Komposisi dan Lapisan Atmosfer
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, the presenter explains the Earth's atmosphere, its composition, and its layers. The atmosphere is made up of nitrogen, oxygen, and trace gases like argon and carbon dioxide. The video explores the five atmospheric layers: the troposphere, where weather occurs; the stratosphere, home to the ozone layer; the mesosphere, where meteors burn up; the thermosphere, responsible for auroras and satellite orbits; and the exosphere, where space begins. The information is essential for understanding the vital functions each layer plays in supporting life and maintaining Earth's climate.
Takeaways
- 😀 The Earth's atmosphere is composed of 78.08% nitrogen, 20.95% oxygen, and less than 1% other gases like argon, xenon, and carbon dioxide.
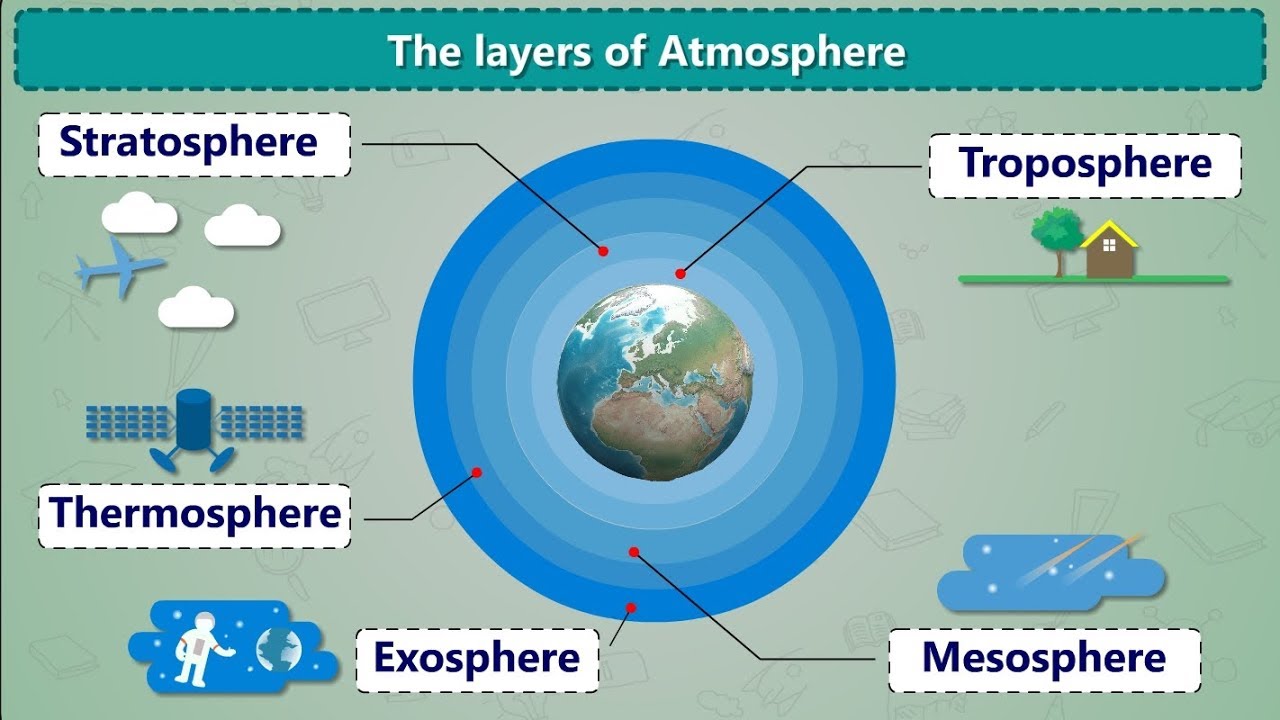
- 😀 The atmosphere is made up of multiple layers, including the troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere, and exosphere.
- 😀 The troposphere, the closest layer to Earth, extends up to about 10 km and is where weather phenomena such as clouds, rain, and wind occur.
- 😀 Temperature decreases with altitude in the troposphere, with a drop of 0.6°C for every 100 m ascent.
- 😀 The stratosphere, which contains the ozone layer, extends from 10 km to 60 km and helps protect life on Earth from harmful UV radiation.
- 😀 The mesosphere, extending from 50 km to 85 km, is where most meteors burn up upon entering Earth's atmosphere.
- 😀 In the thermosphere (85 km to 400 km), temperature rises significantly, and it contains the ionosphere, which is important for radio communication.
- 😀 The thermosphere is also the layer where auroras occur and where many satellites, including the International Space Station, orbit.
- 😀 The exosphere is the outermost layer, extending from 400 km to over 10,000 km, and marks the transition from Earth's atmosphere to outer space.
- 😀 The exosphere has extremely low temperatures, which can drop to as low as -50°C, and satellites orbit in this layer.
- 😀 The different atmospheric layers have unique characteristics and play essential roles in regulating Earth's climate, weather, and protecting life from space hazards.
Q & A
What is the composition of Earth's atmosphere?
-The atmosphere is composed of approximately 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, and trace amounts of other gases, including argon, xenon, helium, krypton, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide.
What is the troposphere, and what is its significance?
-The troposphere is the lowest layer of the atmosphere, extending up to about 10 km above Earth's surface. It contains 80% of the atmospheric mass and is where weather phenomena such as clouds, rain, and winds occur.
How does temperature change in the troposphere?
-In the troposphere, temperature decreases with altitude. For every 100 meters increase in height, the temperature drops by approximately 0.6°C.
What weather phenomena occur in the troposphere?
-The troposphere is where weather events like clouds, various types of precipitation (such as rain), winds, lightning, and even phenomena like rainbows occur.
What is the role of the stratosphere, and what layer does it contain?
-The stratosphere, which extends from 10 km to 60 km, contains the ozone layer. The ozone layer protects life on Earth by absorbing harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the Sun.
What happens to the temperature as you move higher in the stratosphere?
-In the stratosphere, the temperature increases with altitude, especially beyond 20 km, where the ozone layer absorbs UV radiation and warms the surrounding air.
What is the mesosphere, and what is its most notable feature?
-The mesosphere extends from 50 km to 85 km above Earth's surface. It is the layer where meteors burn up as they enter the atmosphere. The temperature in this layer decreases with altitude, reaching as low as -90°C.
Why is the thermosphere important, and what phenomenon occurs there?
-The thermosphere, from 85 km to around 600 km, contains the ionosphere, which plays a crucial role in radio communication by reflecting radio waves. Additionally, auroras, or northern and southern lights, are visible in this layer near the poles.
What is the exosphere, and what is its relationship with space?
-The exosphere is the outermost layer of Earth's atmosphere, extending from about 400 km to beyond 10,000 km. It marks the transition between Earth's atmosphere and outer space.
How does the temperature change in the thermosphere and exosphere?
-In the thermosphere, temperature increases with altitude, reaching up to 2,000°C or higher. In the exosphere, temperatures can be very low, reaching as low as -50°C, depending on exposure to sunlight.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频
The Layers Of Atmosphere | Air and Atmosphere | What is Atmosphere | Earth 5 Layers

The Earth's Atmosphere

LAPISAN BUMI PART 1. ATMOSFER : IPA KELAS 7 SMP

Layers of the atmosphere- Includes temperature and atmospheric pressure
VIDEO DE LAS CAPAS EXTERNAS E INTERNAS DE LA TIERRA. AUTORA VICTORIA GUAMÁN.

Ratnaningsih Projek IPAS kelas X SMKN 1 Padaherang Bumi dan Antariksa 3 Atmosfer April 2023 #PKGTK
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
