Chemical Kinetics | class 12 (part 1) | Rate of Reaction
Summary
TLDRThis video script delves into the intricacies of chemical kinetics, explaining how to calculate and define the rate of reaction. It covers concepts such as instantaneous rate, average rate, and how concentration changes influence the rate of reaction over time. The script walks through various methods to express these rates mathematically, emphasizing the importance of time intervals and concentration changes in determining the reaction speed. Throughout, the speaker provides practical examples to demonstrate how these principles are applied in real chemical reactions.
Takeaways
- 😀 The rate of reaction is a key concept in chemical kinetics, and it can be defined in multiple ways.
- 😀 The average rate of a reaction is calculated by dividing the change in concentration by the change in time, and it's an important measure for understanding the overall reaction speed.
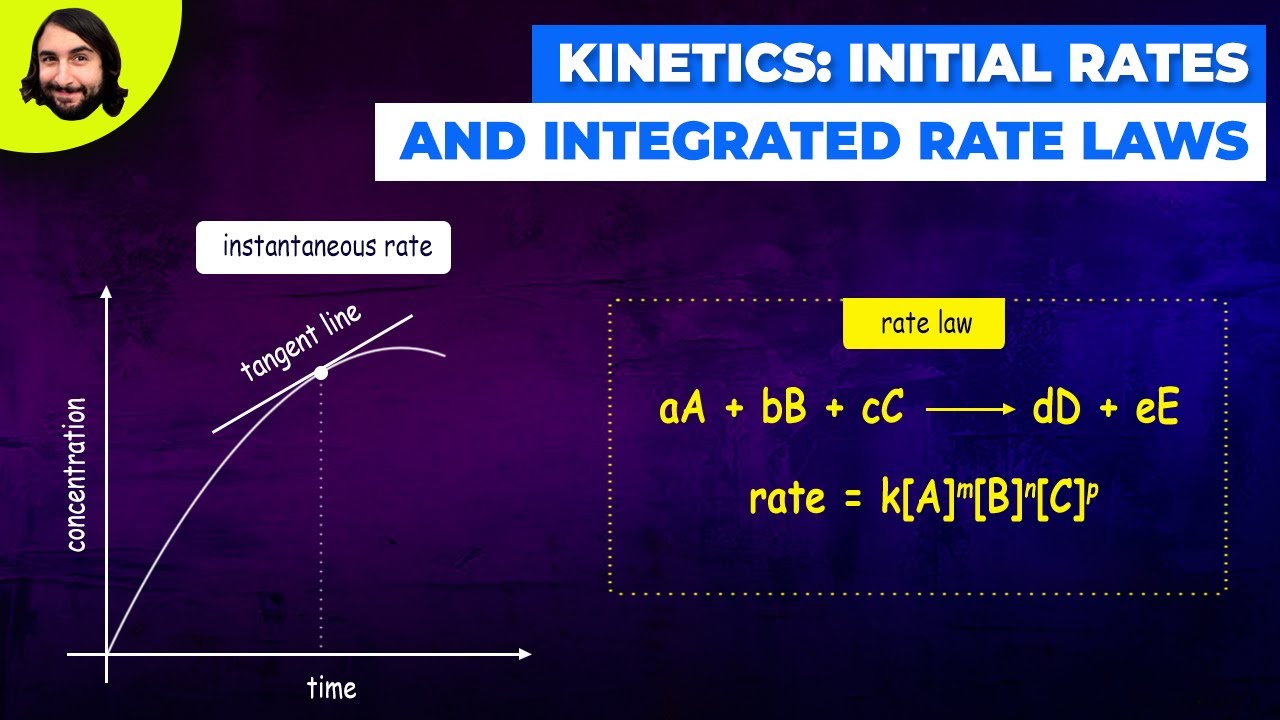
- 😀 Instantaneous rate refers to the rate of a reaction at a specific moment in time, and is crucial for understanding reaction behavior at any given point.
- 😀 The rate of reaction can vary depending on the concentration of reactants, and this relationship is important for determining how reactions proceed.
- 😀 The rate law expresses the rate of a reaction as a function of the concentration of reactants, often with exponents that reflect the reaction order.
- 😀 In the case of a simple chemical reaction, the rate can be expressed as a function of the concentration of one or more reactants.
- 😀 Chemical reactions are generally defined by their rate, and it is important to determine the rate of change for both reactants and products.
- 😀 The instantaneous rate is defined using calculus, with the change in concentration being divided by the change in time over an infinitesimally small interval.
- 😀 The speed of a reaction can be influenced by factors like temperature and the concentration of reactants, which affect the rate at which reactants are converted into products.
- 😀 The mathematical expression for the rate of reaction is crucial for predicting how changes in conditions affect the outcome of a reaction, and it is typically written as rate = Δ concentration / Δ time.
Q & A
What is the significance of the rate of reaction in chemical kinetics?
-The rate of reaction indicates how fast a chemical reaction occurs. It is a key concept in chemical kinetics, providing insight into the speed at which reactants are converted into products.
What is the difference between the average rate and instantaneous rate of a reaction?
-The average rate is calculated over a time interval and gives an overall measure of the reaction speed. The instantaneous rate refers to the rate at a specific moment in time, often calculated using infinitesimally small time intervals.
How is the rate of reaction typically expressed mathematically?
-The rate of reaction is commonly expressed as the change in concentration of a reactant or product divided by the time interval during which the change occurs.
Why is the concentration of reactants important in determining the rate of a chemical reaction?
-The concentration of reactants influences how frequently they collide, which in turn affects the rate of reaction. Higher concentrations typically lead to faster reactions due to more frequent collisions.
What does the term 'instantaneous rate' represent in chemical kinetics?
-The instantaneous rate refers to the rate of reaction at a specific point in time, calculated by considering an infinitesimally small time interval around that moment.
How is the rate of reaction related to the reaction's velocity?
-The rate of reaction and reaction velocity are closely related, with velocity often describing the speed at which reactants are converted into products. Both terms can be used interchangeably, but 'rate' is more commonly used in chemical contexts.
How do we calculate the average rate of reaction for a given time period?
-The average rate is calculated by dividing the change in concentration of a reactant or product by the time period over which the change occurs. This gives a measure of the overall reaction speed.
What is the importance of understanding the rate of chemical reactions in practical applications?
-Understanding the rate of reactions is crucial in various industries, such as pharmaceuticals, manufacturing, and environmental science, as it helps in optimizing processes, ensuring safety, and controlling reaction conditions.
What does it mean when a rate of reaction is described as 'instantaneous'?
-An instantaneous rate refers to the rate of reaction at a specific moment, often calculated by taking a very small time interval to measure the change in concentration of reactants or products.
Why is the method of dividing by change in concentration over time used in reaction rate calculations?
-This method is used because it provides a clear and quantifiable measure of how the concentration of reactants or products changes over time, which directly corresponds to the speed or rate of the reaction.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Physics Pharmacy - Kinetics - Stability 2 - Part 1

12-NCERT-Chemical kinetics- Introduction (with Animation)

Cinétique chimique : comment obtenir la vitesse d'une réaction chimique? - terminale spé

Kinematika Kimia, Laju Kimia, Laju Reaksi KIMIA kelas 11 Latihan soal akhir bab buku Kemendikbud

Chemical Kinetics | A Model for Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis.
Kinetics: Initial Rates and Integrated Rate Laws
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)