Intro to Matrices
Summary
TLDRThis video tutorial introduces the concept of matrices as arrays of numbers arranged in rows and columns. It explains how to determine a matrix's order, identify specific elements, and distinguish square matrices. The script also covers basic matrix operations, including addition and multiplication by a scalar, as well as subtraction, providing examples to illustrate the processes clearly.
Takeaways
- 📊 A matrix is an array of numbers organized into rows and columns.
- 🔢 The order of a matrix is defined by the number of rows followed by the number of columns, e.g., a 2x3 matrix has two rows and three columns.
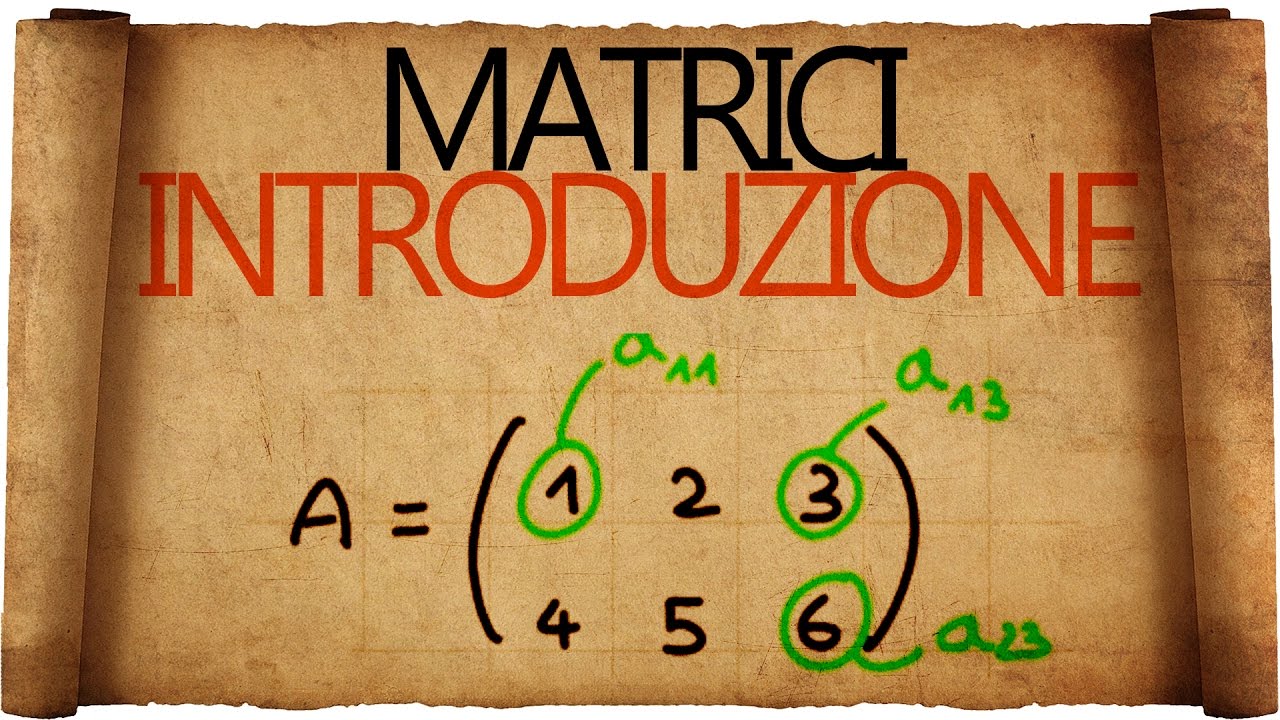
- 📍 Elements in a matrix are identified by their row and column, like 'a23' for the element in the second row and third column.
- 🔑 To find the value of a specific matrix element, identify its position by row and column numbers.
- 🧩 Matrix order must match when performing addition or subtraction of matrices; they must have the same dimensions.
- ➕ Adding matrices involves summing corresponding elements from each matrix.
- 🔍 Multiplying a matrix by a scalar (e.g., 4 times matrix A) means multiplying every element of the matrix by that scalar.
- ➖ Subtracting one matrix from another (A - B) is done by subtracting the corresponding elements of matrix B from A.
- 🔄 The process of identifying matrix elements and performing operations like addition, subtraction, and scalar multiplication is fundamental in matrix algebra.
- 🔍 Square matrices have an equal number of rows and columns, making them distinct from other matrix shapes.
- 📚 Understanding matrix operations is crucial for further studies in pre-calculus and linear algebra.
Q & A
What is a matrix?
-A matrix is an array of numbers organized into rows and columns.
How is the order of a matrix defined?
-The order of a matrix is defined by the number of rows followed by the number of columns it contains, such as a 'two by three' matrix for a 2x3 matrix.
What does the term 'element' in a matrix refer to?
-An 'element' in a matrix refers to a specific number within the matrix, identified by its row and column indices, like 'a23' for the element in the second row and third column.
How do you identify the value of element a12 in a matrix?
-To identify the value of element a12, locate the number in the first row and second column of the matrix.
What is a square matrix?
-A square matrix is a matrix where the number of rows is equal to the number of columns, such as a 2x2 or 3x3 matrix.
How do you determine the order of matrix B with the given elements?
-Matrix B with the given elements has three rows and four columns, making it a 'three by four' matrix.
What is the value of element b23 in the described matrix B?
-The value of element b23 in matrix B is -4, as it is located in the second row and third column.
How do you add two matrices together?
-To add two matrices, add the corresponding elements of the same row and column. The matrices must have the same order to be added together.
What is the result of multiplying every element in matrix A by 4?
-Multiplying every element in matrix A by 4 results in a new matrix with elements that are four times the original elements, such as 8, 12, 20, and -16 for the given matrix A.
How do you subtract one matrix from another?
-To subtract one matrix from another, subtract the corresponding elements of the same row and column. The matrices must have the same order to be subtracted.
What is the difference between matrix A and B if matrix A is [2, 3, 5, -4] and matrix B is [7, 4, -3, 5]?
-The difference between matrix A and B is a new matrix with elements calculated as A - B, which results in [-5, -1, 8, -9].
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)