Types of Plant Layout, Explanation with Advantages and Dis-advantages, Plant layout part 2
Summary
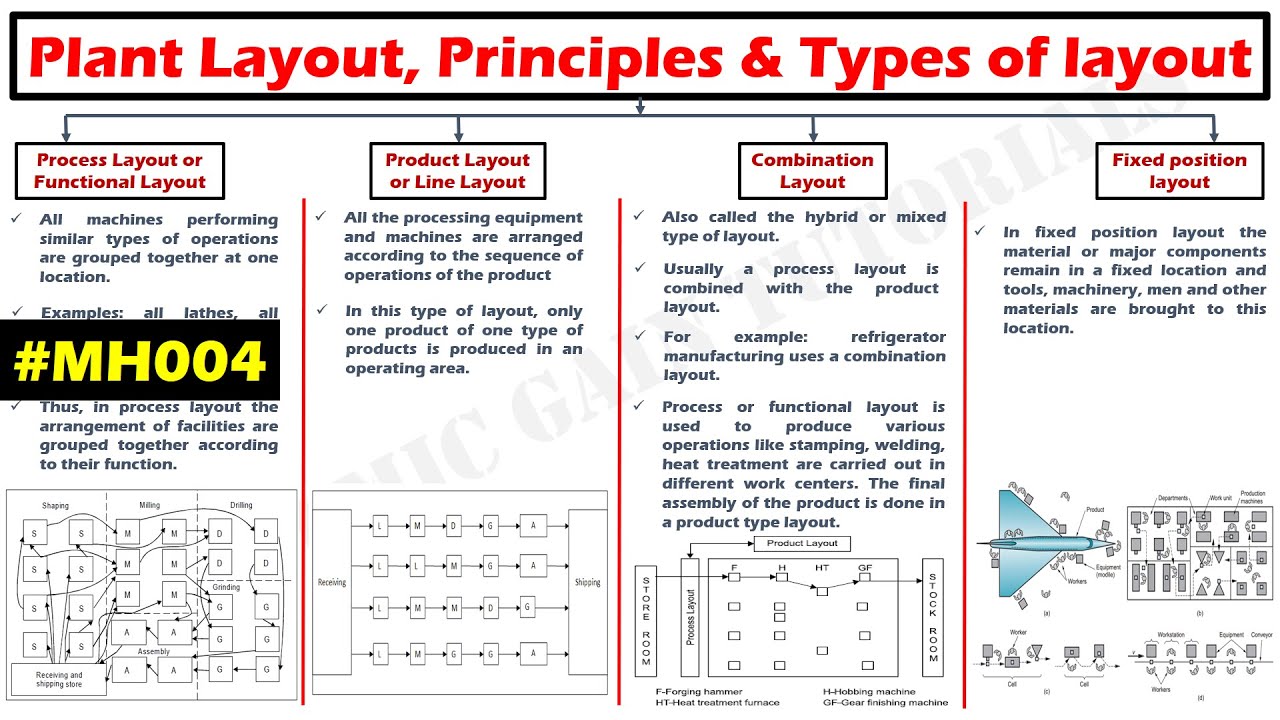
TLDRThis educational video delves into the four types of plant layouts: process, production, combination, and fixed position. It explains each layout's setup, operational flow, and the sequence of machine operations. The video highlights the advantages and disadvantages of each layout, such as space efficiency, production control, and material handling. Ideal for understanding plant organization in manufacturing, from mass production lines to large, stationary projects like shipbuilding.
Takeaways
- 🌱 There are four types of plant layouts: process layout, product layout, combination layout, and fixed position layout.
- 🔄 Process layout arranges similar machines and operations together by their function, such as placing all lathes in one area and all milling machines in another.
- 👍 Advantages of process layout: better equipment utilization, higher product quality due to specialized workers, and reduced impact of operations between sections.
- 👎 Disadvantages of process layout: requires more space, makes automatic material handling and production control difficult, and increases material handling costs.
- 🛠️ Product layout, also known as line layout, involves arranging machines in the order of production flow, which is suitable for mass production of identical products.
- 💡 Advantages of product layout: requires less space, reduces material handling time and costs, simplifies production control, and requires fewer skilled workers.
- ⚠️ Disadvantages of product layout: lacks flexibility in layout changes, is limited by the slowest machine in the production line, and is hard to scale up beyond its capacity.
- 🔗 Combination layout merges the benefits of process and product layouts, ideal for producing multiple item types in varying quantities with a common production sequence.
- 🚢 Fixed position layout keeps the product stationary while workers and equipment move around it, suitable for large products like ships and aircraft.
- 🌟 Advantages of fixed position layout: ensures continuity of work, minimizes material movement, and allows diverse projects with the same layout, but involves high equipment handling costs.
Q & A
What are the four types of plant layouts mentioned in the video?
-The four types of plant layouts are process layout, product layout, combination layout, and fixed position layout.
How are machines arranged in a process layout?
-In a process layout, machines are arranged according to their function. For example, all lathes are placed in one section, all milling machines in another, and so on.
What is a key advantage of a process layout?
-One key advantage of a process layout is better utilization of available equipment, as machines performing similar tasks are grouped together.
What is a major disadvantage of process layout?
-A major disadvantage of process layout is that it requires more space for the same amount of production and involves higher material handling costs.
What is another name for a product layout?
-A product layout is also known as a line layout.
In which type of production is product layout most suitable?
-Product layout is most suitable for mass production, where there is a continuous flow of identical products.
What is one disadvantage of product layout?
-One disadvantage of product layout is that flexibility is reduced; any change in product design may require a major change in the layout.
How does combination layout combine elements of process and product layouts?
-Combination layout arranges machines in a process layout while following the sequence of operations for various products, offering flexibility for small production batches.
In what scenarios is a fixed position layout typically used?
-Fixed position layout is typically used in large-scale manufacturing such as shipbuilding or aircraft manufacturing, where the product is stationary and equipment moves around it.
What is a key advantage of a fixed position layout?
-A key advantage of a fixed position layout is the ability to assign skilled workers to a project from start to finish, ensuring continuity and quality.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频

Plant Layout, Objectives of Plant Layout, Types of Plant Layout [Animated video]
#MH004 Plant Layout, Principles of plant layout & Types of layout.

Lec 19: Plant Layout: Types of Layout

Lec 20: Plant Layout: Cellular and Process Layout

Combination Plant Layout : Boosting Manufacturing Efficiency!

02_06_P1 Three Types of Layouts: Process, Product, and Fixed Position
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
