Packet Tracer - DNS and DHCP
Summary
TLDRIn this Packet Tracer tutorial, the video guides users through the process of configuring DHCP and DNS servers in a home office network. Viewers will learn how to set static IPs, configure a WRS device for DHCP, and assign IP addresses to client devices like a laptop and tablet. The tutorial also demonstrates how to test website access using both IP addresses and domain names. Additionally, users will configure DNS records to resolve domain names for central and branch servers, ensuring full functionality of the network. This practical guide covers key networking concepts with hands-on demonstrations in Packet Tracer.
Takeaways
- 😀 Static IP addressing is crucial for devices like printers to ensure they have a fixed, unchanging IP address.
- 😀 To configure a static IP for a printer in Packet Tracer, go to the Config tab, assign the IP, gateway, and DNS server details manually.
- 😀 The WRS (Wireless Router Server) is configured to provide DHCP services by enabling the DHCP server and setting static DNS servers.
- 😀 Enabling DHCP on the WRS allows devices like laptops and tablets to automatically receive IP addresses from the router.
- 😀 DHCP configuration for devices (e.g., laptops, tablets) can be done by selecting DHCP in the IP configuration tab and waiting for the automatic IP assignment.
- 😀 Testing connectivity to websites involves accessing them via IP addresses, followed by domain names after DNS configuration.
- 😀 DNS servers resolve domain names to IP addresses, allowing users to access websites without needing to use raw IPs.
- 😀 After configuring DNS, verify that the home laptop or tablet can resolve domain names (like centralserver.ptka and branchserver.ptka).
- 😀 Ensure that DNS records are properly set up for each server (Central and Branch), mapping the server names to their respective IP addresses.
- 😀 Use the 'nslookup' command in the command prompt to verify DNS functionality and confirm the correct resolution of domain names.
Q & A
What is the purpose of assigning a static IP address to the printer in this activity?
-The printer is assigned a static IP address to ensure that it always has the same IP address, making it easier for other devices on the network to find and communicate with it. Static IP addresses are commonly used for servers and printers, as their address should not change over time.
Why do we configure a static IP address for the printer instead of using DHCP?
-We configure a static IP for the printer because printers and servers need a fixed, unchanging address to ensure reliable communication. DHCP assigns dynamic IPs that could change over time, which is unsuitable for devices like printers that need a stable address.
How do you configure the DHCP server on the router in this activity?
-To configure the DHCP server, you access the router’s GUI tab, set the router's IP address to `192.168.0.1`, enable DHCP, and define the static DNS server address as `64.100.8.8`. The router will then assign IP addresses dynamically to devices on the network.
What is the significance of setting the static DNS server to `64.100.8.8` on both the printer and the router?
-Setting a static DNS server ensures that devices on the network can resolve domain names to IP addresses. By using `64.100.8.8`, the devices will be able to access websites and services by their domain names rather than just IP addresses.
What is the process for requesting DHCP addressing on the home laptop?
-To request DHCP addressing, you go to the **Desktop** tab of the home laptop, open **IP Configuration**, select **DHCP**, and wait for the laptop to receive an IP address from the router’s DHCP service.
How can you verify that the home laptop has successfully received a DHCP address?
-After selecting DHCP in the laptop's IP configuration settings, the IP address, subnet mask, default gateway, and DNS server should automatically populate. You can confirm the successful request by checking these settings.
What steps are involved in testing website access using IP addresses on the tablet?
-To test website access, you open the **Web Browser** on the tablet and enter the IP address of the central server or branch server. Both websites should load successfully if the IP addresses are correctly configured.
Why might accessing websites by domain name fail initially after configuring DNS?
-Accessing websites by domain name might fail initially because DNS records need to be configured on the DNS server. Until the records are set up, devices may not be able to resolve domain names to the correct IP addresses.
How do you configure DNS records for the central and branch servers in this activity?
-You configure DNS records by accessing the DNS server, adding resource records for the central and branch servers, and specifying their corresponding IP addresses. This allows domain names like `centralserver.ptk` and `branchserver.ptk` to resolve to the correct IPs.
How can you verify that DNS resolution is working correctly after configuring the DNS server?
-You can verify DNS resolution by opening the **Command Prompt** on the laptop or tablet and using the `nslookup` command to check if the domain names (`centralserver.ptk`, `branchserver.ptk`) resolve to their correct IP addresses.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频

Cicsco Packet Tracer Konfiguracija uređaja - Eng
Cara Konfigurasi DNS Server Di Cisco Packet Tracer

CARA MENGHUBUNGKAN KOMPUTER/PC KE JARINGAN LAN DAN INTERNET (UNTUK PEMULA) 2022

Implementation of DHCP using Cisco Packet Tracer
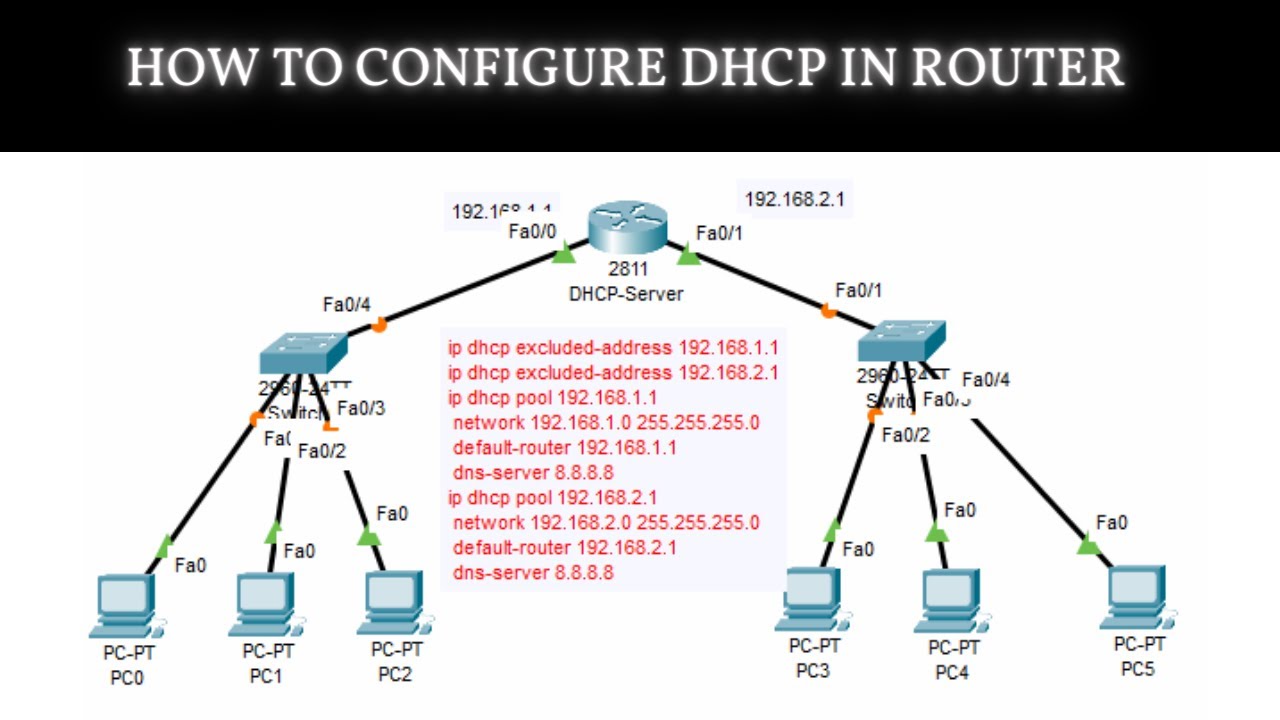
How to Configure DHCP in CISCO router in Packet Tracer | DHCP Server in CCNA | DHCP Configuration
Setting up HTTP, DNS, FTP and DHCP Server Services in Packet Tracer
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
