Understanding Circular Motion
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the concept of circular motion by breaking it down into key elements such as velocity, centripetal force, and centripetal acceleration. Using relatable examples like swinging a ball on a rope and amusement park rides, it clarifies the relationship between force, mass, velocity, and radius. The video also dispels the myth of centrifugal force, emphasizing the real centripetal force that pulls objects toward the center of their circular path. Finally, it explores real-world applications, including gravitational forces in space and friction on curved roads, making the concepts easier to grasp.
Takeaways
- 😀 Circular motion involves an object moving in a circle with its velocity always tangent to the circle at any given point.
- 😀 Velocity in circular motion changes direction continuously, even if its speed remains constant.
- 😀 When velocity changes with respect to time, we say the object is accelerating, and this requires a net force to cause it.
- 😀 The net force causing circular motion is known as centripetal force, which always points towards the center of the circle.
- 😀 The direction of centripetal force changes as the object moves around the circle, but its magnitude remains constant.
- 😀 The angle between the velocity vector and the centripetal force vector is always 90 degrees, defining circular motion.
- 😀 The sensation of being flung outwards in a spinning motion is often confused with centrifugal force, but this is not an actual force.
- 😀 Centripetal force is responsible for keeping an object in circular motion; without it, the object would travel in a straight line.
- 😀 The formula for centripetal force is F_c = (m * v²) / r, where 'm' is mass, 'v' is velocity, and 'r' is the radius of the circle.
- 😀 To increase centripetal acceleration, you can either increase the velocity of the object or reduce the radius of the circle.
- 😀 In real-world examples, such as a car turning on a curved road, friction between the tires and the road provides the centripetal force.
- 😀 Banking roads in corners increases the centripetal force, allowing cars to travel faster without losing grip on the road.
Q & A
What is circular motion?
-Circular motion is the movement of an object along a circular path, where the object continuously changes direction but maintains a constant speed. The direction of the object's velocity is always tangent to the circle at any given point.
What is the relationship between velocity and circular motion?
-In circular motion, velocity is always tangent to the circle at any point. Although the speed of the object can be constant, the velocity is continuously changing because the direction is constantly changing.
Why is an object in circular motion said to be accelerating?
-An object in circular motion is said to be accelerating because its velocity is constantly changing due to the changing direction. Since velocity is a vector, a change in direction means a change in velocity, and therefore acceleration is occurring.
What causes an object to change direction in circular motion?
-The change in direction of an object in circular motion is caused by a net force called centripetal force. This force is always directed toward the center of the circle, constantly pulling the object inward to maintain its circular path.
What is the difference between centripetal force and centrifugal force?
-Centripetal force is the real force that acts towards the center of the circle, causing the object to change direction. Centrifugal force is an apparent force that people feel when they are in a rotating frame of reference; it is not a real force and is a result of inertia pushing the object outward.
What happens if the centripetal force disappears?
-If the centripetal force disappears, the object will no longer experience an inward force and will continue moving in a straight line along the tangent of its circular path, as per Newton's First Law of motion.
How does the angle between velocity and force in circular motion affect the motion?
-In circular motion, the angle between the velocity vector and the centripetal force vector is always 90 degrees. This perpendicular relationship ensures that the force does not change the object's speed but only its direction.
What is the formula for centripetal force, and what does it depend on?
-The formula for centripetal force (Fc) is Fc = (mv^2) / r, where m is the mass of the object, v is the velocity, and r is the radius of the circle. The force increases as the velocity or the inverse of the radius increases.
How does increasing velocity or decreasing radius affect centripetal force?
-Increasing the velocity of an object or decreasing the radius of its circular path increases the centripetal force required to keep the object moving in a circle. This is because centripetal force is directly proportional to the square of velocity and inversely proportional to the radius.
Why do roads curve in circular paths and what role does friction play?
-Roads curve in circular paths to allow vehicles to follow a curved path. The friction between the road surface and the car tires provides the centripetal force that enables the car to turn. Without friction, the car would not be able to turn and would slide straight off the road.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频

Me Salva! CIN11 - MCU

FISIKA KELAS X | GERAK MELINGKAR (PART 1) - Besaran-besaran dalam Gerak Melingkar

Quipper Video - Fisika - Gerak Melingkar Beraturan - Kelas 10

FISIKA Kelas 10 - Gerak Melingkar | GIA Academy

Video Animasi Gerak Melingkar
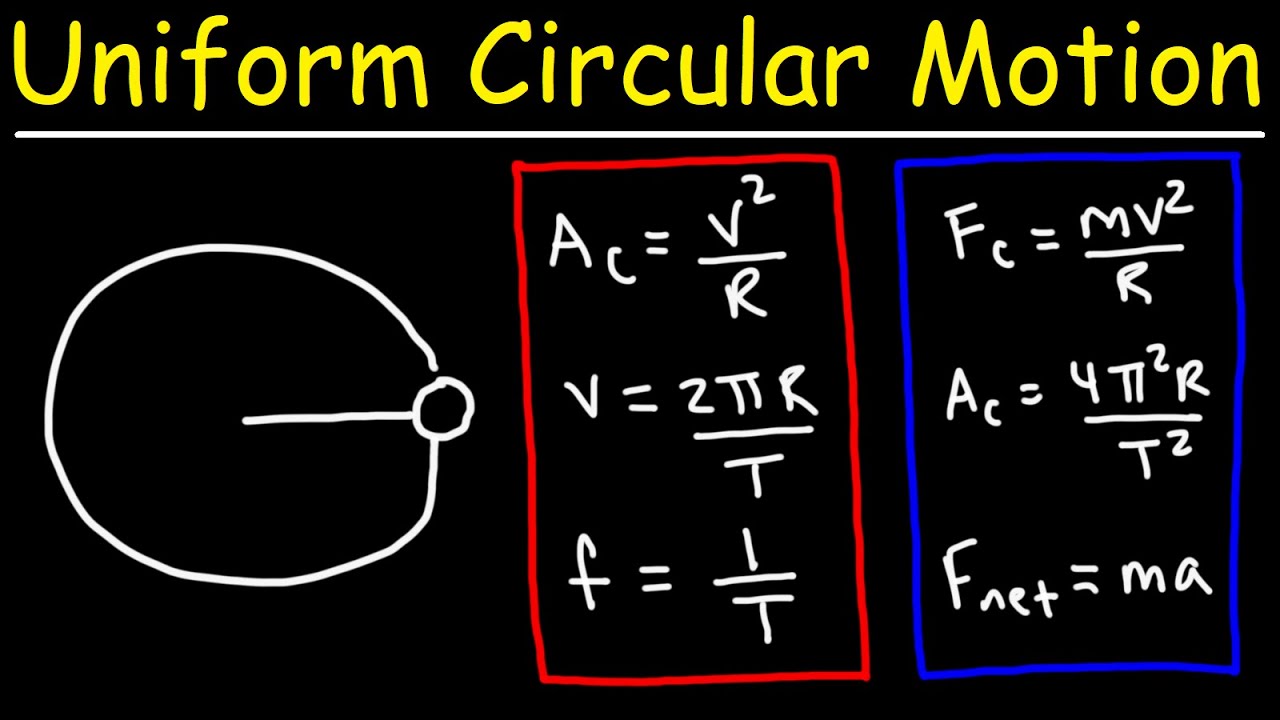
Uniform Circular Motion Formulas and Equations - College Physics
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
