Lapisan Bumi - Lapisan Atmosfer | Asal Usul Atmosfer | Karakteristik Lapisan Atmosfer | IPA Kelas 7
Summary
TLDRThis educational video explores the Earth's atmosphere, describing its structure, components, and significance to life. It covers the atmosphere's layers, from the troposphere to the exosphere, and highlights key gases like oxygen and carbon dioxide. The video also explains the role of ozone in protecting life and the impact of human activities, such as pollution and the burning of fossil fuels, on atmospheric composition. By detailing the history and changes in the atmosphere, it emphasizes the importance of understanding and preserving this vital component for sustaining life on Earth.
Takeaways
- 😀 The Earth is made up of various layers, including the crust, mantle, outer core, and inner core, as well as three main components: atmosphere, lithosphere, and hydrosphere.
- 😀 The atmosphere is a mixture of gases, liquid, and solids that surrounds the Earth, and it plays a critical role in supporting life by providing oxygen and protecting against harmful solar radiation.
- 😀 The Earth's atmosphere was initially composed of nitrogen and carbon dioxide, with oxygen levels increasing over time due to photosynthesis by organisms.
- 😀 The ozone layer, found in the stratosphere, protects life on Earth by shielding it from harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the Sun.
- 😀 The atmosphere currently consists of nitrogen (78%), oxygen (21%), and trace amounts of other gases like carbon dioxide and argon.
- 😀 Human activities, such as burning fossil fuels and industrial emissions, have increased carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere, leading to pollution and climate change.
- 😀 Dust and water vapor are also part of the atmosphere, with dust particles carried by the wind and water vapor forming clouds through evaporation.
- 😀 The atmosphere has five distinct layers: Troposphere, Stratosphere, Mesosphere, Thermosphere, and Exosphere, each with unique characteristics.
- 😀 The troposphere, where most life exists, is the layer closest to Earth, and it contains 75% of the atmosphere's water vapor and experiences weather phenomena like rain and snow.
- 😀 The exosphere, the outermost layer of the atmosphere, is where satellites orbit, and it is made up of hydrogen and has a very low density of particles.
Q & A
What are the three main components of the Earth?
-The three main components of the Earth are the atmosphere (gas), the lithosphere (solid), and the hydrosphere (water).
What is the meaning of the word 'atmosphere'?
-The word 'atmosphere' comes from Greek, where 'atmos' means vapor and 'sphaira' means layer. It refers to the layer of vapor that surrounds the Earth.
How did Earth's atmosphere originally form?
-Earth's atmosphere originally formed from volcanic eruptions, which released nitrogen and carbon dioxide but little oxygen. Over time, photosynthetic organisms produced oxygen, which led to the creation of the ozone layer.
What is the role of the ozone layer?
-The ozone layer protects the Earth from harmful ultraviolet radiation from the sun, which can be dangerous to living organisms.
What gases make up the Earth's atmosphere?
-The Earth's atmosphere is primarily composed of nitrogen (78%) and oxygen (21%), with trace amounts of carbon dioxide, argon, and other gases.
How has human activity affected the composition of the atmosphere?
-Human activities, such as burning fossil fuels and deforestation, have increased the levels of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, contributing to global warming and climate change.
What are clouds made of in the atmosphere?
-Clouds are made of tiny droplets of water that form when water vapor in the air cools and condenses.
What is the function of the troposphere?
-The troposphere is where most of the Earth's weather occurs. It contains 75% of the atmosphere's mass and is where clouds, rain, and winds form.
What is unique about the stratosphere?
-The stratosphere contains the ozone layer, which protects the Earth from UV radiation. It is also the layer where commercial jet planes fly, as it has very little weather activity.
What happens to meteors in the mesosphere?
-When meteors enter the mesosphere, they burn up due to the high friction with the atmosphere, which is why they appear to disintegrate before reaching the Earth’s surface.
Why is the thermosphere so hot?
-The thermosphere is extremely hot due to the absorption of high-energy solar radiation. Temperatures can reach up to 2000°C, as the few particles present absorb a lot of energy.
What is the exosphere, and where is it located?
-The exosphere is the outermost layer of Earth's atmosphere, located above 500 km. It consists mainly of hydrogen and helium and is where satellites orbit the Earth.
What is the ionosphere, and how does it affect radio communication?
-The ionosphere is a region of charged particles in the mesosphere and thermosphere. It reflects radio waves, allowing them to travel long distances, especially at night when solar energy is not present.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

The Origin and Evolution of Earth - Chapter 2 Geography NCERT Class 11

The Planet Earth: Astronomy and Space for Kids - FreeSchool

IPA kelas 7 : Struktur/Lapisan Bumi (Atmosfer)

Intro to Ecology: The Biosphere - Life Science for Kids!

The Earth: Crash Course Astronomy #11
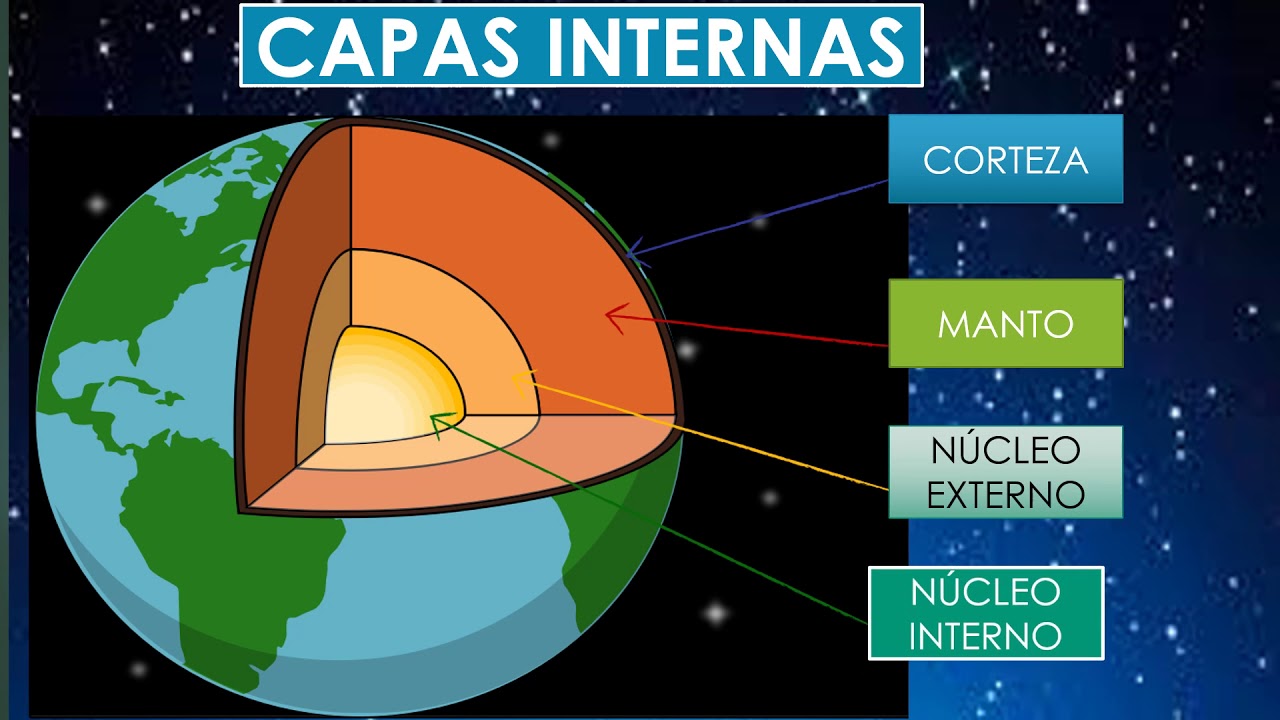
VIDEO DE LAS CAPAS EXTERNAS E INTERNAS DE LA TIERRA. AUTORA VICTORIA GUAMÁN.
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)