Ship Machinery Alarms and Protection Devices
Summary
TLDRThe video script highlights the critical role of alarm and protection systems in preventing machinery breakdowns on ships. It emphasizes the importance of proper operation, maintenance, and testing of these systems to ensure reliability and safety. The script provides insights into the hierarchy of alarm priorities, from top-priority systems like main propulsion engines and steering to less critical ones like cargo pumps. It also stresses the necessity for engineers to understand and respond effectively to alarms, underscoring the significance of good engineering practice in averting disasters.
Takeaways
- 🔍 **Importance of Alarm Systems**: The script emphasizes the crucial role of alarm systems and protection devices in preventing machinery breakdowns and disasters on ships.
- 🛠️ **Maintenance and Operation**: It highlights that many breakdowns occur due to inadequate maintenance, incorrect operation, or deliberate disconnection of alarm systems.
- 🚫 **Consequences of Neglect**: The script warns that neglecting alarm systems can lead to serious incidents, including injuries, major breakdowns, and operational disruptions.
- 🔑 **Attention to Detail**: It stresses the importance of duty engineers paying close attention to detail to avoid unforeseen incidents and maintain the reliability of ship systems.
- 🛑 **Protection Circuits**: The text explains that protection circuits not only provide warnings but also initiate shutdown procedures to prevent damage to critical machinery.
- 📊 **Prioritization of Alarms**: It discusses the prioritization of alarm systems based on their importance to the ship's operation, with some being top priority and others less critical.
- 🔬 **Testing and Calibration**: The script insists on the necessity of regular testing and calibration of sensors and alarm systems to ensure their accurate function.
- 📝 **Documentation**: It mentions the importance of recording test results and maintaining documentation for future reference and quality control.
- 👨🔧 **Engineer's Responsibility**: The text underscores the duty engineer's responsibility to understand the alarm and protection systems, including their relative importance and the necessary actions upon activation.
- 🚫 **Avoidance of Premature Reset**: The script advises against pressing the reset on alarms without understanding and addressing the cause, to prevent recurring issues.
- 🛡️ **Confidence in Systems**: Lastly, it concludes with the need for engineers to have confidence in the alarm system and protection devices for timely warning and remedial action.
Q & A
What are the common causes of machinery breakdowns mentioned in the script?
-The script mentions that a large number of machinery breakdowns occur due to mistakes in operation or maintenance of the alarm systems and protection devices, including being deliberately disconnected, clogged up with paint, or neglected and forgotten.
What is the consequence of ignoring alarm systems and protection devices on a ship?
-Ignoring alarm systems and protection devices can lead to serious breakdowns, potential injuries to people, major machine damage, and disruptions to the commercial operation of the vessel, resulting in extra workload for the ship's personnel.
How does a typical alarm circuit function in the context of the script?
-A typical alarm circuit has a censoring device such as a level sensor, thermocouple, or pressure sensor connected to display devices. When certain values are reached, a switch is activated, sending an electrical or pressure signal to the ship's alarm panels, causing an audio-visual warning that remains until acknowledged and the issue is resolved.
What is the purpose of a protection circuit in addition to a warning circuit?
-A protection circuit, in addition to providing a warning, initiates a shutdown procedure of the affected machines by activating one or more switches or valves, causing the machine to halt in a controlled manner to prevent damage.
Why is it important for engineers to understand the alarm and protection systems on a ship?
-It is important for engineers to understand these systems to ensure they can respond appropriately to alarms, know the relative importance of each system to the ship's operation, and maintain the reliability of the ship's systems by preventing potential hazards.
What are some examples of top-priority alarm and protection circuits on a ship?
-Top-priority alarm and protection circuits include those that protect the main propulsion engine, steering system, power generation plant, and steam boilers, as any breakdown in these systems can be catastrophic.
How do level indicators function as part of the alarm system?
-Level indicators monitor liquid levels in tanks and are activated by the liquid itself. When the level rises or sinks below set safety levels, a sensor sends a signal to warning devices, usually with an indicator.
What is a flame out alarm system and why is it important?
-A flame out alarm system uses optical sensors, known as flame eyes, to continuously monitor the presence of flame in a boiler. It provides an instant warning if the flame goes out, which is critical because a sudden loss of flame can lead to undesirable and dangerous consequences.
How should engineers test sensors to ensure the reliability of the alarm system?
-Engineers should test sensors regularly according to the ship's maintenance or test schedules. They must use calibrated test instruments and record the details of the test for future reference. The testing should cover both minimum and maximum limits of the sensor's operation.
What steps should be taken when an alarm is activated on a ship?
-When an alarm is activated, the duty engineer must identify the significance of the alarm, determine the system's importance, take measures to eliminate the cause of the alarm, and execute countermeasures in the correct order. They should never reset an alarm without understanding and addressing the cause.
Why is it essential for engineers to have confidence in the alarm system and protection devices?
-Confidence in the alarm system and protection devices is essential because it ensures that engineers will be given timely warnings of any changing conditions that may lead to a breakdown, allowing them to take remedial action and maintain good engineering practice.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Ship Hull Protection System

What is Process Safety?

How to Safely Isolate Machinery Onboard Ship? (Lock-Out Tag-Out System)

BASIC OF FIRE ALARM SYSTEMS ( DASAR-DASAR SISTEM DETEKSI KEBAKARAN) - PART 6
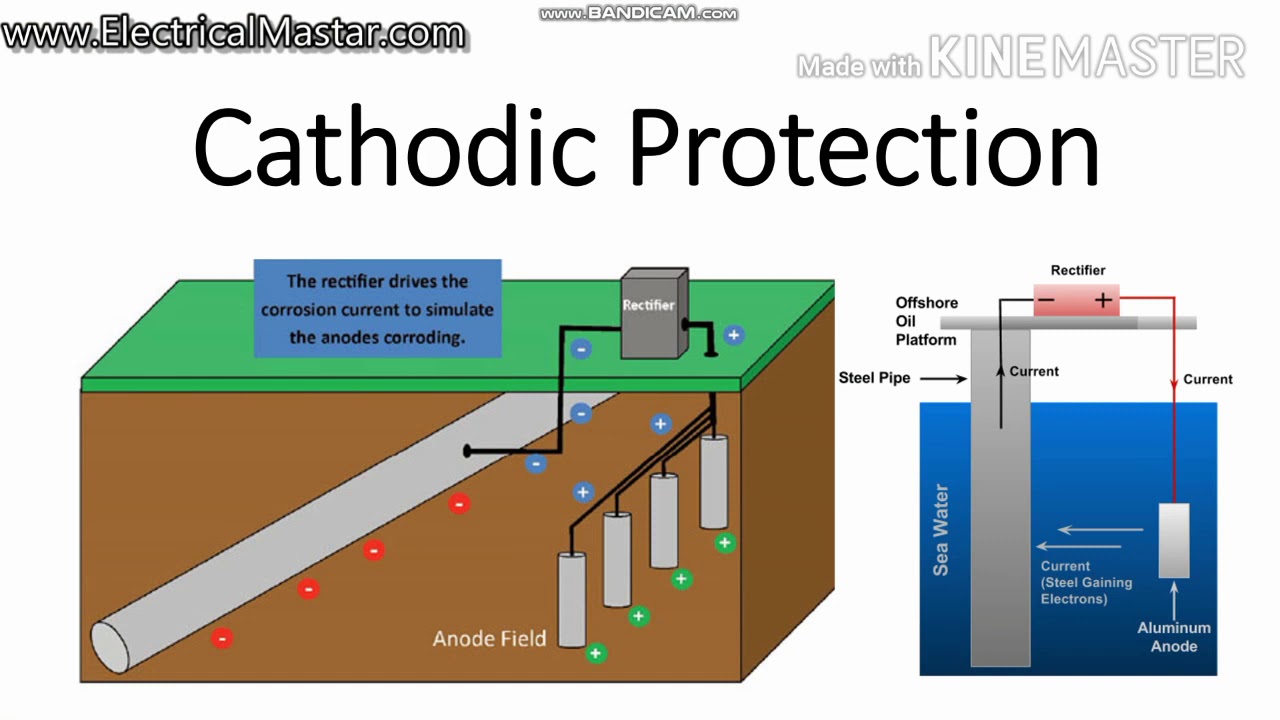
How Cathodic protection system working |Types |Application

Ship's Fresh Water Cooling System | Study Call Ep 003 Chief MAKOi
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)