic reticulum and packages them into vesicles that eventually form lysosomes, which are essential for cellular degradation processes.
How do lysosomes contribute to cellular maintenance?
-Lysosomes contribute to cellular maintenance by breaking down and recycling old or damaged cellular components, which helps maintain proper cell function and health.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)