Video Animasi Gerak Melingkar
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the concept of circular motion, using real-life examples like the Earth's revolution around the Sun and the movement of clock hands. It covers key principles such as constant speed, velocity, and centripetal acceleration. The video also introduces the formula for calculating centripetal acceleration and the period of an object in circular motion. The period refers to the time it takes for an object to complete one full rotation. Overall, it provides a comprehensive overview of how motion in a circle works, emphasizing the relationship between velocity, acceleration, and time.
Takeaways
- 😀 The video introduces the concept of circular motion using examples like Earth's revolution around the Sun and the Moon's revolution around the Earth.
- 😀 Circular motion refers to the movement of an object along a circular path.
- 😀 Even when an object moves with a constant speed in circular motion, it still experiences acceleration.
- 😀 Acceleration in circular motion occurs due to either a change in the speed (magnitude of velocity) or a change in the direction of motion.
- 😀 The direction of the velocity vector in circular motion is always tangent to the circular path.
- 😀 The direction of the acceleration vector in circular motion always points towards the center of the circular path (centripetal acceleration).
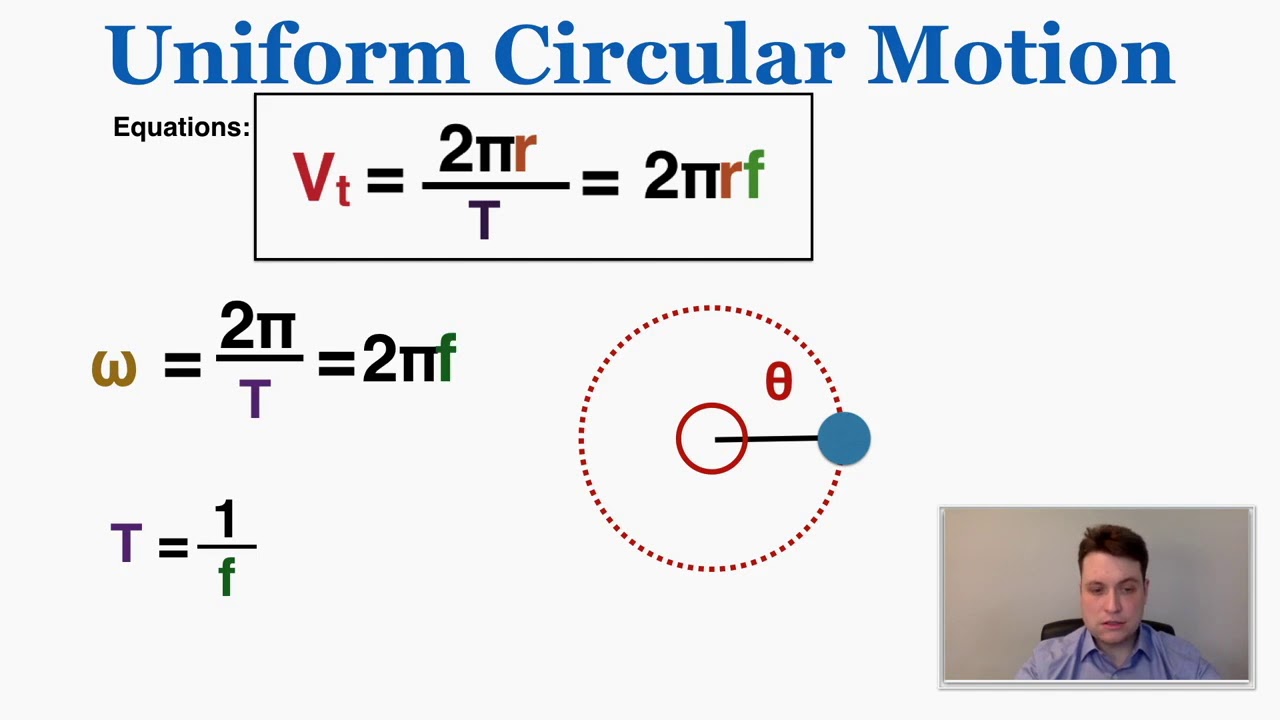
- 😀 Centripetal acceleration is calculated using the formula: a = v² / r, where 'v' is the velocity, 'r' is the radius, and 'a' is the acceleration.
- 😀 The period of an object in circular motion refers to the time taken for one complete revolution.
- 😀 The formula to calculate the period (T) in circular motion is: T = 2πr / v, where 'r' is the radius and 'v' is the velocity.
- 😀 The video concludes with a brief apology and thanks to the viewers, offering a farewell in the Islamic greeting 'Wassalamualaikum.'
Q & A
What is circular motion?
-Circular motion is the motion of an object along a circular path, such as the Earth's revolution around the Sun or the hands of a clock.
Can an object moving in circular motion have constant speed?
-Yes, an object moving in circular motion can have constant speed. However, it still experiences acceleration because the direction of motion continuously changes.
Why does acceleration occur in circular motion?
-Acceleration in circular motion occurs due to two factors: changes in the magnitude of speed (velocity) or changes in the direction of velocity.
What is the direction of the velocity vector in circular motion?
-The velocity vector in circular motion is always tangential to the circular path and perpendicular to the radius of the circle.
What is the direction of acceleration in circular motion?
-The acceleration in circular motion always points towards the center of the circular path and is known as centripetal acceleration.
How is centripetal acceleration calculated?
-Centripetal acceleration is calculated using the formula a = v^2 / r, where 'a' is acceleration, 'v' is the speed, and 'r' is the radius of the circular path.
What does the term 'period' refer to in circular motion?
-The period refers to the time taken for an object to complete one full revolution or rotation around the circular path.
How can we calculate the period of an object in circular motion?
-The period can be calculated using the formula T = 2πr / v, where 'T' is the period, 'r' is the radius of the path, and 'v' is the speed of the object.
What is the relationship between velocity, radius, and period in circular motion?
-The period of an object in circular motion is inversely proportional to its speed. As the velocity increases, the period decreases.
What is the importance of centripetal acceleration in circular motion?
-Centripetal acceleration is essential in circular motion because it keeps the object moving in a curved path instead of a straight line. Without this force, the object would move off in a tangent.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

ROTASI DAN REVOLUSI BUMI || LANJUTAN SISTEM TATA SURYA

Gerak Rotasi dan Revolusi serta Hubungannya dengan Kehidupan Sehari-hari | IPAS SD

How the Sun affects the Earth | Science videos for kids | Kids Academy
Uniform Circular Motion - IB Physics

Peristiwa Rotasi dan Revolusi Bumi | IPA | SayaBisa

Movimento Circular Uniforme
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)