Lec 20: Plant Layout: Cellular and Process Layout
Summary
TLDRThis presentation covers key concepts of plant layouts in industrial engineering. It explains various layout types, including process, product, fixed, combination, and cellular (or group technology-based) layouts. The speaker emphasizes how different layouts are suited for specific production environments, such as batch, mass, and intermediate production. The focus is on cellular layout, which groups machines into cells for specific tasks, streamlining production flow, reducing material movement, and minimizing costs. The presentation concludes by discussing strategies for designing effective process layouts to minimize transportation and handling costs.
Takeaways
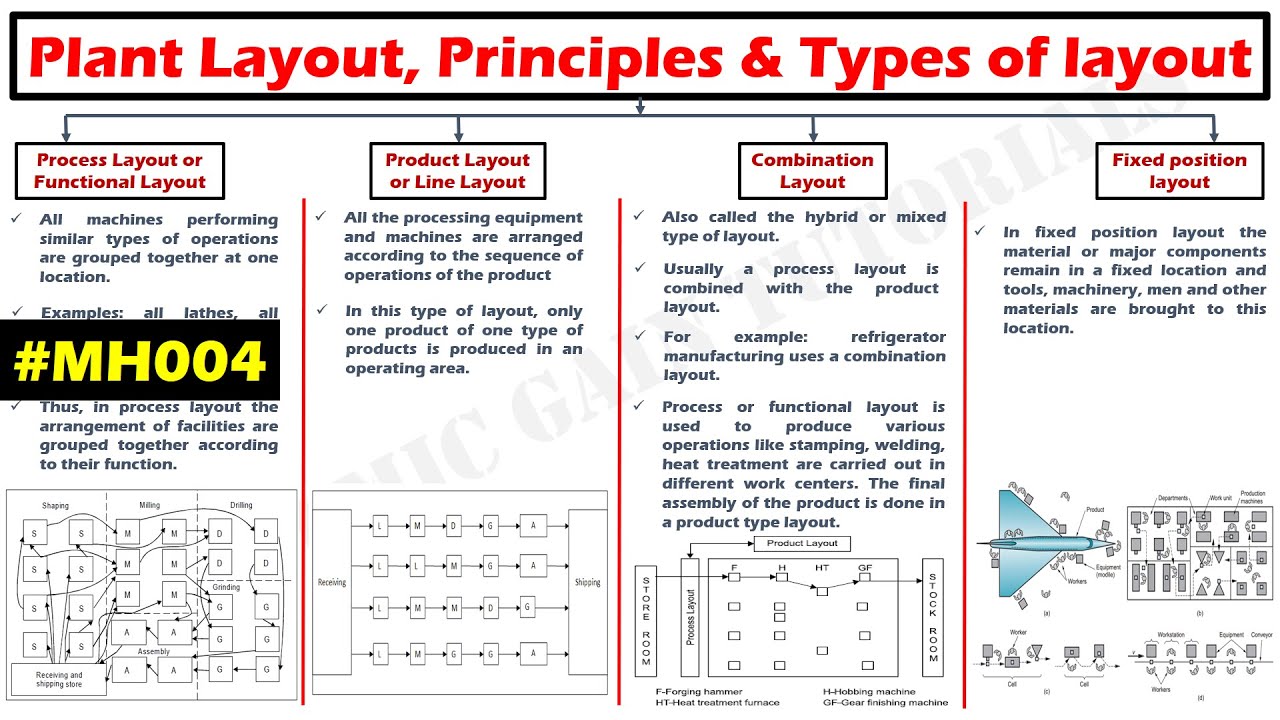
- 🏭 The presentation discusses various plant layouts, including Process Layout, Product Layout, Combination Layout, Fixed Layout, and Cellular Layout.
- 🔄 Process Layout is typically used for batch production, where equipment is grouped by the type of operation.
- 🚀 Product Layout is used for mass production with continuous operations, optimizing high-volume output.
- ⚙️ Fixed Layout is designed for large, immovable products, where materials and workers come to the product for assembly.
- 🔗 Combination Layout merges benefits from both Product and Process layouts, making it useful for intermediate production volumes.
- 📦 Cellular Layout, also known as Group Technology, organizes machines into independent cells for different types of jobs, aiming to minimize movement and production costs.
- 🛠️ The Group Technology approach groups similar parts (part families) based on operations to improve efficiency.
- 🔧 Each cell in the Cellular Layout is independent and tailored to specific operations, allowing for smoother, unidirectional production flows.
- 📊 Cellular Layout is ideal for moderate-volume, high-variety production, accommodating fluctuating batch sizes.
- 🏗️ When designing layouts, the goal is to reduce material handling costs and unnecessary movement between operations, optimizing production flow.
Q & A
What are the different types of plant layouts mentioned in the presentation?
-The presentation mentions Process Layout, Product Layout, Combination Layout, Fixed Layout, and Cellular or Group Technology-based Layout.
When is a Process Layout typically used?
-A Process Layout is typically used for batch production purposes, where similar processes are grouped together.
What is the primary use case for Product Layout?
-Product Layout is used for mass production purposes where continuous operation helps achieve high-volume production.
How is a Fixed Layout different from other layouts?
-In a Fixed Layout, the main component is kept in a fixed location while resources like labor, materials, and machines are brought to it, typically used for large, immobile components.
What is the main advantage of a Combination Layout?
-A Combination Layout exploits the benefits of both Product and Process Layouts, making it suitable for producing similar products of varying sizes and intermediate production volumes.
What is a Cellular or Group Technology-based Layout?
-A Cellular Layout groups machines into cells, with each cell designed to handle specific types of jobs. It is also known as Group Technology-based Layout, where part families that need similar operations are processed in the same cell.
How does Group Technology benefit production?
-Group Technology helps by grouping similar parts (part families) based on the type of operations needed, enabling more efficient production flow, reducing unnecessary movement, and minimizing costs.
In what situations is a Cellular Layout particularly useful?
-Cellular Layout is useful when dealing with moderate volume and moderate variety of products, where flexibility and unidirectional flow of materials are required.
What challenge does Cellular Layout help overcome in production?
-Cellular Layout helps overcome the challenge of fluctuating batch sizes and allows for minor design changes, ensuring smooth production flow and flexibility.
How does the Cellular Layout minimize production complexity compared to Process Layout?
-In Cellular Layout, the machines are grouped according to the specific sequence of operations, avoiding crisscross movement and reducing the distances components must travel, which streamlines production and minimizes complexity.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)