Tertiary structure of proteins | Macromolecules | Biology | Khan Academy
Summary
TLDRThis video provides a detailed overview of protein structures, starting from primary to quaternary levels. It explains how the sequence of amino acids (primary structure) shapes the protein, moving to secondary structures like beta-pleated sheets and alpha helices, which are stabilized by hydrogen bonds. Tertiary structures are formed through interactions between side chains, including hydrophobic interactions, hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds, and disulfide linkages. Finally, quaternary structure describes how multiple polypeptide chains fit together. The video highlights the complexity of protein folding and its crucial role in biological functions, such as enzymes and hormones.
Takeaways
- 🧬 Primary structure refers to the sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain.
- 🔗 Secondary structure is determined by interactions of the backbone, forming structures like parallel and anti-parallel beta-pleated sheets, and alpha helices.
- 🌀 In alpha helices, hydrogen bonds form between different layers of the helix backbone.
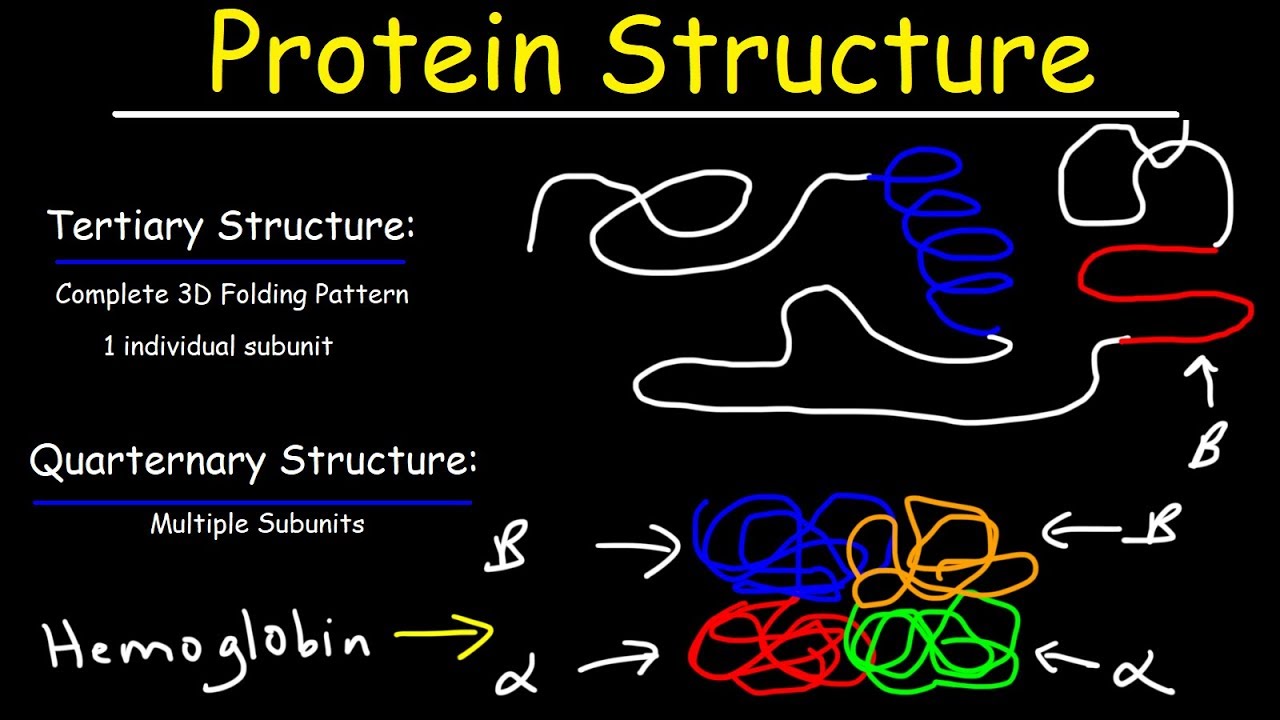
- 🧩 Tertiary structure is influenced by side chain interactions, shaping the overall 3D form of the protein.
- 💧 Hydrophobic side chains tend to clump together away from water, affecting the protein's folding.
- ⚛️ Polar side chains, such as serine, interact with water and can form hydrogen bonds with other side chains.
- 🔋 Charged side chains can form ionic bonds, further stabilizing the protein's structure.
- 🔗 Cysteine side chains can form disulfide bonds, creating strong covalent linkages that stabilize protein structure.
- 🧱 Quaternary structure refers to the assembly of multiple polypeptide chains into a functional protein complex.
- 🔬 Understanding protein structure is crucial for studying how proteins function and how they can be manipulated in various biological processes.
Q & A
What is the primary structure of a protein?
-The primary structure of a protein is the sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain.
How does the secondary structure of a protein differ from the primary structure?
-The secondary structure refers to the interactions between the polypeptide backbone, typically forming structures like alpha helices and beta-pleated sheets, whereas the primary structure is just the linear sequence of amino acids.
What is the difference between parallel and anti-parallel beta-pleated sheets?
-In parallel beta-pleated sheets, the polypeptide backbones run in the same direction, while in anti-parallel sheets, they run in opposite directions. Both are stabilized by hydrogen bonds between the backbones.
What role do hydrogen bonds play in secondary structure formation?
-Hydrogen bonds stabilize the secondary structure by forming between atoms in the backbone of the polypeptide chain, helping maintain alpha helices and beta-pleated sheets.
What is the tertiary structure of a protein?
-The tertiary structure involves the interactions of the side chains (R groups) of the amino acids, leading to the overall 3D folding of the protein.
How do hydrophobic and hydrophilic side chains influence the tertiary structure?
-Hydrophobic side chains tend to cluster inside the protein, away from water, while hydrophilic side chains are more likely to be on the surface, interacting with the aqueous environment. This helps shape the protein's 3D structure.
What is the significance of disulfide bonds in proteins?
-Disulfide bonds are covalent bonds that form between two cysteine side chains, helping stabilize the tertiary or quaternary structure by linking different parts of the protein.
What types of interactions occur between side chains in tertiary structure formation?
-Tertiary structure is stabilized by hydrophobic interactions, hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds between charged side chains, and disulfide bonds between cysteine residues.
What is quaternary structure in proteins?
-Quaternary structure refers to how multiple polypeptide chains (subunits) come together and interact to form a functional protein complex.
Why is understanding protein structure important for scientific research?
-Understanding protein structure is crucial for determining how proteins function, which can help in fields like drug design, enzyme catalysis, and understanding diseases that arise from protein misfolding.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频
Protein Structure - Primary, Secondary, Tertiary, & Quarternary - Biology

Struktur Sekunder, Tersier, Kuartener Protein | Fungsi dan Struktur Protein

Protein Folding Mechanism

Levels of Protein Structure
Protein structure | Primary | Secondary | Tertiary | Quaternary

Struktur Primer Protein | Fungsi dan Struktur Protein
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
