12C04.1 CV2 Average and Instantaneous Rate of Reaction
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the speaker explains the concepts of average and instantaneous rates of reaction. The average rate is calculated by dividing the total change in concentration by the total time interval. For instantaneous rate, the speaker discusses its calculation at a specific moment, represented as the slope of the concentration-time graph. By examining concentration changes over time, viewers can understand how these rates can be quantified and visualized in real-time, offering crucial insights for understanding chemical reactions.
Takeaways
- 😀 Average rate of reaction is calculated as the total change in concentration divided by the time interval.
- 😀 The formula for the average rate is: Average Rate = Δ[C] / Δt.
- 😀 For a reactant or product, the average rate is determined by: Average Rate = (Final Concentration - Initial Concentration) / Δt.
- 😀 Instantaneous rate refers to the rate of reaction at a specific moment in time.
- 😀 Instantaneous rate is calculated using the formula: Instantaneous Rate = Δ[C] / Δt, with Δ[C] being very small.
- 😀 The instantaneous rate can be visualized as the slope of the tangent line at a specific point on a concentration-time graph.
- 😀 Concentration-time graphs help in determining the instantaneous rate at any given moment during the reaction.
- 😀 The slope of the tangent line on the graph gives the instantaneous rate of reaction at that point.
- 😀 Average rate of reaction is used to measure the overall rate over a longer period, while instantaneous rate is for specific moments.
- 😀 The distinction between average and instantaneous rate is crucial in understanding the dynamics of chemical reactions.
Q & A
What is the average rate of reaction?
-The average rate of reaction is calculated by dividing the total change in concentration of a reactant or product by the time interval over which the change occurs.
How is the formula for average rate of reaction written?
-The formula for average rate of reaction is: Average Rate = (Change in Concentration) / (Change in Time).
What does the symbol Δ[Concentration] represent?
-Δ[Concentration] represents the change in the concentration of a reactant or product during a reaction.
How do you find the instantaneous rate of reaction?
-The instantaneous rate of reaction is found by calculating the rate of change of concentration at a specific moment in time, often represented by the slope of the concentration vs. time graph.
What does the term 'instantaneous' mean in the context of reaction rates?
-'Instantaneous' refers to a specific moment or point in time during the reaction, capturing the rate at that precise moment.
How can the instantaneous rate be determined graphically?
-Graphically, the instantaneous rate can be determined by finding the slope of the concentration vs. time graph at a specific point.
What is the relationship between the rate of reaction and concentration in an instantaneous rate?
-In an instantaneous rate, the rate is determined by the difference in concentration of the product or reactant with respect to time.
What is the significance of the slope in a concentration vs. time graph?
-The slope of a concentration vs. time graph at any given moment represents the instantaneous rate of the reaction at that moment.
Can the average rate of reaction be used to determine reaction rates at specific times?
-No, the average rate of reaction provides an overall rate for a time interval but does not give information about the rate at a specific moment. For that, the instantaneous rate is needed.
What type of reaction rate would be used to study reactions at precise time points?
-The instantaneous rate would be used to study reactions at precise time points, as it measures the rate at a specific moment during the reaction.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频
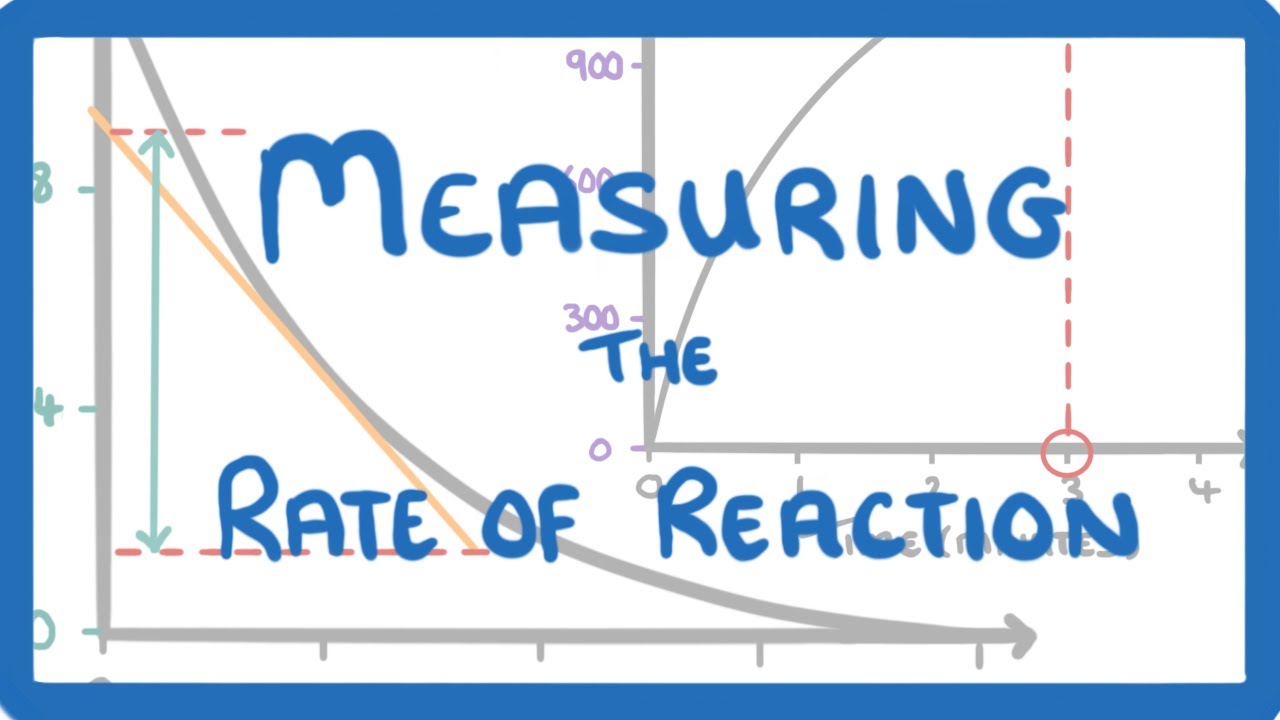
GCSE Chemistry - How to Calculate the Rate of Reaction - Measuring Rate of Reaction #48

Chemical Kinetics | class 12 (part 1) | Rate of Reaction
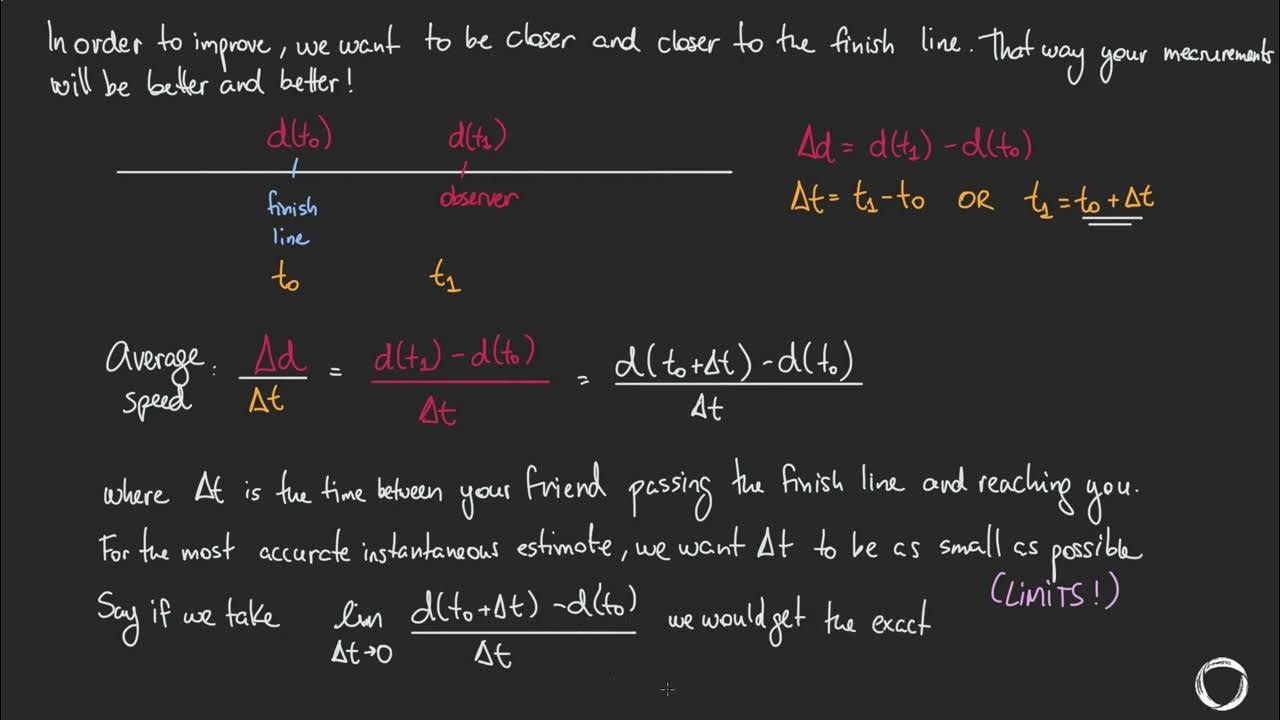
Average and Instantaneous Rates

Laju Reaksi - Kimia Kelas 11 (Quipper Video)

BTEC Applied Science: Unit 3 Skills Tables and Graphs

Average vs Instantaneous Rates of Change
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
