CBSE Class 12 Physics | Electromagnetic Waves in One Shot Revision | NCERT EMW Short Explanation
Summary
TLDRThe script discusses the concept of electromagnetic waves, explaining how electric and magnetic fields are perpendicular to each other and travel at the speed of light. It touches on the history of electromagnetic wave discovery, referencing Faraday and Maxwell's equations. The lecture also covers the properties of electromagnetic waves, including reflection and interference, and their applications in various technologies like radio, microwaves, infrared, and X-rays. The importance of understanding the electromagnetic spectrum for practical applications in communication and medicine is emphasized.
Takeaways
- 🧲 Electromagnetic waves are produced by the interaction of electric and magnetic fields, which are perpendicular to each other.
- 📚 Maxwell's equations are fundamental in understanding how a changing magnetic field induces an electric field and vice versa.
- 🔍 The script discusses the propagation of electromagnetic waves and their properties, such as being transverse waves with properties like reflection and interference.
- 📈 The amplitude of electric and magnetic fields in an electromagnetic wave is directly proportional to the speed of light.
- 🌐 The script touches on the importance of understanding the properties of electromagnetic waves for various applications, including communication and medical treatments.
- 📱 Mobile devices like the Samsung Galaxy S5 Plus are mentioned in relation to their specifications and the electromagnetic spectrum they operate within.
- 🌡️ Infrared radiation is highlighted for its ability to heat objects and its applications in cooking and photography.
- 🏥 Medical applications of electromagnetic waves are discussed, including their use in radiotherapy to treat tumors and in diagnostic tools like X-rays.
- ⚠️ The dangers of ultraviolet radiation are mentioned, including its potential to cause skin cancer, contrasting with its beneficial uses in sterilization and vitamin D synthesis.
- 📡 The script also covers the use of radio waves, with a historical note on Marconi's discovery, and their applications in communication and radar systems.
Q & A
What are electromagnetic waves?
-Electromagnetic waves are a type of wave that consists of oscillating electric and magnetic fields. They are produced by the interaction of moving electric charges and propagate through space, carrying energy.
What is the relationship between electric and magnetic fields in electromagnetic waves?
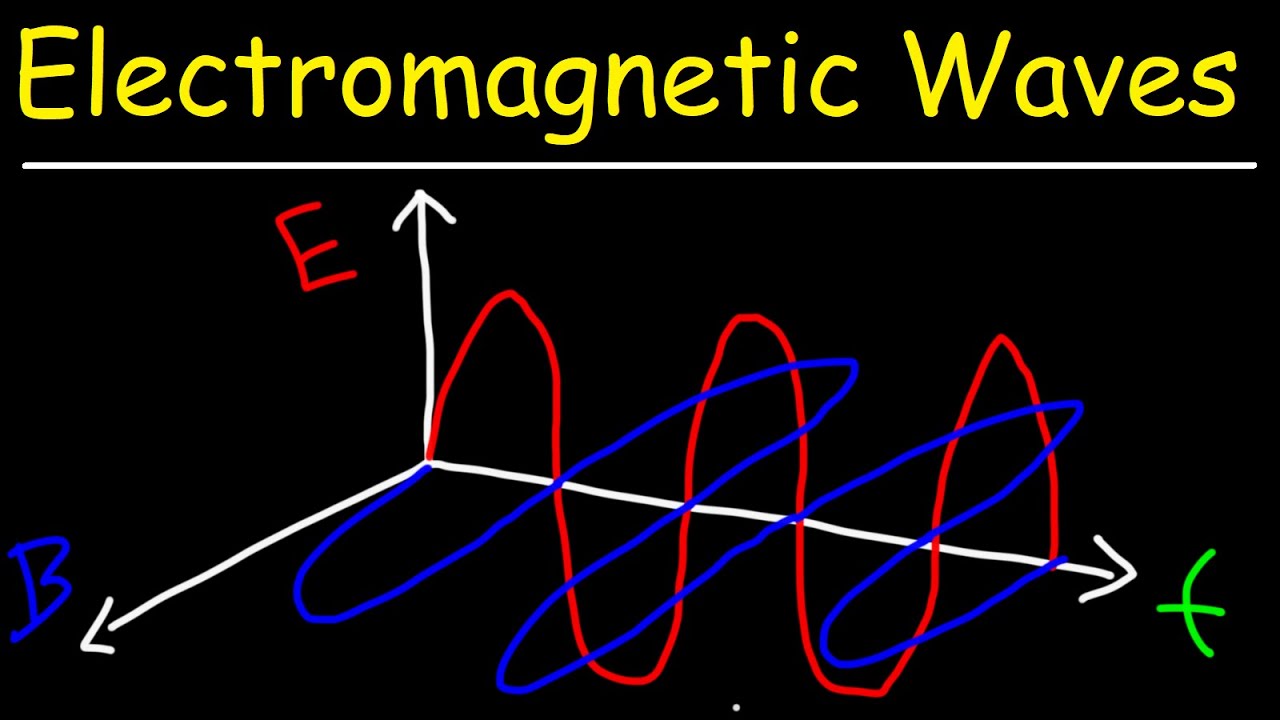
-In electromagnetic waves, the electric and magnetic fields are perpendicular to each other and both are perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation.
Who discovered the relationship between changing magnetic fields and electric fields?
-Michael Faraday discovered that a changing magnetic field induces an electric field. Conversely, James Clerk Maxwell proposed that a changing electric field induces a magnetic field.
What is the speed of electromagnetic waves in a vacuum?
-The speed of electromagnetic waves in a vacuum is equal to the speed of light, which is approximately 299,792 kilometers per second (km/s).
What is the significance of Maxwell's equations in the study of electromagnetic waves?
-Maxwell's equations are fundamental in understanding the behavior of electric and magnetic fields, and they form the basis for the study of electromagnetism, including the generation and propagation of electromagnetic waves.
How are electromagnetic waves generated?
-Electromagnetic waves are generated by the acceleration of electric charges, such as electrons in an antenna. The oscillating charges produce oscillating electric and magnetic fields that radiate outward as electromagnetic waves.
What is the difference between electromagnetic waves and other types of waves?
-Electromagnetic waves do not require a medium to propagate; they can travel through the vacuum of space. In contrast, mechanical waves, like sound waves, require a medium (such as air or water) to travel through.
What are some applications of electromagnetic waves?
-Electromagnetic waves have a wide range of applications, including communication (radio, television, mobile phones), radar systems, medical imaging (X-rays, MRI), and heating (microwave ovens).
How do electromagnetic waves interact with matter?
-The interaction of electromagnetic waves with matter depends on the frequency of the waves. Lower-frequency waves can penetrate deeper into materials, while higher-frequency waves may be absorbed or reflected at the surface.
What is the electromagnetic spectrum, and what are its different categories?
-The electromagnetic spectrum is the range of all possible frequencies of electromagnetic radiation. It is generally categorized into radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays, based on their increasing frequency and energy.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频
Electromagnetic Waves

ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES In 20 Minutes || Complete Chapter For JEE Main/Advanced

What is the ELECTROMAGNETIC SPECTRUM

Class 12 Physics Chapter 8 - Electromagnetic Waves, Part 1

Electromagnetic waves and the electromagnetic spectrum | Physics | Khan Academy

8.02x - Module 12.01 - EM Plane Waves - Poynting Vector - E-fields - B fields - Wavelength
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
